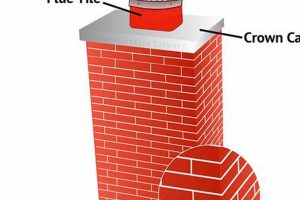
A protective covering designed to fit a variety of chimney flue sizes and shapes. Its purpose is to prevent rain, snow, debris, and animals from entering the chimney. For example, a homeowner with a standard-sized flue could use a square model, while another with an unusual or oval flue might require a round one. The defining characteristic is its adaptability to different chimney dimensions.
Effective chimney protection offers several crucial benefits. It prevents water damage within the chimney structure, mitigating costly repairs caused by freeze-thaw cycles. It also deters birds and other wildlife from nesting inside, preventing blockages that could lead to dangerous carbon monoxide buildup in the home. Historically, simple coverings were used, but modern designs offer improved functionality and durability.
The selection of appropriate chimney protection requires careful consideration of several factors, including flue size, local weather conditions, and the materials used in its construction. Different designs are available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of installation, maintenance, and overall performance.
Essential Considerations for Chimney Flue Protection
Selecting and installing an appropriate chimney covering requires careful evaluation to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the chimney system.
Tip 1: Accurate Flue Measurement: Prior to purchase, precisely measure the flue’s outer dimensions. Inaccurate measurements can lead to an improper fit and compromised protection.
Tip 2: Material Selection: Consider stainless steel for its superior corrosion resistance, particularly in coastal or high-precipitation environments. Galvanized steel offers a more economical option, but may require more frequent replacement.
Tip 3: Mesh Size Evaluation: Select a mesh size that effectively excludes debris and animals while allowing adequate draft. Too fine a mesh can restrict airflow, while too large a mesh can defeat the purpose.
Tip 4: Installation Method: Ensure the chosen installation method is compatible with the chimney’s construction. Band clamps, top-mount designs, and inside-flue installations each present different challenges and require specific tools.
Tip 5: Regular Inspection: Conduct routine inspections, at least annually, to identify any signs of damage, corrosion, or blockage. Promptly address any issues to prevent further deterioration of the chimney system.
Tip 6: Consider Local Climate: In areas with heavy snowfall, choose a design with adequate height to prevent snow accumulation from obstructing the flue opening. Wind-resistant models are beneficial in regions prone to strong gusts.
Tip 7: Professional Installation: For complex chimney configurations or challenging access, consider professional installation. A qualified technician can ensure proper installation and adherence to local building codes.
Adhering to these guidelines contributes to effective chimney protection, preventing costly repairs and ensuring safe operation of heating appliances.
Proper selection and maintenance are essential components of a well-functioning chimney system, warranting careful attention to detail and proactive measures.
1. Adaptable Flue Coverage
Adaptable flue coverage constitutes a primary design feature of the device, representing its capacity to effectively accommodate various chimney flue dimensions. This adaptability is a fundamental aspect that distinguishes a truly universal offering from more limited, size-specific solutions.
- Adjustable Base Mechanisms
Adjustable base mechanisms, commonly employing telescoping sections or expandable collars, enable the alteration of the covering’s dimensions to conform precisely to the outer diameter of the flue. For instance, a model with a telescoping base can be extended or retracted to fit flues ranging from 6 inches to 12 inches in diameter, minimizing the need for custom-fabricated solutions.
- Multi-Size Compatibility
Multi-size compatibility stems from designs that incorporate flexible components or strategically placed hardware, allowing the covering to adapt to both circular and square flues. An example would be a product featuring adjustable clamps that can be tightened to secure it to various flue shapes, ensuring a secure and weatherproof seal regardless of the chimney’s geometry.
- Material Flexibility
Material flexibility, particularly in components such as the mesh or rain hood, contributes to the adaptability of the overall product. A slightly flexible hood can conform to minor irregularities in the flue’s shape, while a malleable mesh can be bent to accommodate slightly non-standard dimensions.
- Installation Hardware Versatility
The design of installation hardware significantly impacts adaptability. Band clamps, for example, offer greater adjustability than fixed mounting brackets. Universal designs often include a variety of hardware options to accommodate different chimney constructions and mounting preferences, enhancing their adaptability to diverse applications.
These facets collectively contribute to the ability of a singular product to provide effective protection across a wide spectrum of chimney types. This adaptability reduces inventory requirements for retailers and simplifies the selection process for homeowners, underscoring the practical benefits of adaptable flue coverage.
2. Debris Exclusion
Effective exclusion of debris represents a core functional requirement of any chimney covering, particularly when considering models intended for widespread application. The ingress of leaves, twigs, animal nests, and other foreign materials into a chimney flue poses significant operational and safety hazards. Blockages restrict airflow, leading to inefficient combustion and increasing the risk of carbon monoxide accumulation within the dwelling. Furthermore, accumulated debris can act as a fire hazard, potentially igniting from stray embers and spreading to the surrounding structure. For instance, a chimney without adequate protection in a wooded area is highly susceptible to leaf accumulation, leading to reduced draft and potentially dangerous backdrafting of flue gases.
The design of an adaptable covering directly influences its ability to prevent debris entry. Mesh screens with appropriate aperture sizes are commonly employed to physically block larger objects while still permitting unobstructed airflow. The choice of mesh material, such as stainless steel or galvanized steel, impacts durability and resistance to corrosion, which can compromise the integrity of the barrier over time. The method of attachment of the mesh to the chimney covering’s frame is equally critical; poorly secured mesh can detach, creating gaps through which debris can enter. Consider a situation where a covering utilizes a mesh screen that is improperly fastened; wind and weather exposure can weaken the attachment points, allowing leaves to bypass the screen and accumulate within the flue.
In summary, the significance of debris exclusion in relation to adaptable chimney coverings cannot be overstated. It directly impacts the safe and efficient operation of the chimney system, preventing hazardous conditions and costly repairs. Proper design, material selection, and installation are essential to ensure long-term, reliable debris exclusion, safeguarding both the structure and the occupants from potential risks. Choosing a model specifically tested and certified for debris exclusion offers an added level of assurance in its performance.
3. Rain protection
Rain protection is a fundamental requirement for chimney coverings, directly affecting the longevity and structural integrity of the chimney system. The ingress of rainwater can lead to significant damage, necessitating a robust defense against moisture penetration. This aspect is paramount when considering coverings designed for diverse installations.
- Hood Design and Overhang
The physical structure of the covering, specifically the hood design, directly impacts its ability to deflect rainwater. A well-designed hood incorporates a sufficient overhang to prevent rain from entering the flue opening, even during periods of heavy precipitation accompanied by strong winds. For example, a model with a deep, conical hood provides superior protection compared to a flat or shallow design. Inadequate overhang allows rain to be driven directly into the flue, negating the intended protection.
- Material Waterproofing Properties
The materials used in the construction of the covering contribute to its overall effectiveness in preventing water intrusion. While stainless steel is inherently resistant to corrosion from water exposure, the joints and seams must also be adequately sealed to prevent leakage. Coatings and sealants can enhance the waterproofing properties of the covering. Consider a situation where a covering made of galvanized steel lacks proper sealant; the steel may corrode over time, creating pathways for water to enter the chimney structure.
- Flue Compatibility and Seal
Effective rain protection is contingent upon a proper fit between the covering and the chimney flue. A poorly fitting covering allows rainwater to bypass the intended barriers and enter the chimney. Models with adjustable bases or flexible components offer improved compatibility with a wider range of flue sizes and shapes, ensuring a tight, weatherproof seal. For instance, coverings designed for square flues must maintain a consistent seal along all edges to prevent water infiltration.
- Drainage Mechanisms
Some designs incorporate drainage mechanisms to channel away any water that may accumulate on the hood or other parts of the covering. These drainage systems prevent standing water, which can lead to corrosion and further damage over time. Examples include small weep holes or channels that direct water away from critical areas of the covering. Failure to provide adequate drainage can result in premature deterioration of the structure and increased risk of water damage to the chimney.
The elements detailed highlight the necessity for effective rain protection to mitigate potential damage and ensure optimal performance. The combination of hood design, material properties, flue compatibility, and drainage mechanisms are key to long term performance. The overall design must integrate these features to make rain protection effective.
4. Animal deterrence
Effective animal deterrence constitutes a critical function of chimney protection, preventing wildlife ingress and nesting within the chimney structure. Unprotected chimney flues offer an attractive shelter for various animals, leading to potential blockages and structural damage. The design and implementation of animal deterrence strategies within chimney covering designs are, therefore, of considerable importance.
- Mesh Aperture Size and Material
The dimensions of the mesh screen are paramount in preventing animal entry. A mesh with apertures too large will permit smaller animals, such as squirrels or birds, to bypass the barrier. Conversely, excessively small apertures can restrict airflow, compromising chimney draft. The material composition of the mesh, typically stainless steel, is also vital. Stainless steel provides durability and resists corrosion, ensuring the longevity of the animal deterrence mechanism. A real-world example involves situations where galvanized steel mesh deteriorates over time, creating entry points for animals previously excluded. This degradation undermines the functionality of the covering, necessitating replacement.
- Hood and Lid Design
The physical configuration of the covering, specifically the presence and design of a hood or lid, further contributes to animal deterrence. A properly designed hood overhangs the flue opening, physically impeding access for larger animals. Some models incorporate hinged lids, allowing for convenient chimney inspection and cleaning while maintaining a secure barrier against animal entry. Instances exist where coverings lacking a substantial hood permit determined animals to climb into the flue from above, circumventing the intended protection. Such occurrences underscore the importance of a comprehensive design that addresses multiple entry points.
- Secure Mounting and Attachment
The method of securing the covering to the chimney is integral to its effectiveness as an animal deterrent. Loose or improperly attached coverings provide opportunities for animals to dislodge or circumvent the protection. Secure mounting systems, such as band clamps or threaded fasteners, ensure a tight and stable connection between the covering and the chimney flue. A common scenario involves situations where poorly secured coverings are pushed aside by animals, particularly raccoons, which are known for their dexterity and strength. This breach of security renders the animal deterrence mechanism ineffective.
- Pest-Resistant Materials and Coatings
The selection of materials inherently resistant to animal gnawing or scratching can further enhance the deterrence capabilities of the product. Certain coatings or surface treatments can deter animals from attempting to gain entry, preventing damage to the covering itself. For instance, coverings coated with a bitter-tasting substance may discourage animals from chewing on the edges or seams. While not a primary line of defense, the use of pest-resistant materials contributes to the overall effectiveness of the animal deterrence strategy. These features prevent the degradation of the assembly, assuring long life.
Animal deterrence strategies employed within chimney coverings play a pivotal role in maintaining chimney system integrity and preventing potentially hazardous situations. The integration of appropriate mesh sizes, robust hood designs, secure mounting systems, and pest-resistant materials represents a multifaceted approach to safeguarding chimney flues from animal intrusion.
5. Corrosion resistance
Corrosion resistance is a critical performance characteristic of chimney coverings, particularly those marketed as “universal” due to their intended application across diverse environmental conditions. Material degradation due to corrosion compromises the structural integrity and protective function of the covering, leading to premature failure and potential safety hazards.
- Material Selection and Galvanic Corrosion
The choice of materials directly impacts corrosion resistance. Stainless steel, particularly 304 or 316 grades, offers superior resistance to atmospheric corrosion compared to galvanized steel or aluminum. The use of dissimilar metals in the chimney covering assembly can lead to galvanic corrosion, an accelerated form of degradation that occurs when two different metals are in electrical contact in the presence of an electrolyte (e.g., rainwater). For example, a galvanized steel mesh attached to a stainless steel frame will corrode preferentially due to galvanic action, even if both materials are individually resistant to corrosion. The mitigation of galvanic corrosion requires careful material selection and the use of insulating materials to prevent electrical contact between dissimilar metals.
- Protective Coatings and Surface Treatments
Protective coatings and surface treatments enhance the corrosion resistance of base materials. Powder coating, for instance, provides a durable, corrosion-resistant barrier on steel surfaces. However, the effectiveness of the coating depends on its adherence to the substrate and its resistance to chipping or scratching, which can expose the underlying metal to corrosion. Surface treatments, such as passivation of stainless steel, create a thin, protective oxide layer that inhibits corrosion. The selection of appropriate coatings and surface treatments depends on the specific environmental conditions to which the chimney covering will be exposed, including the presence of salt spray, industrial pollutants, or high humidity.
- Welding Techniques and Crevice Corrosion
Welding processes used in the fabrication of chimney coverings can significantly impact their corrosion resistance. Improper welding techniques can create crevices or areas of stress concentration that are susceptible to crevice corrosion, a localized form of corrosion that occurs in confined spaces where stagnant electrolyte solutions can accumulate. The use of proper welding procedures, such as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), and the application of post-weld cleaning and passivation treatments can minimize the risk of crevice corrosion. Inspection of welds for porosity or other defects is essential to ensure the long-term integrity of the chimney covering.
- Environmental Factors and Atmospheric Corrosion
The severity of atmospheric corrosion depends on various environmental factors, including temperature, humidity, precipitation, and the presence of corrosive agents, such as chlorides and sulfur dioxide. Chimney coverings installed in coastal areas are exposed to high concentrations of salt spray, which accelerates corrosion. In industrial areas, atmospheric pollutants can react with rainwater to form corrosive acids that attack the metal surfaces. The selection of corrosion-resistant materials and coatings must take into account these environmental factors. For example, a chimney covering installed in a marine environment should be constructed of 316 stainless steel or a comparable alloy with high resistance to chloride-induced corrosion.
These facets collectively underscore the importance of corrosion resistance in maintaining the functionality and safety of “universal” chimney coverings. The design and fabrication of these devices require careful consideration of material selection, protective coatings, welding techniques, and environmental factors to ensure long-term performance and prevent premature failure due to corrosion. Products lacking these considerations could be dangerous to its users.
6. Draft optimization
Chimney draft, the movement of combustion gases upwards through the flue, is fundamentally linked to the effective operation of a chimney system. The introduction of a covering, particularly a “universal” model intended for varied installations, can significantly influence this draft. Improper covering design or installation can impede airflow, leading to incomplete combustion, carbon monoxide buildup, and inefficient heating appliance performance. Thus, draft optimization is not merely a desirable feature but an essential design consideration for any covering. A poorly designed unit acting as an obstruction can negate the intended benefits of the chimney and its connected appliances, even increasing risks.
The impact of a chimney covering on draft manifests in several ways. The covering’s physical structure, including the hood design and the size and configuration of any mesh screens, directly affects airflow resistance. A restrictive design impedes the natural upward movement of gases, while an open design may allow excessive downdrafts, reversing the intended flow. The height of the covering above the flue termination point also influences draft, with taller models potentially enhancing upward flow. For example, a home situated in an area with frequent high winds requires a covering designed to minimize downdrafts, potentially incorporating a wind-directional vane to maintain consistent upward airflow. The selection of the covering has a direct impact on safety and efficiency.
In summary, draft optimization is an integral element in the design and selection of coverings. A well-designed “universal” product accounts for the potential impact on draft and incorporates features to minimize flow resistance and mitigate downdrafts. Understanding the relationship between covering design and draft is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the entire chimney system. Consideration must also be given to local climate conditions, fuel type, and appliance requirements to optimize performance, and a professional inspection is highly advised.
Frequently Asked Questions About Universal Chimney Caps
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, installation, and performance characteristics of chimney coverings, offering clarity on critical aspects of chimney protection.
Question 1: Are chimney coverings truly “universal” in application?
The term “universal” denotes a design intended to fit a range of flue sizes and shapes. However, strict adherence to product specifications, including flue dimensions, is essential for proper fit and functionality. Deviation from specified ranges compromises performance.
Question 2: What constitutes appropriate mesh size for effective debris exclusion?
Mesh size should exclude common debris such as leaves and small animals while permitting unrestricted airflow. A mesh aperture of approximately 3/4 inch typically balances debris exclusion with draft requirements. Smaller apertures may restrict airflow, impeding draft.
Question 3: How frequently should chimney coverings undergo inspection and maintenance?
Annual inspection is recommended to identify damage, corrosion, or debris accumulation. Prompt repair or replacement of compromised components ensures continued protection and prevents costly chimney repairs.
Question 4: What materials offer optimal corrosion resistance in diverse climates?
Stainless steel, particularly 304 or 316 grades, provides superior corrosion resistance compared to galvanized steel, particularly in coastal or high-precipitation environments. Galvanized steel offers a more economical option but requires more frequent replacement.
Question 5: Does installation impact the effectiveness of the chimney covering?
Improper installation compromises the protective function of the covering. Secure attachment to the flue is crucial to prevent dislodgement by wind or animals. Professional installation is recommended for complex chimney configurations or challenging access.
Question 6: What are the potential consequences of neglecting chimney protection?
Neglecting chimney protection leads to water damage, debris accumulation, animal nesting, and increased risk of chimney fires. These consequences necessitate costly repairs and compromise the safe operation of heating appliances.
In summary, the proper selection, installation, and maintenance of chimney coverings are essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of chimney systems. Adherence to recommended practices prevents costly repairs and protects against potential hazards.
The subsequent discussion will explore the economic considerations associated with chimney protection, analyzing the cost-benefit ratio of implementing proactive measures.
Universal Chimney Cap
This exploration has examined the multifaceted aspects of the universal chimney cap, highlighting its role in safeguarding chimney systems. Key considerations encompass adaptable flue coverage, effective debris exclusion, reliable rain protection, animal deterrence, corrosion resistance, and the optimization of chimney draft. The efficacy of any universal chimney cap hinges upon careful design, material selection, and proper installation, directly influencing its ability to prevent damage and ensure safe operation.
The information presented underscores the importance of proactive chimney maintenance. Diligent assessment of chimney requirements and the selection of an appropriate universal chimney cap represent a crucial investment in the longevity and safety of residential or commercial structures. Ignoring these protective measures invites potentially costly repairs and exposes occupants to preventable risks. Prioritizing comprehensive chimney protection remains a prudent and responsible course of action.