The cost of installing a chimney liner, the keyword in question, is a noun. Determining expenditure for this vital component of a chimney system depends on several factors, including the material used (stainless steel, aluminum, or clay), the chimney’s height and diameter, and the complexity of the installation. For example, a straightforward installation of a flexible stainless steel liner in a single-story home might cost significantly less than a complex installation involving a multi-story chimney requiring scaffolding and specialized tools.
A functioning chimney liner is essential for safe and efficient venting of combustion byproducts from fireplaces, stoves, and furnaces. Its installation prevents dangerous carbon monoxide from entering the home and protects the chimney’s masonry from corrosive acids produced during combustion. Historically, chimney liners were not always standard; however, modern building codes increasingly mandate their use to enhance safety and prolong the lifespan of the chimney structure.
Understanding the variables influencing the price is crucial for budgeting and ensuring a safe home heating system. The subsequent sections will delve into specific cost drivers, material options, and installation considerations that affect the final expenditure. These considerations range from the liner material to labor and potential obstacles within the chimney itself.
Tips Regarding Chimney Liner Expenditure
Evaluating the outlay associated with a chimney liner requires a comprehensive assessment of needs and available resources. Several key considerations can help control costs while ensuring a safe and effective installation.
Tip 1: Obtain Multiple Quotes: Secure bids from at least three qualified chimney service providers. This allows for comparison of pricing, material options, and installation techniques, providing a clearer picture of prevailing market rates.
Tip 2: Assess Chimney Condition: A thorough chimney inspection prior to liner installation is crucial. Existing damage may require repairs that will add to the overall cost. Addressing these issues upfront prevents further degradation and potentially more expensive interventions later.
Tip 3: Choose the Appropriate Material: Different fuels necessitate specific liner materials. Stainless steel is generally suitable for wood, gas, and oil, while aluminum is typically reserved for certain gas appliances. Selecting the incorrect material can compromise safety and void warranties, ultimately increasing the lifecycle cost.
Tip 4: Consider Liner Diameter: Selecting the correct liner diameter is crucial for optimal venting performance. An undersized liner can lead to draft issues and incomplete combustion, while an oversized liner can result in creosote buildup. Proper sizing should be determined by a qualified professional based on the appliance being vented.
Tip 5: Factor in Installation Complexity: The accessibility of the chimney and any obstructions within the flue directly impact labor costs. Chimneys with bends, offsets, or narrow clearances require more time and specialized tools, increasing the overall expense.
Tip 6: Check for Rebates and Incentives: Some utility companies or government programs offer rebates or tax credits for energy-efficient upgrades, including chimney liner installations. Researching available incentives can offset a portion of the expenditure.
Tip 7: Verify Contractor Credentials: Ensure the chosen contractor is licensed, insured, and possesses the necessary certifications for chimney liner installation. Hiring an unqualified individual may lead to improper installation, compromising safety and potentially incurring further costs for corrective measures.
Careful planning and diligent research are essential to managing the expenditure associated with a chimney liner. Prioritizing safety and long-term performance will ultimately result in the most cost-effective solution.
The following section will examine potential long-term cost savings associated with proper chimney maintenance and liner selection.
1. Material type
The composition of the chimney liner material is a primary determinant of expenditure. Different materials offer varying levels of durability, heat resistance, and compatibility with specific fuel types, directly influencing the overall installation cost. Stainless steel liners, known for their robust construction and resistance to corrosion, generally command a higher price than aluminum liners. This reflects the enhanced lifespan and suitability for a wider range of fuels, including wood, oil, and gas. Aluminum liners, while more economical, are typically restricted to use with specific gas appliances due to their lower heat tolerance and susceptibility to corrosive byproducts from other fuels. Therefore, the selection of material, driven by the intended fuel source, establishes a baseline for the expenditure.
Clay tile liners, historically a common choice, are less frequently installed today due to their susceptibility to cracking and degradation. While the initial material outlay may be lower compared to stainless steel, the potential for future repairs or replacement significantly impacts the long-term cost. Furthermore, retrofitting a clay tile chimney with a code-compliant liner often necessitates specialized techniques, further influencing total outlay. Consider a scenario where a homeowner initially opts for a less expensive aluminum liner for a gas furnace. Should the homeowner later decide to switch to a wood-burning stove, the aluminum liner would need replacement with a more durable stainless steel option, incurring additional expenditure that could have been avoided with the correct initial material selection.
In summation, the material chosen for a chimney liner has a cascading effect on the overall expense. It is essential to balance upfront expenditure with long-term performance and compatibility with the intended fuel source. Selecting an inappropriate material can lead to premature failure, increased maintenance costs, and potential safety hazards, thereby negating any initial savings. A qualified chimney professional can provide guidance on the optimal material choice based on specific needs and budgetary constraints, ensuring a cost-effective and safe installation.
2. Chimney Height
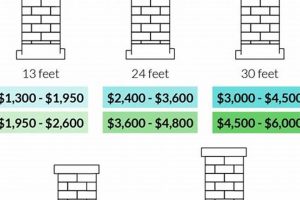
The vertical extent of a chimney, its height, directly influences the quantity of materials required for a liner installation, and consequently, the overall expenditure. A taller chimney necessitates a longer liner, whether constructed from stainless steel, aluminum, or clay. The increased material requirement translates directly into a higher initial outlay. For example, a chimney measuring 30 feet in height will require approximately twice the length of liner material compared to a 15-foot chimney, nearly doubling the material cost component. This correlation between height and material quantity represents a fundamental element in determining the overall project cost. Furthermore, taller structures often present logistical challenges, potentially impacting labor expenses.
Beyond the direct material cost, chimney height indirectly influences expenditure by increasing the complexity of the installation process. Taller chimneys often require specialized equipment such as scaffolding or lifts to safely access the chimney’s apex. The rental or purchase of such equipment adds to the overall project budget. Furthermore, the increased height elevates the risk associated with the installation, potentially requiring a more experienced, and therefore more costly, installation team. Consider a scenario where a homeowner with a two-story house (approximately 25 feet) requires a liner installation. The contractor may necessitate scaffolding to ensure safe access and proper liner insertion, adding several hundred dollars to the bill. In contrast, a single-story home might allow for ladder-based access, reducing or eliminating the need for specialized equipment and its associated costs.
In summary, chimney height serves as a significant cost driver in chimney liner installations. The direct relationship between height and material quantity, combined with the indirect impact on installation complexity and equipment needs, necessitates careful consideration during project planning. Accurate measurement of chimney height is essential for obtaining accurate cost estimates. Homeowners should be aware of this connection to effectively budget and evaluate bids from chimney service providers. Understanding this relationship allows for a more informed assessment of what amount is appropriate for the task, given the physical specifications of the structure.
3. Installation Complexity
The intricacy of a chimney liner installation plays a pivotal role in determining the final expenditure. Complexity encompasses various factors, ranging from physical accessibility to internal chimney structure, each contributing to the labor hours required and the specialized tools necessary.
- Accessibility of the Chimney
The ease with which a contractor can access the chimney significantly impacts labor costs. Chimneys located on steep roofs, or those with limited ground access due to landscaping or structures, necessitate additional safety precautions and potentially specialized equipment such as scaffolding or aerial lifts. The deployment of such resources adds to the project timeline and increases the overall expense. A straightforward installation on a readily accessible chimney can be completed more quickly and with fewer logistical challenges, resulting in lower labor costs.
- Obstructions Within the Flue
Pre-existing obstructions within the flue, such as collapsed tiles, bird nests, or creosote buildup, complicate the installation process. Removing these obstacles often requires specialized tools and techniques, adding to the labor hours. Severe obstructions may necessitate partial dismantling of the chimney, substantially increasing the expense. A clear and unobstructed flue facilitates a smoother and more efficient installation, minimizing labor costs.
- Chimney Offsets and Bends
Chimneys with offsets or bends deviate from a straight vertical path, complicating the insertion of a rigid or semi-rigid liner. Navigating these deviations requires skilled maneuvering and potentially the use of flexible liners, which may command a higher material price. Multiple offsets increase the difficulty and time required for installation, consequently impacting the labor costs. A straight, vertical flue allows for a more streamlined installation process, reducing the overall expense.
- Required Modifications
Existing chimney structures may require modifications to accommodate a new liner. This could involve enlarging the flue opening, removing existing damaged tiles, or installing a chimney cap adapter. Such modifications add to the labor hours and may necessitate specialized tools or materials, impacting the overall expenditure. A chimney that readily accepts a new liner without structural alterations represents a more cost-effective installation.
In conclusion, the complexity of a chimney liner installation is a multifaceted consideration that directly influences the final cost. Accessibility, obstructions, offsets, and required modifications all contribute to the labor hours, equipment needs, and material selection, ultimately determining the project’s expense. A thorough chimney inspection prior to initiating the installation process is crucial for identifying potential complexities and obtaining an accurate cost estimate. Failing to account for these factors can lead to unexpected expenses and project delays.
4. Labor Rates
Labor rates are a significant component of chimney liner installation expenses. The cost of labor reflects the expertise, time, and potential risks involved in the process. A higher degree of skill and experience often correlates with increased labor charges. Installation complexities, as previously discussed, directly influence the number of labor hours required, impacting the overall expenditure. For instance, if a chimney exhibits significant deterioration necessitating extensive preparation or repair prior to liner insertion, the increased labor hours translate directly into a higher bill. Consequently, fluctuations in local market labor rates and the specific contractor’s pricing structure directly influence what a chimney liner project should ultimately cost.
The practical significance of understanding labor rates lies in the ability to compare quotes effectively. Homeowners should scrutinize bids, paying attention to the breakdown of costs, including labor. A seemingly low overall bid may mask lower quality materials or less experienced installers, potentially leading to future problems and expenses. Conversely, an exceptionally high bid warrants a thorough justification, ensuring that the quoted labor rates align with the contractor’s qualifications and the project’s scope. An example would be evaluating two quotes for the same liner installation, one at $2000 and the other at $3000. A detailed analysis reveals that the higher quote includes $1200 for labor at $100/hour for 12 hours, while the lower quote allocates $500 for labor at $50/hour for 10 hours. This comparison highlights the importance of understanding the hourly rates and the estimated labor hours to assess the value proposition.
In summary, labor rates constitute a critical variable in determining the final expenditure for chimney liner installation. Understanding the factors influencing labor costs, scrutinizing bids, and verifying contractor qualifications are essential for making informed decisions. By considering the interplay between labor rates and installation complexity, homeowners can effectively manage their budgets and ensure a safe and code-compliant installation. The challenge lies in balancing the desire for cost savings with the need for qualified professionals and high-quality workmanship.
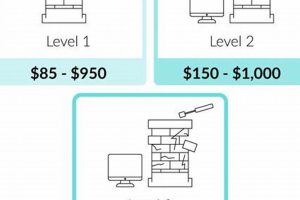
5. Inspection costs
Inspection costs are an integral component of the overall expenditure associated with chimney liner projects. These fees cover a professional evaluation of the chimney’s condition, identifying potential issues such as structural damage, blockages, or improper construction. This assessment directly impacts decisions regarding liner type, installation methods, and the necessity of supplementary repairs, ultimately influencing the total expenditure. Neglecting this initial inspection can lead to inaccurate cost estimates, unforeseen complications during installation, and potentially unsafe outcomes. For example, a homeowner might obtain a quote for a standard liner installation, only to discover during the process that the chimney requires extensive masonry repairs, significantly increasing the overall project cost. The initial inspection, although an added expense, mitigates this risk by providing a comprehensive understanding of the chimney’s true state.
The practical significance of understanding inspection costs lies in its influence on budgeting and project planning. Accurate inspection reports enable informed choices about liner materials and installation techniques, allowing homeowners to compare bids from different contractors effectively. A detailed inspection report serves as a baseline for evaluating the scope of work and identifying potential cost overruns. Consider a situation where two contractors provide quotes for the same chimney liner installation. One quote includes a detailed inspection report outlining specific issues and proposed solutions, while the other offers a lower price without a thorough assessment. While the latter option may appear more attractive initially, the lack of a comprehensive inspection report introduces uncertainty and potential for unforeseen costs. Opting for the more expensive quote with the detailed inspection report provides greater transparency and reduces the risk of unexpected expenses during the project.
In summary, inspection costs are not an optional add-on but rather a crucial investment in ensuring a safe and cost-effective chimney liner installation. These fees provide valuable insights into the chimney’s condition, allowing for informed decision-making and mitigating the risk of unexpected expenses. Homeowners should prioritize a comprehensive inspection as a foundational step in any chimney liner project, recognizing that the initial expenditure can prevent more substantial costs and potential safety hazards in the long run. Ignoring the inspection cost contributes to inaccurate cost estimations.
6. Code compliance
Adherence to local and national building codes exerts a significant influence on the expense associated with chimney liner projects. Code compliance mandates specific materials, installation techniques, and safety standards, directly impacting the overall cost. Ignoring these regulations can result in failed inspections, costly rework, and potential safety hazards, ultimately increasing the financial burden.
- Material Specifications
Building codes frequently dictate the type of liner material permissible for a given application, based on the fuel being burned and the chimney’s construction. For instance, aluminum liners may be prohibited for wood-burning appliances due to their lower heat resistance, necessitating the use of more expensive stainless steel. Compliance with these material specifications directly impacts the initial cost, as code-approved materials may command a higher price. Failure to adhere to these standards results in non-compliance, requiring replacement with the correct material.
- Installation Standards
Building codes often prescribe specific installation techniques, such as the required insulation around the liner, the method of connecting the liner to the appliance, and the proper sealing of joints. These standards ensure safe and efficient venting, preventing carbon monoxide leaks and chimney fires. Complying with these techniques requires skilled labor and potentially specialized tools, adding to the installation expense. Non-compliant installations may fail inspection and require corrective action, leading to additional costs.
- Inspection Requirements
Building codes typically mandate inspections during and after chimney liner installation to verify compliance with regulations. These inspections incur fees, adding to the overall project cost. However, successful inspections demonstrate adherence to safety standards and prevent future issues. Failure to pass inspection necessitates corrective measures, resulting in additional expenses and delays. The upfront cost of inspection is a safeguard, reducing the likelihood of more substantial future outlays.
- Permitting Fees
Many jurisdictions require homeowners to obtain permits prior to initiating chimney liner projects. These permits involve fees that contribute to the overall expenditure. While seemingly an added cost, obtaining the necessary permits ensures that the project complies with local regulations and avoids potential fines or legal issues. Undertaking a project without proper permits can result in stop-work orders and significant financial penalties.
Code compliance represents a crucial element in determining the total expenditure for chimney liner installation. The mandates regarding materials, installation, inspection, and permitting directly impact the project’s cost. Adhering to these regulations, while potentially increasing the upfront expense, ensures safety, prevents future problems, and avoids costly rework. The financial implications of neglecting code compliance far outweigh the initial cost of adhering to established building standards. The best route forward is always to hire only certified professionals that know how much should a chimney liner cost based on experience in code compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Chimney Liner Expenditure
The following addresses common inquiries concerning the pricing and factors influencing the cost of chimney liners. Information provided aims to clarify misconceptions and promote informed decision-making.
Question 1: What constitutes a reasonable price range for chimney liner installation?
A generally accepted price range varies significantly based on material selection, chimney height, accessibility, and local labor rates. A simple installation might start around $1,000, while complex projects involving extensive repairs or difficult access could exceed $5,000. Obtaining multiple quotes from qualified professionals is essential for establishing a fair market value.
Question 2: Does the type of fuel used affect the expenditure of the chimney liner?
Affirmatively. Certain fuels, such as wood and oil, produce corrosive byproducts necessitating the use of durable stainless steel liners. These liners typically command a higher price compared to aluminum liners suitable for some gas appliances. Selecting an inappropriate material can lead to premature failure and potentially hazardous conditions.
Question 3: Is it advisable to opt for the cheapest available chimney liner option?
Pursuing the least expensive option is generally discouraged. Chimney liners are critical safety components, and compromising on quality can have serious consequences. Prioritizing durability, code compliance, and professional installation is paramount, even if it entails a higher initial expenditure.
Question 4: What unforeseen expenditures might arise during chimney liner installation?
Unforeseen costs can stem from pre-existing chimney damage, such as cracked tiles or deteriorated masonry. Obstructions within the flue, such as bird nests or creosote buildup, can also increase labor hours and necessitate specialized equipment, adding to the overall expenditure. Thorough chimney inspection prior to installation mitigates this risk.
Question 5: Can homeowners install a chimney liner independently to reduce costs?
While technically feasible for some, self-installation is generally not recommended. Chimney liner installation requires specialized knowledge, skills, and tools. Improper installation can compromise safety and violate building codes. Engaging a qualified professional ensures code compliance and proper functionality.
Question 6: How frequently should a chimney liner be inspected and/or replaced?
Chimney liners should be inspected annually by a qualified professional. The lifespan of a liner varies depending on material, usage, and maintenance. Stainless steel liners can last 15-20 years or longer with proper care. However, any signs of damage or deterioration warrant immediate replacement.
Careful consideration of these points facilitates a well-informed approach to chimney liner projects. Seeking professional guidance ensures safety and maximizes the value of the investment.
The next segment will explore strategies for long-term cost management associated with chimney maintenance.
Expenditure on Chimney Liners
This exploration underscores the multifaceted nature of determining how much should a chimney liner cost. It highlights the significance of material selection, chimney dimensions, installation complexities, labor rates, inspection protocols, and stringent code compliance. A failure to adequately consider these elements leads to inaccurate cost estimations and potential safety compromises.
Homeowners must recognize that expenditure on a chimney liner is not merely a monetary transaction but an investment in safety, structural integrity, and regulatory adherence. The pursuit of short-term savings must not overshadow the long-term implications of inadequate protection. Seek expert consultation, prioritize quality workmanship, and ensure code compliance to secure peace of mind and protect property and well-being. The consequences of neglect far outweigh any perceived initial cost savings.