The expense associated with relining a flue is a significant consideration for homeowners maintaining a safe and efficient chimney system. This figure represents the total expenditure, encompassing materials, labor, and any necessary permits, to install a new liner within an existing chimney structure. As an example, a basic stainless steel liner installation for a standard residential chimney may fall within a specific price range, while more complex installations involving extensive chimney repairs or custom liners will naturally incur higher fees.
Proper flue maintenance is paramount for ensuring the safe venting of combustion byproducts from heating appliances. A deteriorated or damaged flue can lead to carbon monoxide leaks, chimney fires, and structural damage to the home. Investing in a sound flue safeguards the occupants and property, preventing potentially devastating consequences. Historically, clay tile liners were common, but modern materials offer improved durability and performance, justifying the investment for long-term protection.
Several factors influence the overall investment required for this type of home improvement. These considerations include the chosen material for the flue, the chimney’s height and accessibility, the complexity of the installation, and any preparatory work needed to address existing chimney deficiencies. Understanding these variables is essential for homeowners seeking to obtain accurate estimates and plan accordingly for this critical maintenance task.
Tips for Managing Chimney Lining Expenses
Effective management of expenditure requires a proactive approach. Prioritize safety and longevity while remaining budget-conscious.
Tip 1: Obtain Multiple Estimates: Contact several qualified chimney professionals for detailed quotes. Comparing bids allows for a better understanding of prevailing market and can reveal discrepancies or potential cost-saving opportunities.
Tip 2: Choose the Appropriate Material: Different liner materials, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or cast-in-place options, vary in price and suitability for specific appliances. Consult with a professional to determine the most cost-effective material that meets the appliance’s requirements and local building codes.
Tip 3: Address Chimney Issues Promptly: Neglecting minor chimney repairs can lead to more extensive and costly problems down the line. Addressing cracks, crumbling mortar, or water damage early can prevent the need for a complete relining and can potentially postpone future replacement expense.
Tip 4: Inquire About Warranties: Reputable chimney professionals typically offer warranties on their workmanship and materials. A warranty provides peace of mind and protection against potential defects or premature failures, mitigating future unexpected expenditure.
Tip 5: Schedule Inspections Regularly: Annual chimney inspections are crucial for identifying potential problems before they escalate. Early detection of liner damage or deterioration allows for timely repairs, preventing the need for a complete relining.
Tip 6: Consider DIY Options (with Caution): While some minor chimney repairs can be performed by homeowners, relining a chimney is generally best left to qualified professionals. Improper installation can be dangerous and may void warranties or violate building codes, ultimately increasing total expenditure in the long run.
Tip 7: Explore Financing Options: For significant chimney repairs or relining projects, consider exploring financing options such as home equity loans or lines of credit. Spreading out the payments can make the investment more manageable.
By proactively managing the situation, homeowners can effectively balance safety, functionality, and budgetary constraints. Prudent decision-making ensures a safe and efficient chimney system without incurring unnecessary financial burdens.
The following sections will delve into the long-term value and regulatory aspects of chimney relining, providing a comprehensive perspective on this important home maintenance investment.
1. Material Selection
The selection of materials directly influences the overall expenditure associated with relining a chimney. Different substances offer varying levels of durability, heat resistance, and corrosion protection, which subsequently affect their pricing. Stainless steel, for example, known for its robustness and suitability for a wide range of fuel types, generally incurs a higher initial expense compared to aluminum, which is typically used for venting gas appliances. This direct correlation dictates that choosing a more robust material, although potentially more expensive upfront, could yield long-term savings by reducing the frequency of future repairs or replacements.
For instance, a homeowner opting for a lower-grade aluminum liner for a wood-burning fireplace might face premature deterioration due to the higher temperatures and corrosive byproducts of wood combustion. This could necessitate an earlier replacement, effectively negating any initial savings achieved by selecting the cheaper material. Conversely, investing in a high-quality stainless steel liner, even at a greater initial expenditure, provides superior resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, resulting in a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance demands. This decision ultimately affects the long-term financial implications of maintaining a safe and functional chimney system.
In summation, material selection forms a critical component of the total expenditure required for flue maintenance. While cost considerations are important, prioritizing material quality based on the intended fuel type and chimney conditions is paramount. Understanding the trade-offs between initial cost and long-term durability allows homeowners to make informed decisions, optimizing the return on investment and ensuring the safety and efficiency of their chimney systems.
2. Chimney Accessibility
Accessibility to the chimney significantly influences the expense of flue maintenance. Restricted access adds complexity to the installation process, directly impacting labor costs. A chimney located on a steep roof, obscured by trees, or integrated within a complex architectural design presents logistical challenges for technicians. These challenges necessitate specialized equipment, extended working hours, and potentially a larger crew, all contributing to an elevated overall expense. Consider, for instance, a scenario where a chimney sweep must utilize scaffolding or a boom lift to reach the chimney top, adding several hundred dollars to the project.
Furthermore, internal accessibility also plays a critical role. Narrow flue dimensions or the presence of obstructions, such as collapsed liner sections or heavy creosote buildup, impede the insertion of new liners. These internal obstructions often require removal or remediation before a new liner can be installed, further increasing both labor hours and equipment costs. Failure to address these accessibility issues before initiating the project can lead to unforeseen delays and supplementary charges. For example, the removal of a severely damaged clay tile liner might require specialized tools and techniques, potentially adding days to the installation timeline.
In conclusion, chimney accessibility is a primary determinant of flue maintenance expense. Homeowners should recognize the potential cost implications associated with difficult-to-reach or internally obstructed chimneys. Transparent communication with chimney professionals regarding accessibility challenges allows for more accurate project estimates and proactive planning, potentially mitigating unexpected expenses and ensuring a safe and efficient installation. Overlooking accessibility issues can lead to budget overruns and project delays, highlighting the importance of thorough pre-installation assessments.
3. Liner Diameter
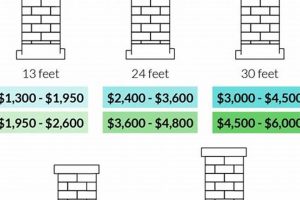
The internal dimensions of the flue directly influence material requirements, subsequently impacting the overall expense of chimney relining. A larger diameter necessitates a greater quantity of liner material, be it stainless steel, aluminum, or a cast-in-place mixture. This increase in material translates to a higher purchase price from suppliers, directly affecting the total expenditure. For instance, a chimney requiring an 8-inch diameter liner will demonstrably require more material than one needing a 6-inch diameter liner, leading to a tangible cost difference. Furthermore, larger diameters can require more complex installation techniques, potentially influencing labor hours and associated fees.
Optimal flue size is critical for efficient venting of combustion gases. An improperly sized flue can result in drafting issues, leading to the inefficient operation of heating appliances and the potential for carbon monoxide buildup. Undersized flues restrict airflow, increasing the risk of dangerous backdrafting, while oversized flues can allow for excessive cooling of exhaust gases, leading to creosote condensation and increased fire risk. Replacing an existing liner with one of an incorrect diameter necessitates careful consideration of appliance specifications and local building codes. This is why a licensed professional is required in many areas for chimney work.
In summary, the liner’s dimensions are an important factor for chimney relining expenditure. The proper diameter is not only required for efficient and safe operation, but also influences the amount of material needed. Understanding this relationship helps homeowners make informed decisions, balancing expenditure with long-term safety and operational efficiency. Correct sizing and installation ensures a safe, reliable venting system and avoid risks of serious consequences.
4. Local Labor Rates
The prevailing hourly or project-based charges for skilled tradespeople within a specific geographic area constitute a key determinant in the overall expense associated with chimney flue maintenance. These regional variations significantly influence the financial burden on homeowners undertaking this necessary home improvement task.
- Supply and Demand Dynamics
The availability of qualified chimney technicians in a given locale exerts a direct impact on labor rates. Regions with a limited pool of skilled professionals often experience higher rates due to increased demand. Conversely, areas with a surplus of technicians may offer more competitive pricing. For instance, a rural area with few specialized chimney services may command a premium compared to a densely populated metropolitan area where competition is rife.
- Cost of Living Considerations
Labor rates typically reflect the overall cost of living in a particular geographic area. Regions with higher costs of housing, transportation, and general expenses tend to have correspondingly higher labor rates across various trades, including chimney maintenance. Technicians operating in these areas require higher compensation to offset their living expenses, directly impacting the final investment required for flue maintenance.
- Union vs. Non-Union Labor
The presence of unionized labor forces can also influence labor rates. Union technicians typically adhere to standardized wage scales and benefit packages, which may result in higher hourly or project-based charges compared to non-union labor. While union labor may command a premium, it often guarantees a higher level of skill, training, and adherence to safety protocols.
- Seasonal Fluctuations
Demand for chimney services often experiences seasonal fluctuations, impacting labor rates. The period leading up to winter typically sees increased demand for inspections and maintenance, potentially driving up labor rates due to heightened demand. Conversely, during off-peak seasons, homeowners may find more competitive pricing as technicians seek to maintain a steady workload.
In conclusion, local labor rates form a crucial component of the financial investment required for chimney flue upkeep. Understanding the interplay between supply and demand, cost of living, union affiliations, and seasonal fluctuations allows homeowners to make informed decisions and budget effectively for this essential maintenance task. Engaging with local chimney professionals to obtain detailed quotes and inquire about labor rate structures empowers homeowners to navigate the economic landscape and secure fair and competitive pricing.
5. Inspection Requirement
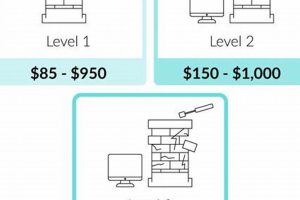
Mandatory assessments by qualified professionals form an integral, and often legally mandated, component of the financial investment in flue maintenance. These examinations, conducted before and sometimes after relining, serve to identify existing structural deficiencies, code compliance issues, and the suitability of the chosen lining material for the intended application. The resulting cost reflects both the direct fee for the inspection itself and any remedial work necessitated by the findings. For instance, a pre-relining inspection may uncover hidden cracks or deteriorated mortar joints requiring repair before the new liner can be installed, adding significantly to the overall project expense. Ignoring these underlying problems can lead to premature liner failure and potentially dangerous operating conditions.
Furthermore, many jurisdictions require a post-relining inspection to verify proper installation and adherence to relevant building codes. This step ensures the liner is correctly connected to the appliance and that venting pathways are unobstructed. Failure to pass this inspection can result in costly rework and potential legal penalties. As an example, improper liner connections may necessitate complete removal and reinstallation, doubling the labor expenditure. These regulatory obligations exist to protect homeowners from substandard workmanship and to mitigate the risk of chimney fires and carbon monoxide poisoning. The cost associated with these safeguards is a necessary investment in safety and regulatory compliance.
In summation, the necessity of professional evaluation directly influences the economic impact of flue maintenance. While inspection fees may appear as an additional burden, they represent a critical investment in preventing more substantial and potentially life-threatening problems. Accurate assessment, followed by appropriate repairs and adherence to building codes, ensures the long-term safety and efficiency of the chimney system. Therefore, integrating the expenditure associated with professional evaluation into the overall project estimate is essential for responsible home maintenance and regulatory adherence.
Frequently Asked Questions About Chimney Lining Expense
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the financial implications associated with flue upkeep.
Question 1: What factors primarily influence chimney flue expenditure?
Material selection, chimney accessibility, liner diameter, local labor rates, and inspection requirements constitute the primary cost drivers.
Question 2: Is it possible to reduce expenditure without compromising safety?
Obtaining multiple estimates, choosing the appropriate lining material for the application, and addressing chimney issues promptly can potentially mitigate expenses without sacrificing safety.
Question 3: Why do labor rates vary significantly across different regions?
Labor rates are influenced by supply and demand dynamics, cost of living considerations, union versus non-union labor, and seasonal fluctuations.
Question 4: Are professional examinations truly necessary, or can they be bypassed to save money?
Professional evaluations are crucial for identifying existing structural deficiencies, ensuring code compliance, and verifying proper installation. Bypassing these assessments can lead to long-term safety risks and potential legal penalties.
Question 5: Does homeowner’s insurance typically cover flue replacement expenditure?
Homeowner’s insurance coverage for flue replacement varies depending on the policy and the cause of the damage. Gradual deterioration is often excluded, while sudden damage from a covered event may be eligible for reimbursement. Consult the insurance provider for clarification.
Question 6: What are the potential long-term financial implications of neglecting flue maintenance?
Neglecting upkeep can result in carbon monoxide leaks, chimney fires, structural damage to the home, and increased energy costs due to inefficient venting. The cumulative financial burden of these consequences can far exceed the expense of proactive maintenance.
Flue investment is a multifaceted issue with numerous influencing factors. Careful planning and informed decision-making are essential for managing expenses effectively.
The subsequent section will explore the return on investment and long-term benefits of proper flue maintenance.
Chimney Lining Cost
This examination has detailed the multifaceted nature of expenses associated with flue maintenance. Material selection, accessibility challenges, flue diameter, local labor rates, and required inspections all contribute significantly to the total expenditure. While cost considerations are vital, prioritizing safety, code compliance, and long-term efficiency remains paramount. Prudent planning, obtaining multiple estimates, and addressing issues proactively can mitigate financial burdens.
Investing in a sound and properly maintained flue is an investment in the structural integrity of a dwelling and the safety of its occupants. The avoidance of potential hazards, coupled with adherence to regulatory standards, underscores the long-term value. Therefore, homeowners are urged to approach this critical maintenance task with diligence, ensuring a safe and efficient chimney system.