The expense associated with the installation or replacement of a flue lining system within a chimney is a significant factor for homeowners. This expenditure encompasses materials, labor, and any necessary permits. The final amount can vary greatly depending on factors such as the type of material selected (stainless steel, clay, or cast-in-place), the chimney’s height and accessibility, and the complexity of the installation. For example, a straightforward stainless steel liner installation in a short, easily accessible chimney will typically be less expensive than a complex installation requiring extensive modifications or a cast-in-place system.
Maintaining a safe and functional chimney is paramount for preventing house fires and carbon monoxide poisoning. A properly installed and maintained flue lining system is crucial for venting combustion gases safely to the outside. Historically, chimneys were constructed without liners, leading to deterioration of the brickwork and potential hazards. The implementation of building codes mandating liners has significantly reduced chimney-related incidents. The investment in this feature protects both the structure and the occupants of the building, providing long-term peace of mind.
Therefore, understanding the elements influencing the price is crucial when budgeting for chimney maintenance or renovation. The following sections will delve into the specifics of these components, providing a detailed breakdown of the factors that impact the final expenditure.
Optimizing Expenditure on Chimney Flue Installation
Strategic planning and informed decision-making are essential to manage the financial implications of installing or replacing a flue lining system.
Tip 1: Obtain Multiple Quotations. Comparing bids from several reputable contractors is a foundational step. These quotations should detail the scope of work, materials to be used, and labor charges. A thorough review allows for identifying the most competitive and comprehensive offer.
Tip 2: Consider Material Longevity. While a lower initial price may be tempting, opting for a less durable material could lead to premature failure and subsequent replacement. Evaluate the long-term value of materials like stainless steel, known for its resistance to corrosion and extended lifespan, despite potentially higher upfront amount.
Tip 3: Schedule Inspections Strategically. Regular chimney inspections can identify potential problems early, preventing minor issues from escalating into major repairs requiring a complete flue lining replacement. This proactive approach can save substantial funds in the long run.
Tip 4: Explore Seasonal Discounts. Demand for chimney services typically fluctuates throughout the year. Consider scheduling the installation or replacement during the off-season (e.g., spring or summer) when contractors may offer reduced rates to attract business.
Tip 5: Ensure Proper Sizing. An improperly sized flue liner can negatively impact the efficiency of the heating appliance and potentially lead to dangerous conditions such as carbon monoxide buildup. Accurate sizing is crucial for safety and optimal performance, avoiding costly rework later.
Tip 6: Verify Contractor Credentials. Select a contractor with proper licensing, insurance, and certifications. This ensures the work is performed to code and protects against liability in case of accidents or substandard workmanship, potentially increasing installation quotes if uncertified personnel perform the installation.
Careful consideration of these strategies can significantly influence the overall investment. Prioritizing long-term value and safety is paramount.
The next section will provide a comprehensive overview of factors impacting the overall price, offering a clearer understanding of the expense incurred.
1. Material Type
The selection of material for a flue lining system is a primary determinant of the overall expense. The characteristics of each material, including its durability, heat resistance, and ease of installation, significantly impact the final investment.
- Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is favored for its robust corrosion resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures. Its versatility allows it to be used with various fuel types, including wood, gas, and oil. The initial cost is typically higher than other options, but the extended lifespan and resistance to deterioration often result in long-term savings, making it a cost-effective choice in many scenarios. For example, in regions with high humidity or frequent temperature fluctuations, a stainless steel liner will provide greater protection against moisture and chemical attack, thus prolonging its functional life.
- Aluminum
Aluminum is primarily suitable for use with specific gas-burning appliances where the flue gas temperatures are relatively low. It is a less expensive option compared to stainless steel but is not appropriate for use with wood-burning stoves or oil-fueled appliances due to its lower heat tolerance and susceptibility to corrosion from the byproducts of these fuels. An instance where aluminum might be considered is for a modern high-efficiency gas furnace installation where flue gas temperatures are controlled and relatively low.
- Clay Tile
Clay tiles have been historically used as flue liners but are increasingly less common in modern installations. While relatively inexpensive, clay tiles are prone to cracking and disintegration over time due to thermal stress and exposure to acidic condensation. Repairing or replacing damaged clay tile liners can be labor-intensive and costly, often necessitating significant chimney reconstruction. Homes built before modern building codes often have this type of system.
- Cast-In-Place
Cast-in-place liners involve pouring a heat-resistant mixture into the existing chimney to create a seamless flue lining. This option is suitable for irregular or damaged chimneys but is generally more expensive than installing a prefabricated liner due to the complexity of the installation process and the need for specialized equipment. In cases where a chimney has significant structural issues, cast-in-place is a viable consideration, despite increased initial expenditure.
Therefore, the choice of material is a critical decision that impacts both the immediate and long-term cost of the system. A comprehensive assessment of the heating appliance, fuel type, and environmental conditions is essential for selecting the most appropriate and financially sound option.
2. Chimney Height
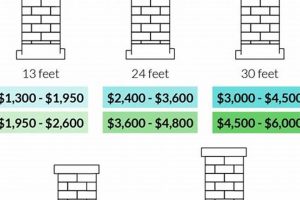
The vertical dimension of a chimney is a primary driver of the expenditure associated with flue lining systems. The direct relationship between chimney height and expense arises from the increased material requirements and labor hours necessary for taller structures. A chimney extending thirty feet, for example, will necessitate a proportionally larger quantity of liner material compared to a chimney measuring only fifteen feet. This linear increase in material directly translates to higher material costs.
Furthermore, the labor component is significantly affected. Installing a flue liner in a taller chimney necessitates more time and specialized equipment to safely and efficiently maneuver materials. The complexity of the task increases with height, often requiring scaffolding or specialized lifting equipment to transport the liner and secure it within the chimney. Safety considerations also play a crucial role, demanding stringent protocols and experienced personnel, which invariably contributes to higher labor charges. The potential risks associated with working at elevated heights necessitate that contractors allocate more resources to ensure a secure working environment.
In summary, the height of a chimney has a direct and quantifiable effect on the installation or replacement cost of its flue liner. This stems from the greater volume of materials required, the increased labor hours involved, and the enhanced safety measures that must be implemented. Understanding this relationship allows homeowners to better anticipate and budget for chimney maintenance or renovation projects, acknowledging that the vertical dimension is a key determinant of the final amount.
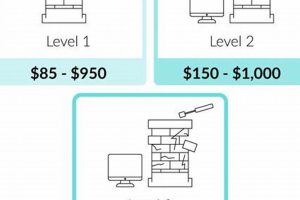
3. Installation Complexity
The intricacy of a flue lining system installation directly impacts the final expenditure. Complexity arises from factors such as chimney offset, the presence of tight clearances, or the need for extensive structural modifications. Each of these elements introduces additional labor hours, specialized tools, and potentially, customized material fabrication. A chimney with multiple bends or offsets, for example, necessitates a flexible liner and requires meticulous maneuvering and connection of sections, increasing the time investment and associated expenses. Furthermore, limited accessibility to the chimney, whether due to surrounding structures or challenging roof access, adds to the logistical hurdles and labor costs.
The requirement for structural modifications introduces another layer of complexity. If the existing chimney structure is damaged or does not meet current building codes, preparatory work, such as repairing brickwork or widening the flue, becomes essential. Such modifications demand specialized masonry skills and may necessitate obtaining additional permits, further augmenting the overall financial amount. Consider a scenario where the existing flue is undersized for a new, more efficient heating appliance. This would necessitate enlarging the flue opening, potentially requiring the removal and rebuilding of a section of the chimney, dramatically increasing the complexity and, consequently, the associated expense.
In summary, the complexity of the installation environment and the scope of required modifications are primary drivers of the expenditure. A thorough assessment of these factors is crucial for accurate cost estimation and effective budgeting. Overlooking these intricacies can lead to unexpected costs and delays, emphasizing the importance of engaging qualified professionals capable of assessing and addressing potential challenges. Addressing complexity proactively can mitigate unforeseen expenses and ensure a successful, code-compliant installation. The next sections will address the impact of accessibility to the chimney and regional code compliance.
4. Accessibility
The ease with which a chimney can be reached significantly influences the cost associated with flue liner installation or replacement. Challenging access translates to increased labor hours, specialized equipment needs, and potential safety risks, all of which contribute to a higher final investment.
- Roof Pitch and Height
Steeply pitched roofs and significant building height pose logistical difficulties for transporting materials and ensuring worker safety. These conditions often necessitate the use of scaffolding, aerial lifts, or specialized rigging equipment, adding to the overall expenditure. For instance, a three-story house with a 45-degree roof pitch will require more extensive safety measures and equipment than a single-story ranch house, directly impacting labor costs and potentially material handling expenses.
- Surrounding Obstacles
Proximity to trees, power lines, or other structures can impede access to the chimney, requiring creative problem-solving and additional precautions. The presence of such obstacles might necessitate tree trimming, power line relocation (which is rarely feasible but an example), or the use of smaller, more maneuverable equipment, each adding to the overall amount. A chimney located in a densely wooded area, for example, might require significant clearing to allow safe and efficient access for workers and equipment.
- Chimney Location on the Roof
A chimney located near the center of a large roof surface is generally more difficult to access than one situated near the edge. This requires workers to traverse greater distances on the roof, increasing the risk of falls and slowing down the work process. The increased time and risk associated with accessing centrally located chimneys often translate to higher labor charges.
- Interior Access Restrictions
In some cases, accessing the chimney flue from within the building is necessary for inspection or installation purposes. Limited interior access due to confined spaces, structural obstructions, or the presence of finished walls can add to the complexity and expenditure of the project. For example, a chimney that is fully enclosed within a finished chase may require demolition and reconstruction to gain adequate access for flue liner installation, adding significantly to the total amount.
Therefore, evaluating the ease of approach is critical when assessing the overall financial burden associated with flue liner projects. Overlooking these access-related factors can lead to inaccurate estimates and unexpected costs. A comprehensive site assessment by a qualified professional is essential to identify potential accessibility challenges and incorporate them into the overall budget.
5. Local Codes
Adherence to local building codes and regulations is a non-negotiable aspect of chimney liner installation and a significant determinant of the overall financial burden. These codes, designed to ensure safety and structural integrity, often dictate specific material requirements, installation techniques, and inspection protocols, all of which directly influence the final expenditure.
- Mandated Materials and Standards
Local codes frequently specify approved materials for flue liners based on fuel type, appliance efficiency, and regional environmental factors. These regulations might mandate the use of stainless steel liners for wood-burning stoves in areas with stringent air quality standards or require specific grades of steel for high-efficiency appliances to resist corrosive flue gases. Non-compliance with these material requirements necessitates corrective action, resulting in increased material expenditure and potential rework charges. An example includes specific regulations on the thickness and alloy of the steel used for chimney liners.
- Required Installation Techniques
Local building codes often prescribe specific installation methods to ensure proper venting and fire safety. These regulations may include requirements for insulation around the flue liner, minimum clearances from combustible materials, and secure connection methods for liner sections. Deviations from these mandated techniques can lead to code violations, necessitating costly rework to bring the installation into compliance. One example is the requirement to use specific connecting hardware that meets safety standards.
- Inspection and Permitting Fees
Most jurisdictions require permits for chimney liner installations or replacements. Obtaining these permits entails application fees and mandatory inspections by local building officials. These inspections ensure compliance with relevant codes and regulations. Failure to secure necessary permits can result in fines, project delays, and potential legal repercussions, adding unforeseen expenses to the project. This could also entail further remedial work and an entire chimney redesign.
- Seismic and Environmental Considerations
In regions prone to earthquakes or extreme weather events, local codes may incorporate specific requirements for chimney bracing, reinforcement, or weatherproofing. These measures are designed to enhance the chimney’s resistance to seismic activity or harsh environmental conditions. Compliance with these specialized requirements can increase material and labor expenses, ensuring structural integrity and safety in the face of natural hazards. Such considerations may be necessary in areas with high wind speeds and heavy snowfall.
In summary, the influence of local codes on the expenses of chimney lining stems from material specifications, installation methodologies, and mandatory inspections. Compliance with these codes is paramount to avoid penalties, ensure safety, and guarantee the long-term functionality of the chimney system. Ignoring local codes is not only illegal but also potentially dangerous.
6. Contractor Fees
The expense associated with hiring a chimney professional constitutes a significant component of the overall flue lining expenditure. These fees are not arbitrary; rather, they represent compensation for expertise, labor, insurance coverage, and overhead costs incurred by the contracting company. Several factors influence the determination of these fees, including the project’s complexity, chimney height, material selection, and local market rates. For example, a contractor installing a stainless-steel liner in a tall chimney with limited accessibility will likely command a higher fee due to the increased labor and specialized equipment required. Conversely, a straightforward replacement of an existing liner in an easily accessible chimney will typically result in a lower rate. Insurance, licensing and bonding are all factors affecting fees.
The selection of a contractor directly impacts the overall financial burden. While opting for the lowest bid might seem appealing, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the contractor’s qualifications, experience, and reputation. A contractor with inadequate experience or lacking proper insurance coverage may offer a lower initial rate but could potentially lead to substandard workmanship, code violations, or liability issues in case of accidents. Conversely, a reputable contractor with a proven track record is more likely to provide a comprehensive assessment, adhere to industry best practices, and ensure code compliance, potentially saving money in the long run by preventing costly rework or safety hazards. Reputable contractors will have appropriate licenses and insurance to perform the required work.
In summary, contractor fees are a substantial and justifiable part of the chimney flue installation cost. These charges cover the contractor’s expertise, labor, and business overhead. Prudent homeowners must carefully consider not only the monetary amount but also the contractor’s qualifications and reputation. Selecting a qualified and insured professional, even at a slightly higher rate, is frequently a prudent investment that safeguards against potential problems and ensures a safe and code-compliant outcome.
7. Permit expenses
The procurement of permits represents a mandatory element within the total outlay for chimney flue installation. These expenses, levied by local governing bodies, ensure adherence to established safety and building regulations. The amounts are not standardized; they fluctuate significantly depending on the jurisdiction, the complexity of the project, and the assessed value of the improvement. For instance, an extensive flue liner replacement involving structural modifications necessitates a more thorough review process, consequently resulting in higher permit fees. Failure to secure the requisite authorization prior to commencing work can result in significant fines, project delays, and potential legal ramifications, all of which directly inflate the overall project expenditure.
These expenses are not merely bureaucratic hurdles; they serve a critical function in ensuring public safety. Permit acquisition triggers inspections by qualified building officials who verify that the installation complies with prevailing codes. This independent verification mitigates the risk of faulty workmanship, improper venting, and potential fire hazards. A real-world example involves a homeowner who bypassed the permit process to save on initial amounts, only to discover that the unpermitted installation failed to meet fire safety standards, necessitating complete removal and re-installation at a substantially greater expense, including fines for non-compliance. Moreover, unpermitted work can affect property values and insurability, creating long-term financial disadvantages.
In conclusion, permit expenses constitute an integral and unavoidable component of the chimney liner amount. Although these charges may seem like an added burden, they provide essential safeguards and quality assurance, protecting both the homeowner and the community. Understanding the significance of these regulatory costs is crucial for accurate project budgeting and avoiding potentially disastrous consequences. Responsible homeowners recognize that securing the proper permits is not merely a legal obligation but a vital step in ensuring a safe and sound chimney system.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding expenditure related to chimney flue lining systems, providing clarity on key aspects.
Question 1: What factors primarily influence the expenditure for a chimney flue lining system?
The selection of material, chimney height, installation complexity, accessibility, local code compliance, contractor fees, and permit costs are all elements that will change the overall amount.
Question 2: How does the choice of liner material impact the total financial requirement?
Different materials, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or cast-in-place systems, exhibit varying price points due to their differing lifespans, heat resistance, and installation complexity. Stainless steel typically commands a higher initial investment but offers superior durability and resistance to corrosion.
Question 3: Does chimney height significantly affect the project budget?
Yes, taller chimneys require more material and labor, leading to increased costs. The longer the chimney, the greater the quantity of liner material needed and the longer the installation time. Labor is often more difficult due to work-at-height concerns.
Question 4: How does the complexity of the installation influence the monetary amount required?
Chimneys with offsets, tight clearances, or structural damage necessitate specialized installation techniques and may require custom fabrication, increasing labor costs and potentially material needs. Significant work must be performed in order to accommodate unusual chimney design and issues.
Question 5: Are permit fees a substantial expense within the overall budget?
While permit fees vary by jurisdiction, they are a necessary cost. Bypassing permit requirements can result in fines, legal repercussions, and potential safety hazards that outweigh the initial savings. In most jurisdictions, such work is illegal.
Question 6: How can homeowners effectively manage expenditure related to chimney flue lining projects?
Obtaining multiple quotes, scheduling inspections strategically, considering material longevity, and verifying contractor credentials are effective strategies for cost management.
Understanding these key factors provides a solid foundation for navigating the complexities associated with this expense.
The next article section provides a conclusion and reiteration of the concepts discussed above.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has elucidated the multifaceted nature of chimney flue lining expenditures. It is established that the total investment is not a monolithic figure, but rather a composite derived from material selection, chimney dimensions, installation intricacies, accessibility constraints, regulatory compliance, and professional service fees. Overlooking any of these contributing factors risks inaccurate budgeting and potentially compromises the safety and longevity of the chimney system. Therefore, a diligent assessment of each component is paramount for informed decision-making.
Ultimately, the expenditure associated with a chimney flue liner should be viewed as an investment in property preservation and, more importantly, occupant safety. While budgetary constraints are a valid consideration, prioritizing quality materials, skilled installation, and adherence to code ensures a reliable and efficient venting system for years to come. Homeowners are encouraged to engage qualified professionals, conduct thorough research, and seek comprehensive estimates to navigate the complexities of this essential home maintenance task, thereby safeguarding their homes and families.