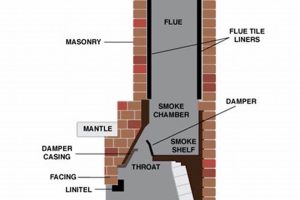
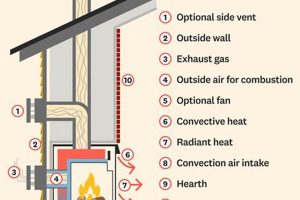
A governing body or established organization provides oversight, regulations, and guidelines concerning the construction, maintenance, and safety of residential and commercial heating structures. This entity ensures adherence to standardized practices and codes, mitigating risks associated with these systems. For example, it might specify requirements for flue liners, clearances to combustible materials, and inspection protocols.
Its existence is predicated on the need to protect property and life from fire hazards and carbon monoxide poisoning. Historically, insufficient regulations and oversight led to numerous preventable incidents. These organizations promote best practices, offer certifications for technicians, and educate the public about safe operation and upkeep, contributing to community well-being and reducing the potential for damage.
The following discussion will delve into specific aspects such as inspection procedures, common defects, maintenance strategies, and relevant safety codes related to these heating systems, all aimed at ensuring their safe and efficient operation.
Guidance for Safe and Efficient Fireplace and Chimney Operation
The following recommendations are provided to ensure the safe and efficient operation of residential heating systems. Adherence to these guidelines minimizes the risk of fire, carbon monoxide exposure, and structural damage.
Tip 1: Annual Inspection is Essential: A qualified technician should conduct a comprehensive inspection at least once per year. This examination identifies potential hazards, such as cracks, obstructions, or deteriorated components, before they escalate into serious problems.
Tip 2: Regular Cleaning Prevents Hazards: Creosote, a byproduct of combustion, accumulates in the chimney. This highly flammable substance should be professionally removed regularly to mitigate the risk of chimney fires. The frequency of cleaning depends on usage and fuel type.
Tip 3: Proper Fuel Selection is Critical: Utilize only seasoned firewood or approved manufactured logs. Burning unseasoned wood produces excessive smoke and creosote, increasing the risk of chimney fires and reducing efficiency.
Tip 4: Ensure Adequate Ventilation: Proper airflow is vital for complete combustion and efficient removal of exhaust gases. Avoid blocking air inlets or outlets, and consider installing a carbon monoxide detector as an added safety measure.
Tip 5: Damper Operation and Maintenance: The damper should be fully functional and properly sealed when the fireplace is not in use. This prevents heat loss and drafts. Inspect the damper regularly for damage or corrosion.
Tip 6: Professional Repairs are Necessary: Any identified defects, such as cracks in the firebox or chimney liner, should be addressed promptly by a qualified professional. Delaying repairs can compromise the structural integrity of the system and create significant safety hazards.
Implementing these guidelines will contribute to the safe and efficient operation of a fireplace and chimney system, ensuring peace of mind and protection for occupants and property.
Subsequent sections will provide a more in-depth look at specific inspection procedures and potential problem areas.
1. Regulation
The regulatory framework governing fireplace and chimney systems is a cornerstone of the authority’s mandate. These regulations dictate construction standards, material specifications, permissible usage parameters, and maintenance protocols. The absence of stringent regulations can lead to substandard installations, increased fire risks, and elevated carbon monoxide exposure within residential structures. The regulations enforced by an authority establish a minimum acceptable level of safety and performance, directly impacting public health and property protection.
An example of this influence is seen in regulations surrounding chimney liner requirements. Many jurisdictions mandate the installation of approved liners to prevent corrosive flue gases from deteriorating the chimney structure and potentially entering living spaces. Without these regulations, homeowners might opt for cheaper, less durable solutions, resulting in significant structural damage and increased safety hazards over time. Furthermore, regulations often specify allowable distances between heating appliances and combustible materials, thereby reducing the risk of accidental ignition and subsequent fires. The authorities’ role in codifying and enforcing these regulations is, therefore, vital.
Ultimately, regulation, as implemented and overseen by a relevant entity, serves as a preventative measure. By setting and enforcing standards, such authorities minimize the likelihood of failures, reduce the severity of incidents when they occur, and promote a culture of safety and responsible operation within the heating appliance industry. These collective benefits underscore the practical significance of understanding the interconnectedness between regulation and the responsible management of fireplace and chimney systems. Ongoing challenges involve adapting regulations to new technologies and ensuring consistent enforcement across different regions.
2. Inspection
Inspection forms a critical operational component of a fireplace and chimney governing body. It provides a mechanism for verifying adherence to established safety standards and regulatory codes. The process entails a systematic assessment of the system’s structural integrity, operational functionality, and potential hazards. Without rigorous and standardized inspection protocols, the effectiveness of regulatory measures diminishes significantly, increasing the likelihood of malfunctions, fires, and carbon monoxide leaks. For instance, annual inspections are often mandated to identify issues such as creosote buildup, damaged flue liners, or improper clearances to combustible materials, conditions directly contributing to fire risks if left unaddressed.
The practical application of inspections extends beyond mere identification of existing problems. They serve as a crucial data-gathering tool for informing future regulatory refinements and safety enhancements. By analyzing inspection reports, authorities can identify common points of failure, emerging risks associated with new technologies, or inadequacies in existing codes. This feedback loop ensures that the regulatory framework remains responsive to evolving challenges. Furthermore, inspection outcomes influence the certification process of technicians, incentivizing competency and adherence to best practices within the industry. Consider a scenario where repeated inspection failures reveal a widespread lack of knowledge regarding a new type of chimney liner. This prompts the governing body to revise training curricula and update certification requirements, ultimately improving the overall quality of installations.
In summary, inspection is not merely a reactive measure but an integral proactive process central to the function of fireplace and chimney regulatory bodies. It provides tangible data for assessing compliance, informing policy adjustments, and promoting ongoing improvements in safety and operational efficiency. The challenges lie in ensuring consistent inspection quality, adequate inspector training, and effective communication of inspection findings to homeowners and relevant stakeholders. By prioritizing these aspects, the efficacy of inspections is maximized, contributing directly to the preservation of life and property.
3. Certification
Certification serves as a critical mechanism through which a fireplace and chimney regulatory body ensures professional competence and adherence to established safety standards within the industry. By establishing and administering certification programs, the authority creates a verifiable benchmark of knowledge, skill, and ethical conduct for technicians involved in installation, inspection, maintenance, and repair activities. The direct consequence of this process is an increased level of consumer protection, reduced risk of faulty workmanship, and improved overall system safety. For example, a certified chimney sweep has demonstrated proficiency in identifying and addressing common hazards like creosote buildup and structural defects, thus mitigating the risk of chimney fires. Certification, therefore, functions as a key assurance of quality and expertise.
The practical benefits of certification extend beyond individual technician competence. Regulatory bodies often mandate certification as a prerequisite for performing specific types of work or obtaining necessary permits. This requirement channels qualified professionals into the market, discouraging unqualified individuals from engaging in potentially dangerous practices. Furthermore, certification programs often incorporate continuing education components, compelling certified technicians to stay abreast of evolving technologies, code updates, and best practices. This ongoing professional development contributes to continuous improvements in industry standards and performance. Insurance companies may also offer reduced premiums to homeowners who utilize certified professionals, acknowledging the reduced risk associated with qualified service providers. The presence of mandatory or incentivized certification promotes a culture of professionalism and safety within the industry.
In summary, certification is not simply a credential but an integral function of a fireplace and chimney regulatory body. It provides a standardized means of validating competence, driving industry improvements, and safeguarding public welfare. Challenges lie in maintaining program rigor, ensuring accessibility to training resources, and preventing fraudulent certification. By effectively managing and enforcing certification programs, the governing body strengthens its capacity to promote safe and efficient fireplace and chimney operations, thereby protecting property and saving lives.
4. Safety Standards
Safety standards constitute the foundational principles upon which a fireplace and chimney authority operates. These standards, encompassing material specifications, installation protocols, and operational guidelines, are instrumental in mitigating fire hazards, preventing carbon monoxide poisoning, and ensuring structural integrity. The absence of rigorous safety standards effectively negates the authority’s purpose. For instance, prescribed chimney height requirements prevent downdrafts and ensure proper ventilation of combustion byproducts, directly impacting indoor air quality and reducing the risk of carbon monoxide accumulation. Without these established benchmarks, the likelihood of malfunctions and associated dangers increases significantly.
The practical application of safety standards manifests in various ways. Installation guidelines mandate minimum clearances between the chimney and combustible materials, preventing the spread of fire to surrounding structures. Requirements for flue liner materials and construction prevent the corrosion and deterioration of the chimney, maintaining its structural integrity over time. Regular inspections, mandated by the authority, assess adherence to these safety standards, identifying potential deviations and prompting corrective actions. Furthermore, investigation reports from incidents involving violations of safety standards serve as a basis for refining existing codes and implementing more effective preventative measures. For example, if an incident is caused by the use of a non-approved liner, the authority may adjust approved liner material and implement more stringent inspections.
In summary, safety standards are indispensable to the effectiveness of a fireplace and chimney authority. They provide the framework for ensuring safe and efficient operation, informing regulatory decisions, and shaping industry best practices. Challenges include keeping standards updated with technological advancements and ensuring consistent enforcement across various jurisdictions. Only through unwavering commitment to robust and consistently applied safety standards can a fireplace and chimney authority fulfill its mandate of protecting property and safeguarding human life.
5. Code Enforcement
Code enforcement represents the active and systematic application of established regulations pertaining to fireplace and chimney construction, installation, and maintenance. The fireplace and chimney authority relies heavily on code enforcement to ensure compliance with safety standards designed to protect lives and property. A direct cause-and-effect relationship exists: lax code enforcement results in increased risks of fires, carbon monoxide leaks, and structural failures. Code enforcement serves as a vital component, converting regulatory frameworks into tangible, on-the-ground practices.
Real-life examples of effective code enforcement include mandatory inspections during the construction of new homes, where building inspectors verify compliance with chimney height requirements and proper clearances from combustible materials. Similarly, enforcement actions against homeowners who fail to address identified chimney defects, such as cracked liners or excessive creosote buildup, exemplify the authority’s commitment to safety. The authority might issue violation notices, impose fines, or even require system shutdowns until compliance is achieved. Furthermore, code enforcement extends to ensuring that chimney sweeps and other fireplace service professionals adhere to licensing and certification requirements, guaranteeing a minimum standard of competency within the industry. Local governments might require that contractors provide proof of licensing and permits before starting work, furthering code compliance.
In summary, code enforcement is indispensable to the efficacy of the fireplace and chimney authority. It translates theoretical standards into practical safeguards. Without diligent and consistent enforcement, regulations become mere suggestions, and the risks associated with improperly constructed or maintained fireplace and chimney systems escalate. The challenge lies in securing adequate funding for enforcement agencies, ensuring consistent application of codes across different jurisdictions, and effectively educating homeowners about their responsibilities. Effective code enforcement mechanisms is fundamental to protecting public safety.
6. Education
Education serves as a cornerstone in the mission of a fireplace and chimney authority, facilitating the dissemination of knowledge to both professionals in the industry and the general public. This function directly supports safety, regulatory compliance, and the overall effectiveness of the authority’s mandate.
- Homeowner Safety Awareness Programs
These programs educate homeowners on safe operating procedures, potential hazards, and preventative maintenance practices. For example, a brochure detailing the dangers of creosote buildup and the importance of annual chimney inspections empowers homeowners to proactively mitigate fire risks. The implications are reduced incidents of chimney fires and carbon monoxide poisoning, contributing to safer residential environments.
- Professional Training and Certification Courses
These courses provide comprehensive instruction to chimney sweeps, installers, and inspectors, ensuring they possess the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their duties safely and effectively. Practical training on proper flue liner installation techniques, for example, minimizes the risk of substandard work that could compromise the structural integrity of the system. The resulting effect is a more competent workforce and enhanced industry standards.
- Code and Regulation Dissemination
The authority actively informs stakeholders about updates to building codes and safety regulations through workshops, online resources, and printed materials. A seminar explaining new requirements for fireplace clearances to combustible materials, for instance, ensures that contractors and builders comply with the latest standards. This proactive approach promotes adherence to regulatory mandates and reduces the likelihood of code violations.
- Public Awareness Campaigns
These campaigns utilize various media channels to raise public awareness about fireplace and chimney safety issues. A public service announcement highlighting the importance of carbon monoxide detectors, for example, encourages homeowners to take proactive steps to protect themselves and their families. Such initiatives can lead to increased adoption of safety measures and a reduction in carbon monoxide-related incidents.
Through these multifaceted educational endeavors, the fireplace and chimney authority strengthens its capacity to prevent accidents, promote best practices, and foster a culture of safety. The investment in education directly translates to a more informed and responsible community, contributing to the long-term effectiveness of the authority’s overall mission. A well-educated public and professional community is the greatest asset the organization can have.
7. Compliance
Strict adherence to the regulations and guidelines set forth is critical for the safe and efficient operation of fireplace and chimney systems. It represents the practical manifestation of the authority’s efforts to mitigate risks and ensure public safety.
- Adherence to Building Codes
Compliance mandates that all new fireplace and chimney installations conform to local and national building codes. These codes specify construction materials, clearances to combustible materials, chimney height requirements, and other critical parameters. For instance, adhering to minimum chimney height requirements ensures proper drafting, minimizing the risk of carbon monoxide entering the dwelling. Failure to comply with these codes can lead to structural instability, increased fire risks, and legal liabilities.
- Routine Inspection and Maintenance
Compliance requires homeowners to undergo regular inspections and maintenance performed by certified professionals. These inspections identify potential hazards, such as creosote buildup, damaged flue liners, or structural defects. Addressing these issues promptly prevents escalation into serious problems, such as chimney fires or carbon monoxide leaks. Neglecting routine inspections constitutes a breach of compliance and increases the likelihood of incidents.
- Corrective Actions and Repairs
Following an inspection, compliance necessitates prompt corrective actions to address any identified deficiencies. This may involve repairing or replacing damaged components, such as flue liners, chimney caps, or dampers. Failure to undertake necessary repairs compromises the safety and efficiency of the system and represents a direct violation of compliance requirements. The authority may issue violation notices and impose penalties for non-compliance.
- Proper Fuel Usage
Compliance dictates the use of appropriate fuels in fireplaces and wood-burning stoves. This includes using seasoned firewood, approved manufactured logs, or other fuels specified by the appliance manufacturer. Burning unseasoned wood or prohibited materials increases creosote buildup, elevates the risk of chimney fires, and violates compliance standards. Public information campaigns often emphasize the importance of selecting appropriate fuels.
These facets of compliance are essential for maintaining safe and efficient fireplace and chimney systems. The regulatory body actively promotes and enforces these measures to protect property and lives. Lack of adherence can result in punitive action, property damage, and physical injury.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding fireplace and chimney systems. The information presented aims to clarify best practices and regulatory requirements, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
Question 1: How often should a fireplace and chimney be inspected?
A professional inspection is recommended annually. More frequent inspections may be necessary based on usage and fuel type. Early detection of potential hazards is crucial for preventing costly repairs and ensuring occupant safety.
Question 2: What are the signs of a chimney fire?
Indications include loud cracking or popping noises, a roaring sound, dense smoke, and an intense, hot odor. If these signs are present, immediate evacuation and notification of emergency services are paramount.
Question 3: What is creosote, and why is it dangerous?
Creosote is a flammable byproduct of combustion that accumulates in the chimney. Its presence significantly increases the risk of chimney fires. Regular cleaning is essential to mitigate this hazard.
Question 4: Can I burn any type of wood in my fireplace?
No. Only seasoned firewood or approved manufactured logs should be used. Burning unseasoned wood produces excessive smoke and creosote, contributing to air pollution and increasing the risk of chimney fires.
Question 5: What are the code requirements for chimney height?
Chimney height requirements vary by jurisdiction but generally necessitate a minimum height above the roofline and nearby obstructions. Adherence to these requirements ensures proper drafting and prevents backdrafts of combustion gases.
Question 6: Who is qualified to perform fireplace and chimney inspections and repairs?
Only certified professionals with appropriate training and credentials should perform these tasks. Verification of credentials is recommended prior to engaging service providers.
Proactive management and knowledge of operation is critical for safety. Maintaining a functional fireplace and chimney reduces risks to inhabitants.
The subsequent section will focus on resources for further information.
Conclusion
This exploration has outlined the critical functions and responsibilities inherent in the operation of a fireplace and chimney authority. The importance of robust regulations, stringent inspections, comprehensive certification programs, unwavering adherence to safety standards, consistent code enforcement, proactive education initiatives, and rigorous compliance monitoring have all been thoroughly examined. These elements, when effectively integrated, form the foundation for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of residential heating systems.
The continued vigilance in upholding and strengthening these principles is paramount. Ongoing efforts to adapt to evolving technologies, refine regulatory frameworks, and promote public awareness are essential for safeguarding both property and human life. The commitment to excellence in fireplace and chimney management remains a shared responsibility, contributing to a safer and more secure environment for all.