A structure positioned at the termination of a flue, usually constructed of metal, ceramic, or stone, serving to prevent precipitation and debris from entering the chimney. This component often incorporates a mesh or screen to deter animals from nesting inside and to reduce the risk of downdrafts. An example includes a stainless steel model designed to fit a standard flue opening.
This protective measure offers several advantages, including the prevention of water damage within the structure, improved draft performance, and a reduction in fire hazards caused by accumulated debris. Historically, simpler forms existed to primarily deflect rain, but modern versions provide enhanced protection and longevity to the chimney system.
The following sections will elaborate on material selection, installation procedures, maintenance guidelines, and factors influencing the overall performance and lifespan of these essential components of a building’s ventilation system.
Essential Considerations for Chimney Termination Protection
Optimizing the effectiveness of a chimney system requires careful attention to the selection, installation, and maintenance of its protective terminal. Implementing the following guidelines can significantly improve performance and extend its lifespan.
Tip 1: Material Selection: Prioritize materials resistant to corrosion and weathering. Stainless steel and copper are often preferred for their durability in harsh environments, while ceramic options provide aesthetic appeal and moderate resistance. Evaluate material compatibility with the flue lining to prevent galvanic corrosion.
Tip 2: Size and Fit: Ensure the selected unit is appropriately sized for the chimney flue. An undersized component restricts airflow, leading to draft issues, while an oversized one may not adequately prevent water intrusion. Consult manufacturer specifications for proper sizing guidelines based on flue dimensions.
Tip 3: Secure Installation: Adhere strictly to manufacturer installation instructions. Improper installation compromises its protective function and can create safety hazards. Use appropriate fasteners and sealant to ensure a secure and weather-tight seal.
Tip 4: Regular Inspection: Conduct routine visual inspections, ideally twice annually, to identify signs of damage or deterioration. Look for rust, cracks, or loose components. Address any issues promptly to prevent further degradation.
Tip 5: Debris Removal: Periodically remove accumulated debris, such as leaves, twigs, or nests, from the mesh or screen. Blockages restrict airflow and increase the risk of chimney fires.
Tip 6: Professional Assessment: Engage a qualified chimney sweep or technician for a comprehensive assessment every 1-3 years. Professionals can identify potential problems not readily visible and recommend necessary repairs or replacements.
Tip 7: Consider Draft Enhancement: In cases of persistent draft issues, consider models designed with features to enhance draft performance, such as wind-directional cowls. These mitigate the effects of negative pressure and improve combustion efficiency.
By implementing these recommendations, homeowners and building managers can ensure that the termination point of their flue provides optimal protection against the elements and contributes to the safe and efficient operation of the entire chimney system.
The subsequent sections will delve into troubleshooting common issues, exploring advanced designs, and providing guidance on selecting the most suitable model for specific architectural styles and regional climates.
1. Material Durability
Material durability is a paramount consideration in the context of a roof chimney cap. Exposure to diverse weather conditions necessitates robust materials capable of withstanding degradation over extended periods. Selection of inappropriate materials can lead to premature failure, compromising the integrity of the chimney system and potentially leading to costly repairs.
- Corrosion Resistance
Atmospheric exposure subjects the chimney termination to corrosive elements, including rain, snow, and pollutants. Materials lacking inherent corrosion resistance, such as untreated steel, will degrade rapidly, leading to structural weakening and eventual failure. Stainless steel, copper, and certain ceramic compositions offer superior resistance to corrosion, extending the lifespan of the component and minimizing maintenance requirements. For instance, a 316 stainless steel cap in a coastal environment exhibits significantly greater longevity than a galvanized steel alternative.
- Thermal Stress Tolerance
Chimneys experience significant temperature fluctuations due to combustion processes. Materials employed in construction must withstand repeated expansion and contraction cycles without cracking or warping. Materials like clay tile can crack over time when exposed to extreme thermal differences, resulting in reduced protection and possible structural failure of the chimney. High-quality metals or specialized ceramic compositions designed for high-temperature applications offer superior thermal stress tolerance.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Degradation Resistance
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation can degrade certain materials, particularly polymers and some painted surfaces. This degradation can lead to embrittlement, discoloration, and eventual structural weakening. The effectiveness of a chimney protector could be shortened by materials that break down under constant solar radiation. Using UV-resistant coatings or selecting materials inherently resistant to UV degradation, such as certain types of stainless steel, mitigates this risk.
- Mechanical Strength
The physical integrity is vital to withstand external forces, such as wind, snow loads, and impact from debris. Materials with insufficient mechanical strength are susceptible to damage, compromising their protective function. A ceramic unit weakened by impacts from falling branches will require repair or replacement. Selecting materials with high tensile and compressive strength ensures that the component can withstand external forces and maintain its structural integrity over time.
The long-term performance and protective capabilities of a roof chimney cap are inextricably linked to the material’s durability. Selection of materials exhibiting superior corrosion resistance, thermal stress tolerance, UV degradation resistance, and mechanical strength is essential for ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of the chimney system. Ignoring these factors can result in premature failure, necessitating costly repairs and potentially compromising the safety of the structure.
2. Correct Sizing
Correct sizing is critical to the functionality of a chimney termination protection device. A mismatch between the component’s dimensions and the flue opening directly affects draft efficiency, weather protection, and overall system performance, potentially leading to adverse consequences.
- Draft Efficiency
An improperly sized component can impede airflow within the chimney. An undersized unit restricts the flue’s cross-sectional area, increasing resistance to flow and causing downdrafts. Conversely, an oversized unit may not adequately seal the flue, allowing cold air infiltration and disrupting the draft. Optimal draft efficiency requires precise matching of the component’s internal dimensions to the flue opening.
- Weather Protection
The primary function of a termination device is to prevent precipitation from entering the chimney. An ill-fitting unit, whether too large or too small, compromises this protective function. An oversized unit may allow rainwater to bypass the edges and enter the flue. An undersized unit may not adequately cover the flue opening, exposing it to direct precipitation. Effective weather protection demands precise adherence to sizing specifications.
- Animal Deterrence
Many chimney protectors incorporate mesh or screening to prevent animals from entering the flue. Gaps or openings created by improper sizing render this feature ineffective. Squirrels, birds, and other small animals can easily bypass a poorly fitted unit, nesting inside the chimney and creating blockages. Reliable animal deterrence necessitates a secure and precisely fitted termination.
- Structural Integrity
The size and weight distribution of the termination point must align with the chimney’s structural capacity. An oversized and excessively heavy unit can place undue stress on the chimney crown, leading to cracking and eventual structural failure. Conversely, an undersized and lightweight unit may be susceptible to wind damage. Maintaining structural integrity demands careful consideration of size and weight in relation to the chimney’s construction.
In summary, appropriate dimensioning is a non-negotiable requirement for a functional and effective chimney termination protection device. Precise matching of the component to the flue opening ensures optimal draft, reliable weather protection, effective animal deterrence, and the long-term structural integrity of the chimney system. Ignoring sizing guidelines can lead to a cascade of problems, compromising safety and necessitating costly repairs.
3. Secure Attachment
Secure attachment represents a foundational aspect of a protective terminal and its role in ensuring chimney system integrity and safety. It is not merely a matter of preventing dislodgement but a comprehensive strategy to maintain long-term functionality and prevent consequential damage.
- Wind Resistance
A primary function of secure attachment is to resist wind forces. High winds can exert significant pressure on the component, potentially dislodging it if not properly secured. Dislodgement exposes the flue to the elements, negating the protective benefits of the device. Secure attachment methods, such as robust fasteners and appropriate sealant, are crucial for mitigating wind-related risks.
- Vibration Mitigation
Chimney systems are subjected to vibrations caused by wind and internal combustion processes. These vibrations can gradually loosen fasteners and compromise the stability of the termination point. Secure attachment techniques that incorporate vibration-dampening materials or locking mechanisms help to maintain a tight and reliable connection over time. Example of this are lock nuts and specialized adhesives designed to withstand constant vibration.
- Thermal Expansion Accommodation
Temperature fluctuations cause expansion and contraction of chimney materials. Secure attachment methods must accommodate these movements to prevent stress-induced failures. Flexible sealants and appropriately sized fasteners allow for thermal expansion and contraction without compromising the integrity of the connection.
- Corrosion Prevention
Incompatible materials between the termination component and the chimney structure can lead to galvanic corrosion, weakening the attachment points. Secure attachment strategies that incorporate corrosion-resistant fasteners and isolation techniques, such as non-conductive washers, are essential for preventing this type of degradation.
The long-term effectiveness of a chimney’s terminal point hinges on the robustness of its attachment. By addressing wind resistance, vibration mitigation, thermal expansion, and corrosion prevention through secure attachment strategies, the service life and protective capabilities of the overall chimney system are significantly enhanced, contributing to a safer and more efficient building.
4. Animal Exclusion
Animal exclusion, in the context of a protective terminal device, refers to the prevention of animals entering the flue. This function is integral to maintaining the chimney’s operational efficiency and preventing potential safety hazards.
- Nesting Prevention
Birds, squirrels, and other small animals frequently seek shelter inside chimneys, particularly during nesting season. Accumulated nests obstruct airflow, leading to draft problems and increasing the risk of chimney fires. A properly designed exclusion system, typically involving a mesh screen, effectively prevents nesting activities and maintains unobstructed airflow. For example, a 1/2-inch mesh screen constructed of stainless steel provides a durable barrier against most common nesting animals.
- Disease Transmission Mitigation
Animal droppings and carcasses within a chimney can introduce harmful bacteria and parasites into the living space. Airborne pathogens can enter the building through the ventilation system, posing a health risk to occupants. An effective exclusion system minimizes the presence of animals within the chimney, thereby reducing the potential for disease transmission. Solid construction with no gaps is imperative.
- Structural Damage Reduction
Animals can cause significant damage to chimney liners and other internal components. Nesting materials can corrode flue liners, leading to structural weakening. Animals may also gnaw on wires and other materials, creating fire hazards. An exclusion system prevents animals from accessing and damaging the chimney’s internal structure, extending its lifespan and reducing the need for repairs.
- Draft Impairment Prevention
Animal nests and debris can significantly impair chimney draft, leading to backdrafting of harmful combustion gases, such as carbon monoxide, into the living space. This poses a serious health risk to occupants. By preventing animal entry and nest construction, the effectiveness and integrity of the ventilation system is preserved.
The integration of robust animal exclusion features into the design and installation of a terminal point is essential for safeguarding chimney functionality, preventing health risks, and mitigating structural damage. The long-term benefits of animal exclusion significantly outweigh the initial investment in a properly designed and installed product.
5. Water Diversion
Effective management of precipitation is a critical function of a roof chimney cap. Water intrusion into a chimney system can lead to significant structural damage, reduced efficiency, and potential safety hazards. The design and implementation of effective water diversion mechanisms are therefore paramount.
- Crown Protection
The chimney crown, typically constructed of concrete or mortar, is particularly vulnerable to water damage. Cracks and deterioration allow water to penetrate the chimney structure, leading to freeze-thaw cycles and accelerated degradation. The overhanging design of many caps provides a physical barrier, deflecting rainwater away from the crown and minimizing water absorption. An example includes a cap with a drip edge extending beyond the crown’s perimeter.
- Flue Liner Preservation
Water entry can damage flue liners, especially those made of clay or metal. Moisture accelerates corrosion in metal liners and can weaken or crack clay liners. A cap with a properly sized and angled top prevents direct rainfall into the flue, thereby preserving the liner’s integrity. Consider a cap with a conical top to efficiently shed water.
- Internal Component Protection
Moisture within the chimney can damage internal components such as dampers and smoke shelves. Rusting dampers become difficult to operate, and water accumulation on the smoke shelf can lead to unpleasant odors and mold growth. The design of a protective terminal should minimize water entry to safeguard these components. As an example, a well-sealed cap can mitigate these issues.
- Freeze-Thaw Mitigation
Water that penetrates the chimney structure can freeze and expand during cold weather, exacerbating cracks and causing further damage. The protective effect of a cap in diverting water reduces the amount of moisture available for freezing, thereby mitigating the effects of freeze-thaw cycles. A durable and waterproof cap is therefore essential.
The effectiveness of water diversion mechanisms in a roof chimney cap directly impacts the lifespan and performance of the entire chimney system. Prioritizing designs that incorporate robust water diversion features is crucial for preventing water-related damage and ensuring long-term functionality.
6. Draft Optimization
Draft optimization, concerning a roof chimney cap, is essential for ensuring efficient and safe venting of combustion gases from a fireplace or heating appliance. Proper draft promotes complete combustion, reduces the risk of carbon monoxide backdrafting, and minimizes creosote buildup within the chimney system.
- Cap Design and Airflow
The design of the chimney cap directly impacts airflow through the flue. Caps that restrict airflow can impede draft, leading to incomplete combustion and potential hazards. Conversely, well-designed caps facilitate smooth airflow, enhancing draft efficiency. For example, a cap with a large opening and minimal internal obstructions promotes better draft compared to a tightly screened cap.
- Wind Effects and Mitigation
Wind conditions can significantly influence chimney draft. Strong winds blowing across the chimney top can create negative pressure, causing downdrafts. Specialized caps, such as those with directional cowls, are designed to mitigate the effects of wind and maintain consistent draft. These cowls rotate to shield the flue opening from the wind, preventing downdrafts and optimizing draft performance.
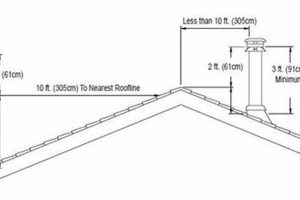
- Height and Location Considerations
The height of the chimney relative to the surrounding roofline and nearby obstructions affects draft. Chimneys that are too short or located in areas with turbulent airflow may experience poor draft. A properly sized cap can help to extend the effective height of the chimney, improving draft in challenging locations. Local building codes often specify minimum chimney height requirements to ensure adequate draft.
- Flue Size Compatibility
The diameter of the flue and the size of the chimney cap must be appropriately matched to ensure optimal draft. An undersized cap can restrict airflow, while an oversized cap may not provide adequate protection from the elements. Proper sizing, determined by calculations based on appliance specifications and chimney dimensions, is crucial for maximizing draft efficiency.
In summary, draft optimization is an essential aspect of chimney cap selection and installation. By considering the design of the cap, wind effects, height and location factors, and flue size compatibility, individuals can ensure efficient and safe chimney operation. Neglecting draft optimization can lead to reduced heating efficiency, increased risk of carbon monoxide poisoning, and potential structural damage to the chimney system.
7. Debris Prevention
Debris prevention, as a core function, is intrinsically linked to the operational efficacy of a roof chimney cap. The accumulation of foreign materials within a chimney flue poses a multifaceted threat, ranging from impaired ventilation to increased fire hazards. The chimney cap, when correctly designed and implemented, serves as the primary barrier against such intrusions, mitigating the associated risks. For instance, a chimney lacking an effective cap is susceptible to the ingress of leaves, twigs, and animal nests, each presenting a distinct impediment to proper chimney function. A consequence of this accumulation is reduced draft, resulting in inefficient combustion and the potential for dangerous carbon monoxide backdraft into the dwelling. Therefore, the debris prevention functionality of the terminal point is not merely an ancillary benefit but a critical component of overall system safety and performance.
Further elaborating on this connection, the physical design of the chimney cap directly influences its ability to impede debris accumulation. Caps incorporating fine mesh screens effectively block smaller particles, such as leaves and insects, while those with larger openings are more prone to blockage and subsequent draft impairment. Real-world scenarios illustrate the practical significance of this design consideration. Consider a residential chimney located in a heavily wooded area; the absence of a fine-mesh cap would likely result in frequent blockages from falling leaves, necessitating regular cleaning and maintenance to ensure safe operation. Conversely, a cap featuring a well-designed screen would significantly reduce the frequency of such interventions, enhancing the long-term reliability of the system. The use of durable, non-corrosive materials, such as stainless steel, in the construction of the debris prevention components ensures prolonged functionality, even in harsh environmental conditions.
In summary, debris prevention constitutes a fundamental aspect of a roof chimney cap’s role in maintaining a safe and efficient chimney system. By effectively preventing the accumulation of foreign materials within the flue, the cap contributes to optimal draft, reduced fire risk, and the preservation of air quality within the dwelling. The selection of a cap with appropriate mesh size and durable construction is essential for ensuring long-term performance and minimizing the need for costly maintenance. The challenge lies in balancing debris prevention with the need for adequate airflow, a compromise that is often addressed through careful design and material selection. Understanding the critical link between debris prevention and the overall functionality underscores the importance of the protective terminal as an integral element of a well-maintained chimney.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries concerning protective terminal devices, their function, selection, maintenance, and impact on overall chimney system performance.
Question 1: What constitutes a chimney’s “cap” and why is it a crucial component?
The device positioned atop a chimney flue, designed to prevent the ingress of precipitation, debris, and animals. Its crucial nature stems from the protection it provides against water damage, draft impediments, and potential fire hazards.
Question 2: What materials are suitable for a construction, and what factors influence material choice?
Common materials include stainless steel, copper, and ceramic. Material choice is influenced by factors such as corrosion resistance, thermal stress tolerance, aesthetic considerations, and budget constraints.
Question 3: How does correct sizing impact chimney system performance?
Correct sizing ensures optimal draft efficiency, prevents water intrusion, and effectively deters animal entry. An improperly sized model can impede airflow, compromise weather protection, and negate animal exclusion features.
Question 4: What maintenance procedures are essential for ensuring long-term device functionality?
Essential maintenance procedures include routine visual inspections, debris removal, and periodic professional assessments. Addressing issues promptly prevents further degradation and ensures continued protection.
Question 5: Can a chimney system influence draft performance, and if so, how?
Certain designs incorporate features to enhance draft performance, such as wind-directional cowls. These mitigate the effects of negative pressure and improve combustion efficiency. The height of the chimney from the roof is also relevant.
Question 6: What are the potential consequences of neglecting maintenance or allowing damage to persist?
Neglecting maintenance or allowing damage to persist can lead to water damage within the structure, impaired draft performance, increased risk of chimney fires, and potential structural failure of the chimney.
Proper selection, installation, and maintenance are vital for maximizing the effectiveness and lifespan of this essential component. Addressing these considerations proactively ensures a safe and efficient chimney system.
The subsequent section will provide guidance on troubleshooting common issues, exploring advanced designs, and selecting the model best suited for specific architectural styles and regional climates.
Conclusion
This exploration has underscored the critical role a roof chimney cap plays in ensuring chimney system integrity, safety, and efficiency. Key points include the importance of material selection, correct sizing, secure attachment, animal exclusion, water diversion, draft optimization, and debris prevention. The absence of, or failure of, any one of these elements can compromise the functionality of the entire venting system.
Continued vigilance in maintenance and informed decision-making regarding replacement are imperative. Recognizing the significance of the roof chimney cap is not merely about preserving a structure but safeguarding its inhabitants from the inherent dangers associated with improperly vented combustion byproducts. Ignoring this fundamental aspect can have severe, and potentially fatal, consequences. Therefore, regular inspection and prompt remediation are not optional, but essential, responsibilities.