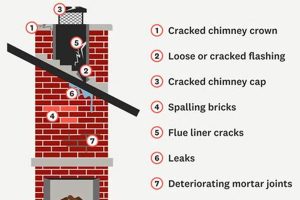
A visual representation of a protective covering for a flue’s opening serves to illustrate its design and functionality. These images commonly depict the cap’s construction, including the mesh, lid, and attachment mechanism. For example, the photographs often showcase the cap’s placement atop a chimney, highlighting its relationship to the overall structure.
The presence of these visuals is important for demonstrating the device’s protective qualities against rain, snow, debris, and animals. It clarifies how the component prevents downdrafts and enhances chimney draft. Historically, simpler versions existed, but modern designs emphasize durability and efficient ventilation, which imagery effectively conveys.
Understanding the components through depictions allows for informed decisions regarding selection, installation, and maintenance. Further exploration will detail the types available, the materials used, and factors influencing the most suitable choice for a specific application.
Chimney Cap Visual Analysis
Analyzing visual representations of flue coverings provides valuable insights before procurement or installation. Thorough observation is crucial for ensuring appropriate selection and functionality.
Tip 1: Evaluate Mesh Density: The visual should clearly show the mesh screen’s gauge. Finer mesh offers better protection against small animals but may restrict airflow. Assess the balance between protection and ventilation based on local fauna and climate.
Tip 2: Examine Lid Design: Notice the lid’s shape and overhang. A substantial overhang deflects more rain and snow. Observe the slope; steeper slopes facilitate quicker drainage, reducing potential for ice buildup.
Tip 3: Observe Attachment Method: The imagery should detail the cap’s attachment mechanism. Clamp-on models require secure clamping. Mortar-mounted options demand a sound mortar bed. Verify compatibility with the flue’s construction.
Tip 4: Assess Material Integrity: Distinguish between stainless steel, copper, or galvanized steel. Stainless steel provides the highest corrosion resistance. Copper offers aesthetic appeal. Galvanized steel represents a cost-effective alternative, but visual inspection should reveal the coating’s completeness.
Tip 5: Analyze Height Above Flue: Note the height of the cap above the flue opening. Insufficient height can impede draft. Consult local building codes for minimum height requirements and ensure the image suggests compliance.
Tip 6: Check for Spark Arrestor Compliance: In areas prone to wildfires, verify that the model in the visual includes a spark arrestor screen. Local regulations may mandate this feature. The photograph should clearly depict the presence and condition of the spark arrestor.
Visual assessment ensures optimal protection and functionality of the flue system. These observations should be integrated with professional advice before implementation.
Following these visual analysis techniques assists in making an informed choice. The subsequent sections will explore the long-term maintenance and performance characteristics of various models.
1. Material Durability
The depiction of a flue termination component’s material directly correlates to its perceived and actual durability. Visuals that clearly present the material’s composition, surface finish, and joint integrity allow informed judgment regarding its potential lifespan. For instance, a photograph showcasing a stainless-steel cap with smooth, consistent welds suggests superior resistance to corrosion compared to an image of a galvanized steel alternative displaying rust spots or uneven coating.
Material durability is a critical performance factor; the selected material affects long-term cost and system functionality. A compromised cap allows water infiltration, accelerating chimney degradation and creating fire hazards. Examples include the selection of copper caps in coastal environments due to their high salt-spray resistance. High-quality images detailing material thickness and construction methods reinforce confidence in its robust properties.
Analyzing visuals for material integrity is paramount. Identifying signs of degradation, assessing weld quality, and recognizing material types contribute to a more accurate expectation of longevity. This process minimizes premature replacements and ensures continued chimney system integrity, safeguarding against potential structural damage and safety hazards.
2. Mesh Size
The aperture dimensions within a flue termination component, commonly designated as “mesh size,” significantly impact its protective and performance characteristics. Visual representations of the structure must accurately depict mesh characteristics to allow for informed evaluation.
- Debris Exclusion Efficiency
Finer mesh patterns, with smaller apertures, excel at preventing the entry of particulate matter such as leaves, twigs, and nesting materials. A higher density mesh, as discernable in a close-up image, demonstrably reduces the risk of flue obstruction and subsequent draft impedance. However, overly fine mesh may restrict airflow, impacting combustion efficiency.
- Animal Intrusion Prevention
The visual representation is crucial in assessing the capability to deter animal entry. Large openings can allow birds, squirrels, or other animals to nest within the flue, creating blockages and potentially hazardous conditions. Images should clearly show the mesh dimensions relative to potential animal sizes prevalent in the installation environment.
- Impact on Draft Performance
Mesh size directly influences chimney draft. Restrictive mesh, visible as densely packed in the image, can impede airflow, leading to backdrafting or inefficient combustion. Images should allow for visual estimation of the mesh’s open area to gauge its potential impact on draft. Manufacturers often provide specifications regarding airflow reduction related to specific mesh configurations.
- Material Gauge and Durability
Photographs of the protective structure should also clarify the gauge, or thickness, of the mesh material. Thinner gauge materials, while potentially offering less airflow restriction, are more susceptible to damage from impacts, corrosion, or animal activity. Images must provide sufficient detail to assess material robustness and resistance to environmental factors.
Therefore, depictions of these components should accurately represent mesh size, density, and material gauge. Evaluating these characteristics through clear visual media allows for informed decisions regarding the selection of an appropriate flue termination component, balancing debris exclusion, animal deterrent, and optimal draft performance.
3. Lid Overhang
The extent to which a covering’s upper portion projects beyond its base, commonly termed “lid overhang,” is a critical feature often depicted in a visual of a flue termination component. Its design significantly impacts the component’s effectiveness in protecting the chimney from environmental factors.
- Water Diversion Efficiency
The primary function of a lid overhang is to divert precipitation away from the flue opening. A larger overhang, clearly visible in the photographs, provides more extensive protection against rain and snow, reducing the amount of moisture entering the chimney. Visuals showcasing the overhang’s dimensions relative to the flue opening are crucial in assessing its water diversion capabilities.
- Snow Load Management
In regions with heavy snowfall, the lid overhang plays a vital role in preventing snow accumulation within the flue. A well-designed overhang sheds snow, minimizing the risk of blockage and potential structural damage from the weight of accumulated snow. Visuals should indicate the slope of the overhang, influencing snow shedding efficiency.
- Wind Resistance Considerations
An excessively large overhang can create a greater surface area susceptible to wind forces. High winds may exert undue stress on the cap’s mounting structure, potentially leading to damage or dislodgement. Therefore, the illustration must balance protection with wind resistance. Visual analysis should consider the overhang’s shape and the overall structural integrity of the cap.
- Aesthetic Integration
While functionality remains paramount, the lid overhang also contributes to the overall aesthetic of the chimney. Its design can complement the architectural style of the building. Visuals highlighting different overhang styles (e.g., conical, curved, flat) allow for selection based on personal preference and architectural compatibility. These aesthetic considerations, while secondary, play a role in homeowner satisfaction.
In conclusion, the lid overhang, as depicted in a visual, directly influences the effectiveness of a flue termination component. Balancing water diversion, snow load management, wind resistance, and aesthetic integration is crucial. Clear and detailed photographs are essential for informed decision-making regarding its selection and implementation.
4. Attachment Style
The method by which a flue termination device is affixed to a chimney, designated as “attachment style,” is a critical element visually represented in images of these components. The efficacy and longevity of the device are directly contingent upon a compatible and properly executed attachment. Visual depictions should clearly illustrate the attachment mechanism, facilitating accurate assessment of its suitability for a given chimney configuration.
Variations in attachment styles include clamp-on, set-screw, leg-mount, and masonry-embedded designs. Clamp-on models are suited for flue pipes with adequate external surface area for secure grip, as visual detail should confirm. Set-screw types require a compatible flue collar for reliable fixation. Leg-mount options, depicted with supporting legs extending onto the chimney crown, offer stability but necessitate a sound crown surface. Masonry-embedded configurations involve integrating the device directly into the chimney structure, requiring specialized installation knowledge. For example, a poorly secured cap can detach during high winds, negating its protective function and potentially causing property damage. Clear images detail the specific components involved and their integration with the existing chimney structure.
Understanding the correlation between a visual depiction of the attachment style and its practical application is paramount. Images revealing corrosion or structural weakness in the attachment mechanism highlight potential failure points. Selection of an appropriate attachment style, informed by visual inspection, ensures the flue termination component remains securely in place, providing continued protection against environmental elements and maintaining chimney system integrity. Furthermore, verifying the material compatibility between the chimney and attachment component is a critical evaluation point.
5. Height Above Flue
Visual representations of flue termination components, particularly illustrations displaying a covering, inherently depict the “Height Above Flue”. This dimension dictates the efficiency of exhaust venting and the component’s capacity to prevent downdrafts. Inadequate height, as illustrated in the image, can lead to compromised draft, potentially causing combustion byproducts to enter the dwelling. Conversely, excessive height may increase wind resistance, destabilizing the component. Accurate visual assessment of this dimension is crucial for selecting an appropriately sized covering. A common example is when a photograph shows a very low cap in a windy area; there is a high probability of backdraft problems.
The image facilitates verification of compliance with local building codes mandating minimum height requirements for flue termination devices. These regulations are designed to ensure adequate ventilation and prevent carbon monoxide buildup. Further, the visual should allow assessment of the relationship between this height and the surrounding structures. Nearby trees or buildings can affect airflow patterns, requiring an adjusted height to maintain optimal venting. The visual, therefore, becomes a tool for pre-installation planning and code compliance verification, reducing the risk of hazardous conditions.
Understanding the “Height Above Flue,” as conveyed through a visual depiction, is essential for safe and efficient chimney operation. Incorrect dimensioning, readily identifiable in an image, can negate the protective benefits of the component. Careful visual analysis mitigates the risks associated with improper installation, contributing to overall building safety and indoor air quality, thereby emphasizing the picture element in this context.
6. Spark Arrestor
A flue termination component incorporating a spark arrestor is designed to prevent the emission of flammable embers from the chimney. Visual representations of these components are essential for verifying the presence and proper configuration of this critical safety feature. The presence of a functional spark arrestor significantly reduces the risk of initiating wildfires, particularly in regions with dry vegetation or high wind conditions. These images must provide sufficient detail to assess the mesh size and overall condition of the spark arrestor screen. For example, a clear depiction of a damaged or corroded screen indicates a compromised safety device that requires replacement to maintain its effectiveness.
The relationship between a depiction of a flue termination component and its integral spark arrestor is crucial for code compliance. Many jurisdictions mandate the use of spark arrestors on chimneys servicing wood-burning appliances. Visual documentation aids in confirming adherence to these regulations during inspections. Images demonstrating proper installation, including secure attachment and appropriate mesh size, contribute to verifying code compliance and minimizing legal liabilities. Forested communities, for instance, often enforce stringent requirements regarding spark arrestors due to the elevated risk of fire propagation. Images of conforming caps are used to document compliance during home sales or rentals.
In summary, visual analysis of a flue termination device incorporating a spark arrestor provides critical information concerning fire safety and regulatory compliance. Evaluating mesh condition, attachment security, and overall configuration through photographs ensures the component is functioning as intended. Addressing deficiencies identified through visual inspection minimizes fire hazards and promotes responsible operation of wood-burning appliances, emphasizing the necessity of this information from a picture to make a well-informed decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries related to the interpretation and utility of visual representations of flue termination components, specifically those depicting protective coverings. These questions aim to clarify key aspects of selecting and maintaining these components based on visual analysis.
Question 1: Why is the visual inspection of a flue termination device’s structure essential?
Visual inspection allows for assessment of material condition, structural integrity, and overall design, informing decisions about compatibility, durability, and code compliance.
Question 2: How can the visual analysis of mesh size inform purchasing decisions?
Visuals depicting mesh size determine the balance between debris exclusion, animal deterrence, and airflow restriction, guiding the selection of an appropriate mesh configuration for specific environmental conditions.
Question 3: What design features are crucial to discern when inspecting the lid overhang?
Key design aspects to observe include the overhang’s dimensions relative to the flue opening, the slope for snow shedding, and overall structural integrity to withstand wind forces. These factors impact protection against weather elements.
Question 4: What are the key considerations when observing different attachment styles in a photograph?
Compatibility with the existing chimney structure, the security of the attachment mechanism, and material compatibility between the chimney and the attachment component are vital. Identifying these elements ensures proper installation and lasting performance.
Question 5: Why is the height of the flue termination component above the flue important?
The height above the flue impacts draft efficiency and the prevention of downdrafts. Proper height, as visually verified, ensures compliance with local building codes and optimizes chimney venting.
Question 6: What should be considered when visually examining a spark arrestor?
Verify the mesh size, its attachment security, and overall condition. Assessing these factors ensures the spark arrestor functions effectively, mitigating fire hazards and adhering to relevant regulations.
Visual evaluation provides valuable insights into the characteristics of flue termination devices. Properly analyzing the image beforehand can ensure informed decision-making, improving system safety and performance.
The following sections will explore detailed maintenance strategies and troubleshooting techniques relevant to such components.
Conclusion
A comprehensive visual analysis is essential for determining the efficacy of any flue termination component, and the picture of a chimney cap provides the initial data point. This detailed assessment allows for an informed decision regarding material, mesh size, lid overhang, attachment style, height above flue, and the inclusion of a spark arrestor. Understanding these visual cues translates to a safer and more efficient chimney system.
Therefore, the selection and maintenance process should prioritize accurate visual assessment, supplemented by professional expertise when necessary. Neglecting this step increases risks and negates the protective benefits such components are designed to provide. The integrity of the system, and potentially the structure itself, depends on diligent application of this visual scrutiny.



![Top-Rated Chimney Cap Installer Near You: [City] Experts Chimney Works – Expert Chimney Repair, Cleaning & Installation Services Top-Rated Chimney Cap Installer Near You: [City] Experts | Chimney Works – Expert Chimney Repair, Cleaning & Installation Services](https://thechimneyworks.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-355-300x200.jpg)