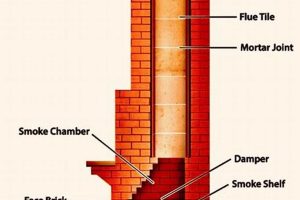
A vertical structure designed to expel combustion byproducts from heating appliances or industrial processes, specifically one with a 36-inch diameter, serves a critical function in venting gases safely and efficiently. This dimension is a significant factor in determining the volume of exhaust it can handle and the draft it creates. For example, a furnace rated at a specific BTU output may require a flue of this size to ensure proper venting and prevent the buildup of dangerous gases like carbon monoxide.
The purpose of such a component extends beyond mere expulsion; it contributes to maintaining optimal combustion efficiency and indoor air quality. Historically, these structures have evolved from simple brick stacks to engineered systems incorporating advanced materials for improved thermal performance and corrosion resistance. The benefits include enhanced safety by preventing backdrafting, improved appliance efficiency through consistent draft, and extended lifespan of connected equipment due to reduced exposure to corrosive flue gases.
The following sections will delve further into the selection criteria, installation considerations, maintenance requirements, and applicable safety standards relevant to these vital venting components, offering a practical guide for ensuring their effective and safe operation.
Essential Considerations for Optimal Performance
The following recommendations are crucial to ensure the safe and efficient operation of a 36-inch diameter exhaust chimney system.
Tip 1: Proper Sizing is Paramount: Ensure the component’s diameter aligns precisely with the appliance’s BTU output and venting requirements. Undersized chimneys impede exhaust flow, leading to backdrafting and potential carbon monoxide exposure. Oversized chimneys can cool exhaust gases prematurely, causing condensation and corrosion. Consult with a qualified HVAC professional to calculate the appropriate dimensions.
Tip 2: Material Selection Matters: Opt for materials rated for the specific temperatures and corrosives present in the exhaust stream. Stainless steel alloys, for instance, offer superior resistance to acidic condensation from high-efficiency appliances compared to traditional galvanized steel.
Tip 3: Prioritize Proper Installation: Adhere strictly to manufacturer specifications and local building codes during installation. Ensure adequate clearances from combustible materials and implement proper sealing techniques to prevent leaks. Improper installation can compromise structural integrity and increase fire hazards.
Tip 4: Regular Inspections are Non-Negotiable: Conduct routine visual inspections for signs of corrosion, damage, or obstructions. Pay particular attention to joints and seams, as these are common points of failure. Schedule professional chimney sweeps annually to remove creosote buildup and ensure unobstructed airflow.
Tip 5: Draft is Key: Verify adequate draft throughout the heating season. Insufficient draft can indicate obstructions, leaks, or imbalances in the system. Implement draft-inducing technologies, such as induced-draft fans, if natural draft is consistently inadequate.
Tip 6: Cap it Off: Install a properly sized chimney cap to prevent rainwater, debris, and animal intrusion. Choose a cap constructed of durable, corrosion-resistant materials to withstand the elements.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures efficient and safe operation, minimizing risks and extending the life of the exhaust system.
The subsequent sections will explore advanced diagnostic techniques and troubleshooting strategies to address common issues, offering a deeper understanding of optimal exhaust system management.
1. Diameter's Flow Capacity
The flow capacity of a 36-inch diameter exhaust chimney is intrinsically linked to its ability to efficiently remove combustion byproducts from a connected appliance or process. This dimension directly influences the volume of gases it can handle and the resulting draft, impacting both safety and operational effectiveness.
- Volumetric Flow Rate
The 36-inch diameter dictates the cross-sectional area available for exhaust gas flow. A larger diameter inherently allows for a greater volumetric flow rate, enabling the chimney to accommodate the exhaust output of more powerful appliances or processes. Insufficient flow capacity can lead to backdrafting, incomplete combustion, and the accumulation of hazardous gases.
- Draft Characteristics
Diameter influences the chimney’s draft, or the pressure differential that draws exhaust gases upwards. A properly sized 36-inch flue, considering height and thermal conditions, creates adequate draft for efficient venting. An undersized diameter may restrict airflow, reducing draft and compromising venting performance. Conversely, an excessively large diameter could diminish draft due to cooling, leading to condensation and reduced buoyancy of the exhaust gases.
- Friction Losses
The diameter impacts frictional resistance to gas flow within the chimney. Smaller diameters inherently increase frictional losses, hindering exhaust velocity and potentially leading to backpressure. A 36-inch diameter offers a balance between minimizing friction and maintaining sufficient exhaust velocity to prevent settling of particulate matter and condensation within the chimney.
- Appliance Compatibility
Matching the chimney diameter to the specific appliance’s venting requirements is crucial. A 36-inch diameter is typically suited for larger residential or commercial applications with significant BTU outputs. Incompatibility can result in inefficiencies, safety hazards, and premature component failure.
In summary, the flow capacity dictated by a 36-inch exhaust chimney’s diameter is a critical factor in ensuring proper venting, combustion efficiency, and overall system safety. Careful consideration of volumetric flow rate, draft characteristics, friction losses, and appliance compatibility is essential for optimizing performance and preventing potential problems.
2. Material Specifications
Material specifications are paramount when considering a 36-inch exhaust chimney. The choice of material directly impacts the component’s durability, safety, and long-term performance. For instance, if an exhaust chimney of this size is intended for venting flue gases from a coal-fired furnace, it necessitates materials capable of withstanding high temperatures and corrosive substances like sulfur dioxide. A common specification might call for high-grade stainless steel with specific alloy compositions known for their resistance to acidic corrosion at elevated temperatures. Using an inadequate material, such as standard carbon steel, would lead to premature degradation and potential structural failure, posing significant safety risks. Similarly, chimneys venting high-efficiency condensing furnaces must be constructed of materials resistant to the acidic condensate produced during combustion, often requiring specialized plastics or coated metals. The wrong material can result in leakage, compromised draft, and potential damage to surrounding structures.
Further, material specifications encompass more than just the primary chimney liner. Insulation materials, joint sealants, and exterior cladding must also be carefully selected. Insulation plays a crucial role in maintaining proper draft by minimizing heat loss in the exhaust gases. Improperly insulated chimneys may experience reduced draft, leading to incomplete combustion and potential carbon monoxide buildup. Joint sealants must be resistant to high temperatures and corrosive chemicals to prevent leaks, which can compromise the system’s integrity and safety. Exterior cladding, if present, provides protection against environmental elements and enhances the chimney’s aesthetic appeal while contributing to its structural stability. Specific cladding materials, such as brick or stone, may be chosen for their fire resistance properties, particularly in areas prone to wildfires.
In conclusion, the connection between material specifications and the performance of a 36-inch exhaust chimney is undeniable. Selecting appropriate materials based on the specific application, operating conditions, and regulatory requirements is essential for ensuring safety, longevity, and efficient operation. The challenges lie in accurately assessing the corrosive and thermal stresses to which the chimney will be subjected and selecting materials that provide adequate resistance at a reasonable cost. Addressing these challenges requires a thorough understanding of combustion processes, material properties, and relevant industry standards to achieve optimal performance and minimize potential risks.
3. Structural Integrity
The structural integrity of a 36-inch diameter exhaust chimney is paramount to its safe and effective operation. This dimension, while providing ample capacity for exhaust flow, also introduces significant engineering considerations to ensure stability against various environmental and operational stressors.
- Wind Load Resistance
Given its height and diameter, a chimney is subjected to considerable wind loads. Structural design must account for these forces, ensuring the chimney remains stable under high wind conditions. Adequate reinforcement, secure anchoring, and appropriate material selection are critical to prevent leaning, cracking, or collapse. Local building codes often specify minimum wind load requirements based on geographic location and exposure.
- Seismic Stability
In seismically active regions, the ability of a chimney to withstand earthquake forces is crucial. Design considerations include incorporating flexible connections to accommodate ground movement, using reinforced materials to resist shear forces, and ensuring proper anchorage to the building’s foundation. Failure to address seismic risks can lead to catastrophic collapse, posing significant safety hazards.
- Thermal Stress Management
Exhaust chimneys experience significant temperature fluctuations during operation, leading to thermal expansion and contraction. The structural design must accommodate these movements to prevent cracking and material fatigue. Expansion joints, flexible liners, and appropriate insulation can mitigate the effects of thermal stress, ensuring the chimney’s long-term integrity.
- Material Degradation Over Time
Exposure to corrosive flue gases, moisture, and ultraviolet radiation can degrade chimney materials over time. Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to identify and address any signs of deterioration, such as cracking, spalling, or rust. Selecting durable, corrosion-resistant materials and implementing protective coatings can extend the chimney’s lifespan and maintain its structural integrity.
These facets underscore the critical role structural integrity plays in the safe and reliable operation of a 36-inch exhaust chimney. Without careful consideration of wind loads, seismic activity, thermal stress, and material degradation, the chimney’s structural integrity can be compromised, leading to potential hazards and costly repairs. Consequently, adherence to engineering best practices and regular maintenance protocols are essential for ensuring its long-term performance.
4. Draft Optimization
Draft optimization, within the context of a 36-inch exhaust chimney, directly pertains to ensuring efficient and consistent removal of combustion byproducts. A chimney of this diameter, if improperly drafted, can lead to significant operational issues. Inadequate draft causes incomplete combustion, increasing pollutant emissions and posing a risk of carbon monoxide buildup. Conversely, excessive draft can lead to rapid heat loss, reducing appliance efficiency. A properly optimized system, therefore, balances these opposing forces.
Achieving draft optimization involves several factors. These include chimney height, internal surface roughness, and insulation levels. For example, a taller 36-inch chimney will naturally generate more draft due to the increased pressure differential. However, excessive height can exacerbate heat loss, necessitating insulation to maintain exhaust gas temperature. Surface roughness affects frictional resistance; smoother interiors promote better draft. Real-world examples include situations where relining an older, rough-interior chimney with a smooth stainless-steel liner significantly improved draft and appliance efficiency.
Therefore, understanding and implementing draft optimization principles is of practical significance for ensuring safe, efficient, and code-compliant operation of a 36-inch exhaust chimney system. The goal is to achieve a balance between adequate exhaust removal and minimizing energy waste, resulting in a system that performs optimally and adheres to environmental and safety regulations. Ongoing monitoring and adjustments may be necessary to accommodate changing weather conditions and appliance operating parameters.
5. Emission Compliance
Emission compliance, in the context of a 36-inch exhaust chimney, refers to the adherence to regulatory standards governing the release of pollutants into the atmosphere. This is critical because a structure of this size typically services larger combustion appliances or industrial processes, which are often subject to stringent emissions limits. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines, operational shutdowns, and legal liabilities.
- Stack Height Regulations
Regulations often dictate minimum stack heights based on the type and quantity of emissions. A 36-inch chimney must be of sufficient height to ensure adequate dispersion of pollutants, preventing localized concentrations that could violate air quality standards. For instance, regulations might specify a minimum height to mitigate the impact of sulfur dioxide emissions from a coal-fired boiler. Ignoring these regulations leads to non-compliance and potential enforcement actions.
- Pollutant Monitoring Requirements
Many jurisdictions mandate continuous or periodic monitoring of emissions from exhaust systems. This may involve installing monitoring equipment within the chimney to measure levels of pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and carbon monoxide. Data from these monitors must be reported to regulatory agencies, and exceedances of permitted levels trigger corrective actions. Absence of such monitoring constitutes a compliance failure.
- Permitting and Licensing
Operating a facility with a 36-inch exhaust chimney often requires obtaining permits and licenses from environmental agencies. These permits specify allowable emission rates and operating conditions. Failure to secure the necessary permits or to adhere to their stipulations is a violation of emission compliance regulations. This could involve operating without a valid permit or exceeding permitted emission limits.
- Control Technology Implementation
To meet emission standards, facilities may be required to implement control technologies, such as scrubbers or filters, to reduce pollutant emissions. The effectiveness of these technologies must be demonstrated through performance testing and ongoing monitoring. Failure to properly operate or maintain control equipment, or to achieve required emission reductions, constitutes non-compliance.
These facets are interconnected and crucial for ensuring that a 36-inch exhaust chimney operates within regulatory boundaries. Compliance requires a proactive approach, encompassing careful design, ongoing monitoring, and the implementation of appropriate control measures. Failure to address any of these elements can result in significant penalties and operational disruptions, highlighting the importance of prioritizing emission compliance in the management of such exhaust systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding 36-inch exhaust chimneys. These answers aim to clarify essential aspects of their selection, operation, and maintenance.
Question 1: What applications necessitate a 36-inch diameter exhaust chimney?
A 36-inch exhaust chimney is typically required for larger residential, commercial, or industrial applications involving high-BTU appliances or processes that generate significant volumes of exhaust gases. This size is often specified for furnaces, boilers, or industrial equipment with substantial exhaust flow requirements.
Question 2: How does the material selection impact the longevity of a 36-inch exhaust chimney?
Material selection is crucial for resisting corrosion and degradation from flue gases. Stainless steel alloys, for example, offer superior resistance to acidic condensation and high temperatures compared to galvanized steel. The appropriate material choice directly impacts the chimney’s lifespan and structural integrity.
Question 3: What are the primary safety considerations when installing a 36-inch exhaust chimney?
Safety considerations include maintaining proper clearances from combustible materials, ensuring adequate structural support, implementing proper sealing techniques to prevent leaks, and adhering to all applicable building codes and manufacturer specifications. Improper installation can lead to fire hazards and carbon monoxide exposure.
Question 4: How frequently should a 36-inch exhaust chimney be inspected?
A 36-inch exhaust chimney should undergo regular visual inspections at least annually. More frequent inspections are recommended for systems subjected to heavy use or corrosive environments. Professional chimney sweeps should be scheduled periodically to remove creosote buildup and ensure unobstructed airflow.
Question 5: What factors contribute to insufficient draft in a 36-inch exhaust chimney?
Insufficient draft can result from obstructions, leaks, inadequate chimney height, excessively long horizontal runs, or imbalances in the system. Implementing draft-inducing technologies, such as induced-draft fans, may be necessary if natural draft is consistently inadequate. Ensure proper sizing from the start as well.
Question 6: What regulatory requirements govern emissions from a 36-inch exhaust chimney?
Emissions from a 36-inch exhaust chimney are subject to regulations regarding stack height, pollutant monitoring, permitting and licensing, and control technology implementation. Adherence to these regulations is essential for maintaining compliance and avoiding penalties. Consult with environmental agencies for specific local requirements.
Understanding these key points enables informed decisions regarding the selection, installation, maintenance, and safe operation of these significant venting components.
The next section will explore troubleshooting common issues encountered with these systems, offering practical guidance for effective problem-solving.
Exhaust Chimney 36 Inch
The preceding discussion has highlighted the critical aspects of a 36-inch exhaust chimney, encompassing its selection, design, installation, operation, and maintenance. The importance of proper sizing, material specifications, structural integrity, draft optimization, and emission compliance cannot be overstated. Neglecting any of these factors can lead to compromised performance, safety hazards, and regulatory violations.
Given the substantial role these components play in both residential and industrial settings, a commitment to diligent oversight is paramount. Continued adherence to best practices, rigorous monitoring, and proactive maintenance are essential to ensuring the long-term reliability and safety of these systems. Failure to prioritize these measures carries significant risks, underscoring the need for a responsible and informed approach.