Expenditure associated with the installation of a corrosion-resistant flue lining system fabricated from a specific alloy is a significant consideration for homeowners. This expenditure encompasses the material itself, necessary components for proper installation, and the labor required for professional fitting. For example, a dwelling with a multi-story chimney will generally require a greater length of material, thus influencing the total expenditure.
Implementing such a lining offers numerous advantages, including enhanced safety by mitigating the risk of carbon monoxide intrusion and improved appliance efficiency through optimized venting. Historically, deteriorating masonry chimneys posed significant fire hazards. Employing a modern lining material provides a durable and code-compliant solution, extending the lifespan of the existing chimney structure.
Understanding the factors that influence pricing, including diameter, gauge, and insulation options, is crucial for informed decision-making. Further discussion will address these variables, along with the impact of regional labor rates and the potential for long-term savings derived from increased heating system performance and reduced maintenance needs.
Considerations for Managing Expenses Associated with Chimney Relining
Effective planning is essential when undertaking a flue lining project. Careful consideration of the following points can assist in optimizing the investment.
Tip 1: Obtain Multiple Quotes: Contact several qualified chimney professionals for detailed estimates. Compare not only the overall price but also the included materials and the scope of work outlined.
Tip 2: Evaluate Material Quality: Different grades of alloys exist. Selecting a higher gauge material, while initially more expensive, may provide greater longevity and corrosion resistance, ultimately proving more cost-effective.
Tip 3: Assess Insulation Needs: Insulating the flue lining improves draft and minimizes condensation. Determine if insulation is necessary based on climate, appliance type, and chimney location. Failure to insulate when required can lead to operational inefficiencies and premature deterioration.
Tip 4: Verify Contractor Credentials: Ensure the chosen installer possesses the necessary certifications and licenses. Improper installation can void warranties and compromise safety, leading to additional remediation expenses.
Tip 5: Plan for Future Fuel Changes: Anticipate potential shifts in fuel types for heating appliances. Select a lining system compatible with various fuels to avoid the need for replacement if fuel sources evolve.
Tip 6: Schedule During Off-Peak Seasons: Demand for chimney services often fluctuates seasonally. Scheduling the project during the spring or summer months may result in lower labor rates.
Tip 7: Explore Available Rebates and Incentives: Research potential energy efficiency rebates or tax credits offered by local utilities or government agencies. These incentives can help offset a portion of the expenditure.
By proactively addressing these aspects, property owners can ensure a durable and appropriately priced flue lining installation. A strategic approach minimizes long-term operational expenditure and maximizes safety.
The subsequent sections will address the implications of selecting specific alloys and the impact of regional cost variations.
1. Material Gauge
The gauge of the stainless steel utilized in a chimney liner directly correlates with its cost. Gauge refers to the thickness of the metal; a lower gauge number signifies a thicker, more robust material. Thicker materials inherently require more raw material to produce, thus elevating the initial purchase price. For instance, a 24-gauge liner will generally cost more than a 26-gauge liner of the same diameter and length due to the increased quantity of stainless steel.
The selection of an appropriate gauge is not solely a financial decision. The intended application and the type of appliance venting through the chimney significantly influence the optimal gauge. Appliances that produce high flue gas temperatures or corrosive byproducts necessitate a thicker gauge to resist degradation and ensure longevity. Insufficient gauge selection can result in premature liner failure, requiring costly replacement and potentially posing safety hazards. A common example is wood-burning stoves, where the higher flue temperatures often mandate a heavier gauge liner compared to gas-fired appliances.
Ultimately, the relationship between material gauge and expenditure underscores the importance of balancing initial cost with long-term value and safety. While a thinner gauge may present immediate savings, the increased risk of failure and subsequent replacement expenses can negate these initial benefits. Therefore, consulting with a qualified professional to determine the appropriate gauge for the specific application is paramount for optimizing the return on investment and ensuring safe operation.
2. Diameter Required
The required diameter of a chimney liner directly impacts the associated expense. This dimension is determined by the appliance being vented and is a critical factor influencing the quantity of material needed and the overall complexity of the installation.
- Appliance Venting Requirements
Different appliances, such as furnaces, stoves, and water heaters, have specific venting requirements dictated by their BTU output and fuel type. These requirements often necessitate a specific flue diameter to ensure proper draft and safe removal of combustion byproducts. A larger BTU output generally requires a wider diameter liner. Failure to adhere to these requirements can lead to inefficient operation, carbon monoxide hazards, and code violations, potentially leading to a more costly remediation.
- Material Quantity and Cost
The diameter of the liner directly influences the surface area of stainless steel required for its construction. As the diameter increases, so does the amount of material necessary, resulting in a proportional increase in material cost. For instance, a 8-inch diameter liner will require significantly more stainless steel than a 6-inch diameter liner of the same length, directly impacting the final cost.
- Installation Complexity and Labor
A wider diameter liner can present challenges during installation, especially in older chimneys with tight clearances or obstructions. Navigating a larger liner through a narrow chimney may necessitate specialized tools or techniques, increasing labor time and associated expenses. In some cases, minor modifications to the chimney structure may be required to accommodate the larger diameter, further contributing to the overall expenditure.
- Standard Sizes and Availability
Stainless steel chimney liners are typically manufactured in standard diameter increments. If the calculated diameter falls between standard sizes, it may be necessary to opt for the next larger size. This decision, while ensuring adequate venting capacity, will inevitably increase the material expense. Additionally, less common diameters may be subject to longer lead times and higher prices due to lower production volumes.
In summary, the required diameter of a stainless steel chimney liner is a primary cost driver. Understanding the interplay between appliance requirements, material quantity, installation complexity, and available sizes is crucial for accurately estimating the total expenditure and ensuring a safe and code-compliant installation.
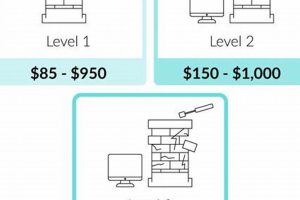
3. Installation Complexity
The intricacy of a stainless steel chimney liner installation directly influences the total project expenditure. Chimney anatomy, accessibility, and required modifications contribute to the overall difficulty, impacting labor hours and specialized equipment needs.
- Chimney Accessibility and Height
Limited access to the chimney, whether due to location or structural impediments, increases labor time. High chimneys necessitate specialized scaffolding or lifting equipment, adding to the cost. Interior chimney installations within multi-story dwellings, for instance, present logistical challenges compared to easily accessible exterior chimneys on single-story residences.
- Chimney Condition and Preparation
Pre-existing damage, such as cracks, spalling, or creosote buildup, requires remediation prior to liner installation. Extensive cleaning, repair, or structural reinforcement adds to the project scope and increases expenses. For example, a severely deteriorated chimney may require partial rebuilding before a liner can be safely installed.
- Obstructions and Offsets
Chimneys with offsets or internal obstructions, such as dampers or debris, necessitate specialized techniques and flexible liner sections. Navigating these obstacles increases labor and material costs. In some instances, the chimney may require modification to remove the obstruction or accommodate the liner, further elevating expenses.
- Code Compliance and Permitting
Adherence to local building codes and acquisition of necessary permits contribute to the overall project cost. Complex installations may require detailed engineering assessments to ensure code compliance, adding to the initial expenses. Furthermore, inspection fees and potential rework resulting from non-compliance can significantly increase the final expenditure.
In conclusion, the complexity of the installation is a significant determinant of the final cost. Thorough assessment of the chimney’s condition, accessibility, and code requirements is crucial for accurate cost estimation and successful project completion. Ignoring these factors can lead to unforeseen challenges and increased expenses during the installation process.
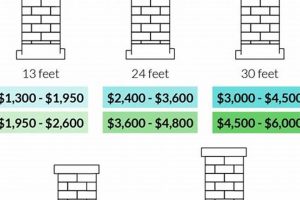
4. Chimney Height
Chimney height exerts a considerable influence on the overall expenditure associated with stainless steel flue lining installations. The vertical dimension of the chimney directly impacts material requirements, labor demands, and logistical considerations, thereby significantly affecting the final cost.
- Material Quantity
A direct correlation exists between chimney height and the amount of stainless steel liner required. Taller chimneys necessitate a greater length of liner to traverse the entire flue, resulting in increased material costs. For example, a two-story house typically requires a longer liner than a single-story dwelling, proportionally elevating the materials budget.
- Labor and Installation Time
The vertical distance of the chimney affects the labor required for installation. Higher chimneys demand more time for maneuvering the liner into place, securing connections, and ensuring proper sealing. Reaching elevated portions of the chimney may necessitate specialized equipment and scaffolding, further increasing labor expenses. A taller structure inherently requires more effort, translating to greater labor input.
- Liner Weight and Handling
The weight of the stainless steel liner increases with length, posing logistical challenges during installation, particularly in taller chimneys. Managing and lifting heavier liner sections requires additional manpower or specialized lifting equipment. The inherent difficulty of handling substantial weight at height contributes to both labor costs and potential safety concerns.
- Code Compliance and Support
Local building codes often mandate specific support and anchoring requirements for chimney liners exceeding a certain height. These requirements may necessitate additional hardware, such as support clamps or bracing, to ensure structural integrity and prevent liner sagging. Compliance with these regulations adds to the material and installation expenditure.
In summary, chimney height is a key cost driver in stainless steel flue lining projects. The interplay between material quantity, labor demands, liner handling challenges, and code compliance considerations underscores the importance of accurately assessing chimney height during the project planning phase. Neglecting this factor can lead to inaccurate budget projections and unforeseen expenses during installation.
5. Regional Labor
Regional labor costs exert a significant influence on the total expenditure associated with stainless steel chimney liner installation. The price of labor, comprising the wages paid to skilled technicians and the associated overhead costs, varies substantially across different geographical locations. These variations stem from several factors, including the local cost of living, prevailing wage rates for construction trades, union density, and the overall demand for chimney services in a given area. For instance, metropolitan areas characterized by a higher cost of living and strong union presence typically exhibit elevated labor costs compared to rural areas with a lower cost of living and a non-unionized workforce. Consequently, the installation of an identical chimney liner in two distinct regions can incur significantly different labor charges, directly impacting the overall project expenditure.
The complexity of the installation, combined with regional labor rates, further amplifies the effect on the final cost. Installations requiring specialized skills, such as navigating challenging chimney configurations or addressing structural issues, demand experienced technicians. The premium charged for these specialized skills is subject to regional variations. As an example, a historical building in a major city might require a chimney liner installation that adheres to stringent historical preservation guidelines, necessitating a highly skilled and licensed professional. This specialized labor will command a higher hourly rate than a standard chimney liner installation in a suburban area with fewer regulatory constraints. The influence of regional labor is pervasive throughout the entire process, from initial inspection and preparation to the final liner installation and system testing.
In summary, regional labor costs represent a critical component of the overall expenditure for stainless steel chimney liner installation. Understanding these regional variations is essential for accurate budget planning and cost comparison. Homeowners are advised to obtain multiple quotes from qualified contractors within their locality to gauge prevailing labor rates and make informed decisions. Furthermore, consideration should be given to the long-term implications of employing qualified and experienced technicians, even if their hourly rates are higher, as proper installation ensures safety, efficiency, and compliance with local building codes.
6. Insulation Needs
The requirement for insulation significantly impacts the overall expenditure associated with a stainless steel chimney liner installation. Insulation’s primary function is to mitigate heat loss within the flue and maintain optimal draft. This directly influences liner diameter, material type, and labor complexity, consequently affecting costs. For instance, uninsulated liners in colder climates can experience excessive condensation, leading to accelerated corrosion and premature failure. Addressing this necessitates more frequent maintenance or liner replacement, incurring additional costs over the system’s lifespan. Proper insulation, although adding to the initial expense, can prevent such issues.
The necessity for insulation depends on several factors, including climate, appliance type, and chimney location. Gas-burning appliances often require insulated liners due to lower flue gas temperatures compared to wood-burning stoves. This difference in temperature makes the flue gas more prone to cooling, leading to condensation of water and acidic compounds within the chimney. Insulation prevents this cooling, maintaining flue gas temperatures above the dew point, and minimizing corrosive effects. Neglecting insulation where required increases the likelihood of costly repairs and potential safety hazards like carbon monoxide backdraft. Furthermore, insulating a liner may reduce the necessary diameter for proper draft, which can partially offset the insulation’s material cost.
In summary, insulation needs represent a crucial component in the cost equation for stainless steel chimney liners. While insulation adds to the initial project expenses, it safeguards against long-term issues, such as corrosion and inefficient appliance operation. A comprehensive assessment of the applications specific conditions is paramount to determine the appropriate insulation level, balancing upfront costs with the overall lifecycle expenditure and safety considerations. The challenge lies in accurately predicting long-term performance and selecting insulation that provides optimal protection without excessive expenditure.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Stainless Steel Chimney Liner Expenditures
The subsequent queries address prevalent uncertainties pertaining to the financial considerations involved in installing a stainless steel chimney liner.
Question 1: What factors contribute most significantly to the price of a stainless steel chimney liner installation?
Material grade (alloy type and gauge), chimney height, installation complexity (accessibility, obstructions), and regional labor rates are the primary determinants of overall expenditure. Each of these components contributes substantially to the final project cost.
Question 2: Is it possible to reduce costs by opting for a thinner gauge stainless steel?
While utilizing a thinner gauge may yield initial savings, it compromises durability and corrosion resistance. For appliances generating high flue gas temperatures or corrosive byproducts, a thicker gauge is recommended to prevent premature failure and subsequent replacement expenses. This ensures long-term cost effectiveness.
Question 3: How does chimney height affect the cost of a liner installation?
A taller chimney necessitates a greater length of liner material, directly increasing material costs. Moreover, increased height elevates labor expenses due to the complexities of handling longer and heavier liner sections, potentially requiring specialized equipment and more time.
Question 4: Does insulation noticeably impact the overall cost, and is it always necessary?
Insulation does add to the upfront investment; however, it is not universally required. The necessity for insulation is contingent upon climate, appliance type, and chimney location. Insulation minimizes heat loss and condensation, which can lead to corrosion. While increasing initial expenses, it can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement expenditures.
Question 5: What role do regional labor rates play in the final price?
Regional labor costs can vary substantially. Factors such as the local cost of living, prevailing wage rates for construction trades, union density, and demand for chimney services influence labor expenses. Obtaining multiple quotes from qualified local contractors is crucial for accurate cost comparison.
Question 6: Are there any opportunities for rebates or tax credits to offset the expense of a stainless steel chimney liner?
Potential energy efficiency rebates or tax credits may be available from local utilities or government agencies. Researching applicable incentives can help offset a portion of the expenditure and improve the overall return on investment.
In conclusion, several interdependent elements dictate the financial implications of installing a stainless steel chimney liner. A thorough understanding of these variables allows for more accurate budget forecasting and informed decision-making.
The following sections will provide insights into selecting reputable contractors and avoiding potential pitfalls in the chimney liner installation process.
Cost of Stainless Steel Chimney Liner
The expenditure associated with a corrosion-resistant flue lining represents a significant investment in property safety and heating system efficiency. This exploration has addressed the multifaceted nature of this expense, encompassing material grade, chimney dimensions, installation complexities, regional labor variations, and insulation requirements. A comprehensive understanding of these interconnected variables is paramount for informed budgetary planning.
The long-term benefits of a properly installed liner, including enhanced safety, improved appliance performance, and reduced maintenance, warrant careful consideration of all cost factors. Further research into local building codes and contractor qualifications is strongly advised to ensure a durable and code-compliant installation. Prudent assessment and diligent planning are essential for optimizing the expenditure and maximizing the value derived from this critical home improvement investment.