The term refers to the comprehensive system encompassing the design, construction, maintenance, and repair of structures that vent combustion byproducts from fireplaces, stoves, and furnaces. These systems are critical components of building infrastructure, enabling the safe and efficient removal of smoke, gases, and particulate matter. An example includes the process of relining a flue to restore its structural integrity and ensure proper draft.
Properly functioning systems are essential for preventing carbon monoxide poisoning, reducing fire hazards, and optimizing heating appliance performance. Their historical context reveals evolving designs and materials influenced by advancements in combustion technology and building practices. Their integrity directly impacts indoor air quality and the overall safety of a building’s occupants, making regular inspection and upkeep vital.
The following sections will delve into specific aspects of this critical area, covering topics such as flue lining techniques, masonry repair, draft optimization, and relevant safety regulations. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in ensuring that these systems operate effectively and safely.
Chimney Works
Maintaining the integrity and functionality of venting systems is crucial for safety and efficiency. The following tips provide guidance on ensuring optimal operation.
Tip 1: Regular Inspections: Schedule annual professional inspections to identify potential issues like cracks, blockages, or deterioration. Early detection prevents costly repairs and hazardous situations.
Tip 2: Flue Cleaning: Creosote buildup is a significant fire hazard. Schedule routine cleaning based on usage frequency to remove accumulated deposits from the flue liner.
Tip 3: Cap Installation: A properly installed cap prevents rain, snow, and debris from entering the system, which can cause damage and reduce efficiency. It also deters animals from nesting inside.
Tip 4: Masonry Repair: Address any cracks or crumbling mortar joints promptly. Damaged masonry compromises structural integrity and allows moisture penetration, accelerating deterioration.
Tip 5: Smoke Testing: Conduct smoke tests to verify proper draft and identify any leaks in the system. This ensures efficient venting and prevents backdrafting of harmful gases.
Tip 6: Carbon Monoxide Detectors: Install and maintain carbon monoxide detectors on every level of the home, particularly near sleeping areas, to provide early warning of potential leaks.
Tip 7: Proper Appliance Operation: Adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for operating heating appliances to ensure efficient combustion and minimize the production of harmful byproducts.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures safe and efficient operation, minimizing fire risks and maximizing appliance performance.
The subsequent section explores specific techniques for addressing common issues encountered in maintaining these critical systems.
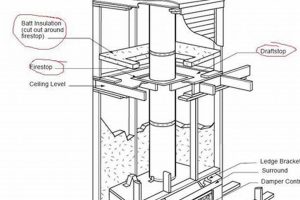
1. Design and Construction
The initial design and construction phase of venting systems profoundly influence their long-term performance, safety, and durability. A well-conceived and executed design ensures optimal draft, efficient removal of combustion byproducts, and structural stability, directly impacting the overall effectiveness of the entire system.
- Sizing and Height
The dimensions of the flue, including its diameter and height, must be precisely calculated to match the heating appliance’s requirements. Undersized flues restrict airflow, leading to backdrafting of dangerous gases. Insufficient height can impede draft, resulting in inefficient combustion and increased creosote buildup. Properly sized and elevated flues promote optimal draft and safe exhaust removal.
- Material Selection
The choice of materials, such as masonry, stainless steel, or ceramic liners, dictates the system’s resistance to heat, corrosion, and thermal stress. Inferior materials are susceptible to cracking, spalling, and deterioration, compromising structural integrity and creating pathways for gas leakage. Selecting appropriate, durable materials ensures longevity and safe operation.
- Joint Integrity
The method of joining flue sections, whether through mortar joints, interlocking sleeves, or sealant application, is critical to preventing leaks. Poorly sealed joints allow combustion gases to escape into the building, posing a significant health hazard. Careful attention to joint integrity during construction ensures a gas-tight system.
- Foundation and Support
The foundation and supporting structure must be capable of bearing the weight of the system and withstanding environmental forces such as wind and seismic activity. Inadequate support can lead to structural instability, cracking, and even collapse. A solid foundation and robust support system are essential for maintaining the long-term integrity of the structure.
These design and construction elements are inextricably linked, each contributing to the overall functionality and safety. Neglecting any aspect can compromise the entire system, underscoring the importance of meticulous planning and execution in ensuring efficient and secure venting for the life of the structure.
2. Material Durability
Material durability constitutes a cornerstone of effective and safe venting systems. The materials employed in their construction are subjected to extreme conditions, including high temperatures, corrosive combustion byproducts, and fluctuating environmental factors. The selection of materials directly influences the longevity, performance, and safety of the entire system. Premature material failure can lead to compromised structural integrity, leakage of harmful gases, and increased fire risk. For example, traditional masonry flues, while offering a degree of durability, are susceptible to degradation from acidic condensation prevalent in modern, high-efficiency appliances. This acidic attack weakens the mortar joints, leading to flue deterioration and potential carbon monoxide infiltration into living spaces.
The introduction of stainless steel liners represents a significant advancement in material durability for venting systems. Stainless steel exhibits superior resistance to corrosion and high temperatures compared to traditional materials, extending the lifespan of the flue and minimizing the risk of failure. Furthermore, properly installed stainless steel liners create a sealed pathway for combustion gases, preventing leaks and improving overall system efficiency. The practical significance of this understanding lies in the ability to proactively mitigate potential hazards and reduce long-term maintenance costs. Investing in durable materials during initial construction or renovation translates to enhanced safety and reduced risk of costly repairs down the line.
In summary, material durability is not merely a desirable attribute, but an essential requirement for safe and effective operation. The selection of appropriate, robust materials directly impacts the system’s ability to withstand the harsh operating environment, prevent hazardous failures, and ensure the safe and efficient removal of combustion byproducts. Addressing the challenges posed by material degradation requires careful consideration of appliance type, operating conditions, and material properties, ultimately contributing to the longevity and safety of building occupants.
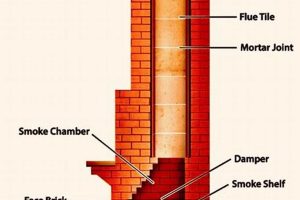
3. Flue Integrity
Flue integrity, a critical aspect of venting systems, directly impacts their ability to safely and efficiently remove combustion byproducts. Damage or deterioration within the flue liner compromises its primary function, creating pathways for gas leakage and increasing the risk of fire. The relationship between flue integrity and the overall effectiveness of this complex system is causal: a compromised flue leads to reduced draft, incomplete combustion, and the potential for carbon monoxide infiltration into living spaces. For example, cracking or spalling in a masonry flue, often caused by thermal stress or moisture penetration, allows hot gases to come into direct contact with combustible building materials, increasing the likelihood of a chimney fire. The practical significance lies in recognizing that maintaining flue integrity is not merely a preventative measure, but a fundamental requirement for safe and efficient appliance operation.
Assessment of flue integrity involves visual inspections, smoke tests, and, in some cases, video scanning. Visual inspections can reveal obvious signs of damage, such as cracks, missing mortar joints, or creosote buildup. Smoke tests verify draft and identify leaks by observing smoke flow and escape points. Video scanning, using specialized cameras, allows for a thorough examination of the flue’s interior, detecting hidden cracks and defects. Remedial actions to restore flue integrity range from minor repairs, such as patching mortar joints, to complete flue relining. Relining involves installing a new liner, typically made of stainless steel or ceramic, within the existing flue, creating a sealed and durable pathway for combustion gases. Choosing the appropriate repair or relining method depends on the extent and nature of the damage, appliance type, and local building codes. Improper repairs can exacerbate existing problems and create new hazards.
In conclusion, flue integrity is an indispensable component of a functional and safe venting system. Its maintenance demands regular inspection, prompt repair, and adherence to industry best practices. Ignoring potential issues can result in significant hazards, including carbon monoxide poisoning and chimney fires. Understanding the intimate connection between flue integrity and the operation of venting systems enables informed decision-making regarding maintenance, repair, and renovation, ensuring the continued safety and well-being of building occupants.
4. Draft Optimization
Draft optimization is a critical factor in the proper operation of venting systems. The term denotes the process of ensuring adequate airflow through the flue to effectively expel combustion byproducts, preventing dangerous conditions within a building. Its relevance to these systems lies in its direct impact on appliance efficiency, safety, and longevity, making it a primary consideration in their design and maintenance.
- Flue Sizing and Height
The dimensions of the flue, specifically its diameter and height, directly influence draft. An undersized flue restricts airflow, while an excessively large flue can cool exhaust gases, reducing buoyancy. Insufficient height diminishes the stack effect, inhibiting the upward movement of gases. Proper sizing and height, determined by appliance specifications and local codes, are essential for establishing optimal draft.
- Air Supply and Combustion Efficiency
Adequate air supply to the combustion chamber is paramount for complete and efficient burning of fuel. Insufficient air leads to incomplete combustion, generating excessive amounts of carbon monoxide and creosote. Ensuring unobstructed air intake and proper appliance venting configuration improves combustion efficiency, reducing the production of harmful byproducts and enhancing draft.
- Flue Cleanliness and Obstructions
Accumulated creosote, debris, or animal nests within the flue impede airflow, diminishing draft and increasing the risk of chimney fires. Regular cleaning and inspection are necessary to remove obstructions and maintain optimal draft. A clear, unobstructed flue allows for the unimpeded passage of combustion gases, ensuring safe and efficient venting.
- Appliance and Vent Connector Compatibility
Proper matching of the appliance to the venting system, including the vent connector, is crucial for draft optimization. Incompatible components can restrict airflow, leading to backdrafting and reduced appliance efficiency. Selecting vent connectors of appropriate size, material, and configuration ensures seamless integration and promotes optimal draft throughout the system.
The interplay of these facets demonstrates the multifaceted nature of draft optimization. Their careful consideration ensures the proper functioning of venting systems, promoting safety and efficiency. Prioritizing draft optimization during installation and maintenance represents a commitment to both occupant well-being and the long-term integrity of building infrastructure.
5. Safety Regulations
Adherence to safety regulations is paramount in all aspects of venting systems. These regulations, established by governing bodies and industry organizations, aim to mitigate fire hazards, prevent carbon monoxide poisoning, and ensure structural integrity. Strict compliance protects building occupants and property by dictating specific requirements for design, installation, maintenance, and inspection.
- Building Codes and Standards
Local and national building codes mandate specific requirements for materials, construction methods, and clearances. These codes often reference industry standards developed by organizations such as the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and the International Code Council (ICC). For instance, NFPA 211 outlines standards for chimneys, fireplaces, vents, and solid fuel-burning appliances. Failure to comply with these codes can result in fines, legal action, and increased risk of fire and carbon monoxide exposure.
- Permitting and Inspection Processes
Most jurisdictions require permits for the installation or modification of venting systems. The permitting process ensures that proposed work complies with applicable building codes and safety regulations. Inspections, conducted by qualified building officials, verify that the installation meets code requirements. These processes provide a crucial layer of oversight, preventing unsafe practices and ensuring proper installation.
- Qualified Professionals and Certification
Many jurisdictions require or recommend the use of qualified professionals for the installation, inspection, and maintenance of venting systems. Certification programs, such as those offered by the Chimney Safety Institute of America (CSIA), demonstrate a professional’s competence and adherence to industry best practices. Utilizing certified professionals ensures that work is performed safely and effectively, reducing the risk of errors and omissions.
- Carbon Monoxide Detection Requirements
Safety regulations often mandate the installation of carbon monoxide detectors in residential buildings, particularly near sleeping areas. These detectors provide an early warning of carbon monoxide leaks, allowing occupants to evacuate the building before exposure reaches dangerous levels. Regular testing and maintenance of carbon monoxide detectors are essential for ensuring their proper function.
The consistent application and enforcement of these safety regulations contribute significantly to the safe and reliable operation of venting systems. Ignoring or circumventing these regulations can have severe consequences, jeopardizing the health and safety of building occupants. Therefore, a thorough understanding of and adherence to applicable safety regulations are essential for all stakeholders involved in the design, installation, and maintenance of these critical building components.
Frequently Asked Questions about Chimney Works
The following questions address common inquiries and misconceptions regarding the function, maintenance, and safety of venting systems. The information provided aims to clarify key aspects of this critical building component.
Question 1: How frequently should a venting system be inspected?
Venting systems should undergo professional inspection at least annually, or more frequently if the appliance is used extensively. Inspections identify potential hazards, such as creosote buildup or structural damage, before they escalate into serious problems.
Question 2: What are the primary indicators of a compromised venting system?
Indicators of a compromised system include visible cracks or spalling in the masonry, excessive creosote buildup, backdrafting of smoke into the building, and the presence of carbon monoxide. Any of these signs warrant immediate professional evaluation.
Question 3: Does the type of fuel influence maintenance requirements?
Yes, the type of fuel significantly impacts maintenance needs. Wood-burning appliances produce more creosote than gas or oil-burning appliances, requiring more frequent cleaning and inspection.
Question 4: Is professional chimney sweeping necessary, or can it be performed independently?
While basic maintenance, such as removing loose debris, can be performed independently, professional chimney sweeping is recommended. Professionals possess the necessary tools and expertise to thoroughly remove creosote and identify potential structural issues.
Question 5: What is the purpose of a flue liner, and why is its integrity important?
The flue liner protects the masonry from corrosive combustion byproducts and prevents gases from escaping into the building. Its integrity is crucial for preventing structural damage and reducing the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Question 6: How does proper draft contribute to appliance efficiency and safety?
Proper draft ensures the efficient removal of combustion gases, preventing backdrafting and promoting complete combustion. This improves appliance efficiency, reduces emissions, and minimizes the risk of carbon monoxide exposure.
Understanding these frequently asked questions is essential for maintaining the safety and efficiency of venting systems. Regular inspections, proper maintenance, and prompt repairs are crucial for preventing hazards and ensuring the well-being of building occupants.
The following section delves into specific technologies employed to enhance the functionality and safety of these systems.
Conclusion
This exploration has detailed the multifaceted nature of chimney works, encompassing design, construction, maintenance, and adherence to safety standards. Key points include the critical importance of flue integrity, the selection of durable materials, the optimization of draft, and compliance with relevant regulations. Each element contributes significantly to the safe and efficient operation of venting systems.
The understanding and implementation of best practices in chimney works are paramount for mitigating risks associated with combustion byproducts. Prioritizing regular inspections, prompt repairs, and adherence to established codes ensures the continued safety and well-being of building occupants. Further research and technological advancements will continue to refine practices and enhance the longevity and safety of these essential systems.