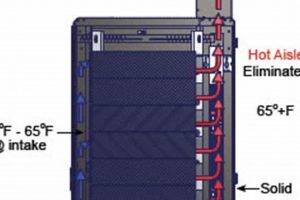
A specific method involving modifications to residential heating systems focuses on maximizing efficiency and reducing emissions. This approach centers around optimizing airflow and combustion processes within the system to achieve improved performance.
The significance of these modifications lies in their potential to lower energy consumption and decrease the environmental impact of residential heating. Historically, inefficient heating systems have contributed significantly to both increased energy costs for homeowners and higher levels of atmospheric pollution. Implementing such refinements can offer a pathway to more sustainable and cost-effective heating solutions.
The following sections will delve into the practical aspects of implementing such adjustments, exploring specific techniques and technologies used, and examining the long-term advantages they provide for homeowners and the environment.
Enhancement Strategies for Residential Heating Systems
The following recommendations are designed to optimize the functionality and efficiency of residential heating systems. These strategies emphasize improved performance and reduced environmental impact.
Tip 1: Optimize Airflow Dynamics: Ensure unobstructed airflow within the system. Blockages restrict efficient combustion and heat transfer. This may involve cleaning or replacing air filters and ensuring proper venting.
Tip 2: Conduct Regular System Inspections: Perform routine examinations of system components to identify potential issues early. This preventative measure can mitigate costly repairs and improve overall performance. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks.
Tip 3: Implement Proper Insulation Techniques: Improve insulation around heating system components, such as ductwork and pipes, to minimize heat loss. Adequate insulation maximizes energy efficiency and reduces operating costs.
Tip 4: Regulate Fuel Combustion Parameters: Monitor and adjust fuel combustion settings to achieve optimal air-to-fuel ratios. Precise combustion improves efficiency and reduces emissions of harmful pollutants.
Tip 5: Upgrade to High-Efficiency Components: Consider replacing outdated or inefficient components with modern, high-efficiency alternatives. This upgrade significantly enhances system performance and reduces energy consumption over the long term.
Tip 6: Maintain Cleanliness of System Elements: Regular cleaning of heat exchangers and other key components ensures efficient heat transfer. Accumulated soot and debris hinder performance and increase fuel consumption.
These strategies are crucial for maximizing the lifespan and efficacy of residential heating systems. By adopting these techniques, homeowners can achieve substantial energy savings, reduce environmental impact, and improve overall system reliability.
The subsequent sections will provide a detailed analysis of specific technologies and methodologies associated with improving system performance.
1. Airflow Optimization
Airflow optimization is a fundamental component within chimney tek principles, representing a critical determinant of system efficiency and performance. The proper management of airflow directly influences combustion processes, heat transfer rates, and the effective removal of combustion byproducts. Restrictions or inefficiencies in airflow impede complete combustion, leading to increased fuel consumption, higher levels of emissions, and potential safety hazards. For example, a chimney obstructed by debris or a poorly designed ventilation system restricts the flow of exhaust gases, causing backdrafting or the accumulation of carbon monoxide within a dwelling. This situation underscores the importance of maintaining a clear and unobstructed pathway for airflow.
The impact of optimized airflow is further demonstrated in the reduction of particulate matter emissions. Efficient combustion, facilitated by adequate oxygen supply, minimizes the production of soot and other airborne pollutants. In practical applications, this translates to cleaner air within the home and reduced environmental impact. Regular inspection and maintenance of chimneys, vents, and air intakes are essential to ensuring consistent and reliable airflow. Properly sized flues and strategically positioned air inlets further contribute to achieving optimal airflow conditions.
In summary, airflow optimization constitutes a foundational aspect of the broader scope. It directly impacts system efficiency, safety, and environmental performance. Understanding and implementing strategies to improve airflow are critical to maximizing the benefits. Challenges such as aging infrastructure and inadequate maintenance practices necessitate a proactive approach to ensure the long-term effectiveness. These efforts align with the objective of promoting efficient, safe, and environmentally responsible residential heating practices.
2. Combustion Efficiency
Combustion efficiency stands as a pivotal factor in chimney tek, directly influencing both energy consumption and environmental emissions. Proper combustion ensures that fuel is completely oxidized, releasing maximum heat and minimizing the creation of harmful byproducts. The principles of chimney tek emphasize achieving and maintaining optimal combustion to maximize the benefits of the heating system.
- Air-to-Fuel Ratio Optimization
The stoichiometric ratio of air to fuel is critical for complete combustion. Deviations from this ratio can result in incomplete combustion, leading to increased levels of carbon monoxide, unburned hydrocarbons, and particulate matter. Chimney tek methodologies involve adjusting air intakes, fuel delivery systems, and burner settings to maintain the ideal air-to-fuel mixture. For example, insufficient air supply in older systems often results in smoky flames and reduced heat output, which can be corrected through proper adjustments and upgrades.
- Burner Design and Maintenance
The design of the burner itself plays a significant role in combustion efficiency. Modern burner designs often incorporate features such as staged combustion or pre-mixing of air and fuel to enhance combustion completeness. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and inspection of burner components, is essential for preventing soot buildup, nozzle blockages, and other issues that can compromise combustion efficiency. A well-maintained burner ensures consistent and efficient fuel combustion over the system’s lifespan.
- Flue Gas Analysis and Monitoring
Flue gas analysis is a diagnostic tool used to assess the completeness of combustion. By measuring the concentrations of oxygen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and other gases in the exhaust stream, technicians can determine whether the system is operating at optimal efficiency. These data inform adjustments to air-to-fuel ratios, burner settings, and other parameters to achieve improved combustion. Continuous monitoring systems can provide real-time feedback, enabling proactive management of combustion efficiency.
- Impact of Chimney Design on Draft
The chimney’s design and integrity significantly affect the draft, which in turn influences combustion efficiency. A properly sized and maintained chimney creates the necessary suction to draw combustion air into the system and expel exhaust gases effectively. Insufficient draft can lead to incomplete combustion, backdrafting, and the accumulation of dangerous gases within the dwelling. Chimney tek principles include ensuring proper chimney height, diameter, and insulation to maintain optimal draft conditions and support efficient combustion.
These interconnected facets of combustion efficiency highlight its integral role within the framework of chimney tek. By addressing each of these elements comprehensively, homeowners and technicians can significantly enhance the performance of residential heating systems, reduce energy consumption, and mitigate environmental impact. The focus on optimized combustion contributes to improved safety, increased cost-effectiveness, and a more sustainable approach to residential heating.
3. Insulation Integrity
Insulation integrity is intrinsically linked to effective chimney tek strategies, directly influencing the performance and efficiency of residential heating systems. The presence of adequate insulation minimizes heat loss, ensuring that generated heat is effectively utilized within the intended space. Conversely, compromised insulation integrity results in significant energy wastage, as heat dissipates through uninsulated or poorly insulated surfaces. This phenomenon necessitates increased fuel consumption to maintain the desired temperature, thereby reducing overall system efficiency. The cause-and-effect relationship is clear: deficient insulation leads to higher energy bills and increased environmental impact. Real-life examples include homes with uninsulated attics or crawl spaces, where substantial heat loss occurs during colder months, demanding more energy to compensate. Therefore, maintaining insulation integrity is not merely an ancillary concern but a fundamental component of successful chimney tek implementation. The practical significance lies in reducing operational costs, lowering carbon footprint, and enhancing the overall comfort of the living environment.
Further analysis reveals that insulation integrity extends beyond the primary building envelope to include insulation around heating system components such as ductwork, pipes, and the chimney itself. Properly insulating these components reduces heat loss before it reaches the intended space, thereby improving the systems energy efficiency. For instance, uninsulated ductwork in an unconditioned attic can lose a significant portion of the heated air before it ever reaches the living space. In practical applications, this translates to higher heating costs and reduced comfort. Therefore, addressing insulation gaps and deficiencies in these secondary areas is as crucial as insulating the primary building structure. Thermographic inspections can be used to identify areas of heat loss, enabling targeted improvements to insulation and minimizing energy waste. This methodical approach ensures that the heating system operates at peak performance and efficiency.
In summary, insulation integrity represents a cornerstone of effective chimney tek practices. By minimizing heat loss and optimizing energy utilization, proper insulation contributes directly to reduced operational costs, lower environmental impact, and enhanced thermal comfort. Challenges such as aging infrastructure and inadequate initial installation underscore the need for regular inspections and upgrades to maintain optimal insulation performance. Addressing these challenges and prioritizing insulation integrity aligns with the broader theme of sustainable and efficient residential heating, promoting cost-effective and environmentally responsible practices.
4. System Inspections
Systematic examinations constitute a fundamental component of chimney tek, serving as a proactive approach to identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate into significant problems. These assessments encompass a comprehensive evaluation of the heating system’s components, performance metrics, and safety features, ensuring optimal functionality and adherence to safety standards. Their relevance to chimney tek lies in their ability to diagnose inefficiencies, detect structural weaknesses, and prevent hazardous conditions that can compromise the system’s performance and longevity.
- Structural Integrity Assessment
This facet focuses on evaluating the physical condition of the chimney structure, including the flue liner, masonry, and overall stability. Inspections often reveal cracks, spalling, or deterioration due to weathering, corrosion, or improper maintenance. Neglecting structural integrity can lead to chimney collapse, flue gas leakage, or reduced draft, all of which compromise the system’s efficiency and safety. Addressing these issues promptly through repairs or relining is critical for preserving the chimney’s functionality and preventing further damage.
- Combustion Efficiency Evaluation
A thorough inspection includes an assessment of the combustion process, involving measurements of flue gas composition, draft, and overall burner performance. Analysis of these metrics can identify inefficiencies such as incomplete combustion, excessive air intake, or fuel-air imbalances. Correcting these issues through adjustments to burner settings, air intakes, or fuel delivery systems can significantly improve combustion efficiency, reduce emissions, and lower fuel consumption. For example, detecting high levels of carbon monoxide in the flue gas indicates incomplete combustion and necessitates immediate investigation and adjustment.
- Safety Component Verification
Inspections routinely involve verification of safety components such as smoke detectors, carbon monoxide alarms, and draft regulators. Proper functioning of these devices is crucial for alerting occupants to hazardous conditions and preventing carbon monoxide poisoning or fire hazards. Inspections ensure that these devices are in good working order, properly positioned, and regularly tested. Replacing outdated or malfunctioning safety components is a vital step in safeguarding occupants and mitigating potential risks.
- Ventilation System Examination
The examination of the ventilation system is an integral part of chimney tek inspections, focusing on ensuring proper airflow and exhaust of combustion gases. Blocked vents, restricted air intakes, or inadequate ventilation can lead to backdrafting, reduced combustion efficiency, and the accumulation of hazardous gases within the dwelling. Inspections often involve clearing obstructions, verifying proper sizing of ventilation components, and assessing the overall effectiveness of the ventilation system. Maintaining adequate ventilation is essential for preventing moisture buildup, minimizing indoor air pollution, and ensuring a safe and healthy living environment.
These distinct facets of system inspections collectively contribute to the core principles of chimney tek by providing a comprehensive evaluation of the heating system’s performance, safety, and structural integrity. By proactively identifying and addressing potential issues, these inspections help to optimize system efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and enhance the overall reliability of residential heating. Regular system inspections are not merely a reactive measure but rather a proactive investment in the long-term health and performance of the heating infrastructure.
5. Component Upgrades
Component upgrades represent a crucial intersection within chimney tek principles, functioning as a tangible means of enhancing the efficiency, safety, and environmental performance of residential heating systems. Outdated or inefficient components, by their nature, impede optimal functionality, leading to increased energy consumption and higher emissions. The strategic replacement of these elements with modern, high-efficiency alternatives forms a cornerstone of chimney tek, enabling systems to operate at peak performance. The cause-and-effect relationship is direct: improved components yield enhanced system-wide performance. As an example, replacing an old, inefficient burner with a modern, high-efficiency model results in more complete combustion, reducing fuel consumption and emissions of harmful pollutants. Similarly, upgrading to a variable-speed blower motor in a forced-air system can significantly reduce energy consumption by optimizing airflow. The importance of these upgrades lies in their capacity to provide quantifiable improvements in system efficiency and long-term cost savings.
Further analysis reveals the practical significance of component upgrades in various aspects of residential heating. For instance, the installation of a programmable thermostat allows homeowners to precisely control heating schedules, reducing energy consumption during periods of absence. Upgrading to a sealed combustion system, which draws combustion air from outside the dwelling, eliminates the risk of backdrafting and improves indoor air quality. The adoption of modulating and condensing furnaces, which adjust their heating output based on demand, further enhances efficiency and reduces energy waste. Each of these upgrades, when implemented strategically, contributes to the overall effectiveness of chimney tek strategies. The selection and integration of new components necessitate careful consideration of compatibility, performance specifications, and installation requirements to ensure optimal system functionality. Consulting with qualified heating professionals is essential for making informed decisions and maximizing the benefits of component upgrades.
In conclusion, component upgrades serve as a pivotal mechanism for implementing chimney tek principles, facilitating the optimization of residential heating systems. By replacing outdated or inefficient elements with modern alternatives, homeowners can achieve significant improvements in energy efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and enhance the overall reliability of their heating infrastructure. Challenges such as the initial investment costs and the complexity of selecting appropriate components underscore the need for informed decision-making and professional guidance. Addressing these challenges and prioritizing component upgrades aligns with the broader theme of sustainable and efficient residential heating, promoting cost-effective and environmentally responsible practices for the long term.
6. Emission Reduction
Emission reduction is an indispensable goal of chimney tek, representing a tangible measure of its effectiveness in promoting environmentally responsible residential heating practices. Chimney tek methodologies, at their core, aim to minimize the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere through the optimization of combustion processes, the enhancement of energy efficiency, and the adoption of cleaner technologies. The connection between emission reduction and chimney tek is causal: effective implementation of chimney tek principles directly results in decreased emissions. For instance, optimizing the air-to-fuel ratio in combustion processes reduces the production of carbon monoxide and particulate matter. The importance of emission reduction as a component of chimney tek lies in its contribution to improved air quality, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and the mitigation of environmental health risks. Real-life examples include areas with stringent emission regulations for residential heating, where chimney tek practices are essential for meeting compliance standards and protecting public health.
Further analysis reveals that chimney tek encompasses a range of strategies specifically designed to target different types of emissions. These strategies include the installation of catalytic converters to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions, the use of cleaner-burning fuels such as natural gas or propane, and the implementation of advanced combustion technologies that minimize the formation of soot and other particulate matter. Practical applications involve regular monitoring of flue gas emissions to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and to identify potential areas for improvement. The adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar thermal systems, can also complement chimney tek strategies by reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and lowering overall emissions. Addressing the underlying causes of emissions through preventive maintenance and system upgrades further enhances the long-term effectiveness of emission reduction efforts.
In summary, emission reduction stands as a central objective of chimney tek, driving innovation and best practices in residential heating. By minimizing the release of harmful pollutants, chimney tek contributes significantly to improved air quality, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced public health. Challenges such as the cost of implementing emission reduction technologies and the complexity of regulatory compliance require ongoing efforts to promote sustainable and cost-effective solutions. Addressing these challenges and prioritizing emission reduction aligns with the broader theme of environmental stewardship, ensuring that residential heating systems operate in a manner that protects both human health and the natural environment.
7. Fuel Regulation
Fuel regulation, within the context of chimney tek, denotes the precise management of fuel supply and delivery to ensure optimal combustion efficiency and minimal emissions. This aspect plays a pivotal role in maximizing the benefits of residential heating systems, aligning with the core principles of chimney tek.
- Metering and Control
Accurate metering of fuel supply is essential for maintaining consistent combustion. Systems incorporating precise control mechanisms can adjust fuel delivery based on demand, preventing over-fueling and reducing energy waste. For example, modern heating systems equipped with electronic fuel injection can deliver the precise amount of fuel needed for efficient combustion, regardless of external factors such as temperature or altitude. The implications of accurate metering in chimney tek include reduced fuel consumption, lower emissions, and improved system stability.
- Fuel Quality Management
Maintaining fuel quality is critical for preventing system malfunctions and ensuring clean combustion. Contaminants in fuel, such as water, sediment, or additives, can clog fuel lines, damage burners, and increase emissions. Fuel regulation strategies include the use of filters, additives, and regular tank inspections to ensure that fuel remains clean and free of contaminants. The consequences of poor fuel quality in chimney tek are reduced system efficiency, increased maintenance costs, and elevated levels of pollutants.
- Air-to-Fuel Ratio Optimization
Achieving and maintaining the optimal air-to-fuel ratio is a cornerstone of efficient combustion. Too little air results in incomplete combustion, producing carbon monoxide and soot, while too much air reduces combustion temperature and decreases efficiency. Fuel regulation strategies include adjusting air intakes, burner settings, and fuel delivery systems to achieve the ideal mixture. For example, oxygen sensors and automatic dampers can regulate airflow to maintain the optimal air-to-fuel ratio in real-time. The implications of air-to-fuel ratio optimization in chimney tek are reduced emissions, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced system performance.
- Pressure Regulation
Maintaining consistent fuel pressure is essential for reliable combustion, particularly in gas-fired systems. Fluctuations in fuel pressure can lead to unstable flames, incomplete combustion, and safety hazards. Fuel regulation strategies include the use of pressure regulators to maintain a constant supply pressure, regardless of fluctuations in the main supply line. The consequences of inconsistent fuel pressure in chimney tek are reduced system efficiency, increased emissions, and potential safety risks.
The interrelation of these facets directly influences the effectiveness of chimney tek practices. Through precise metering, quality management, air-to-fuel ratio optimization, and consistent pressure regulation, residential heating systems can achieve improved performance, reduced emissions, and enhanced energy efficiency. The long-term benefits of fuel regulation underscore its importance in achieving sustainable and cost-effective residential heating solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding chimney tek, providing concise answers based on established principles.
Question 1: What defines chimney tek?
Chimney tek encompasses strategies aimed at optimizing residential heating systems for enhanced efficiency, reduced emissions, and improved safety. It involves a combination of techniques, including airflow optimization, combustion efficiency improvements, insulation enhancements, and regular system inspections.
Question 2: How does chimney tek impact energy consumption?
By implementing chimney tek principles, energy consumption can be significantly reduced through optimized combustion, minimized heat loss, and the use of high-efficiency components. These improvements translate to lower fuel consumption and reduced operational costs.
Question 3: What role does insulation play in chimney tek?
Insulation integrity is a crucial element of chimney tek, preventing heat loss and ensuring that generated heat is effectively utilized within the intended space. Adequate insulation minimizes energy waste and contributes to lower heating costs.
Question 4: How do regular system inspections benefit chimney tek implementation?
Routine system inspections enable the early detection of potential issues, allowing for timely repairs and adjustments that maintain optimal performance and prevent costly breakdowns. Inspections also ensure adherence to safety standards and regulatory requirements.
Question 5: Can component upgrades contribute to chimney tek effectiveness?
Strategic component upgrades, such as replacing outdated burners or installing programmable thermostats, can significantly enhance system efficiency, reduce emissions, and improve overall reliability. Selecting the right components based on system requirements is essential.
Question 6: How does chimney tek contribute to emission reduction?
Chimney tek directly contributes to emission reduction through optimized combustion, which minimizes the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. The use of cleaner-burning fuels and advanced combustion technologies further enhances emission reduction efforts.
Adhering to chimney tek principles facilitates cost savings and environmental responsibility.
The next section will explore advanced technologies used in chimney tek.
Conclusion
This exploration has delineated “chimney tek” as a multifaceted approach to enhancing residential heating systems. Key areas such as airflow optimization, combustion efficiency, insulation integrity, system inspections, component upgrades, emission reduction, and fuel regulation have been identified as critical for achieving improved performance and environmental responsibility. Effective implementation across these domains yields tangible benefits in energy conservation and reduced pollutant output.
Given the increasing emphasis on energy efficiency and environmental sustainability, adherence to the principles of “chimney tek” becomes increasingly vital. Continuous evaluation and refinement of heating systems, coupled with adherence to established best practices, are imperative for ensuring long-term performance and minimizing environmental impact. Such proactive measures serve not only to reduce operational costs but also to contribute to a more sustainable future.