An assembly of components designed to facilitate the safe and effective venting of combustion byproducts through a metal roof is often required for structures employing wood-burning stoves, furnaces, or fireplaces. These pre-engineered systems typically include a length of chimney pipe, flashing specifically designed to integrate with metal roofing profiles, a storm collar to prevent water ingress, and a cap to prevent debris and animal intrusion. Proper installation is crucial to prevent leaks and ensure safe operation of the venting appliance.
The implementation of a purpose-built venting solution offers several key advantages. It mitigates the risk of fire hazards associated with improperly vented appliances, protects the building envelope from water damage caused by leaks around the chimney penetration, and ensures compliance with local building codes and safety regulations. Historically, improper chimney installations have been a significant cause of residential fires, making the adoption of engineered systems increasingly important.
The following sections will delve into the specific considerations for selecting the appropriate system, the installation process, essential safety precautions, and maintenance requirements to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the ventilation system. Further details will outline the various types available based on metal roof profile and appliance requirements.
Essential Considerations
The successful integration of a venting system with a metal roof requires careful planning and execution. These tips provide essential guidance for selecting, installing, and maintaining such a system.
Tip 1: Compatibility is paramount. Verify that the selected system is specifically designed for use with the metal roof profile. Incompatible flashing can lead to leaks and premature roof degradation.
Tip 2: Prioritize professional installation. While DIY installation may seem appealing, improper installation can compromise safety and void warranties. Employing a qualified professional is strongly recommended.
Tip 3: Conduct thorough inspections. Regularly inspect the flashing, storm collar, and chimney cap for signs of damage or deterioration. Address any issues promptly to prevent water ingress or structural problems.
Tip 4: Ensure proper pipe sizing. Consult the appliance manufacturer’s specifications to determine the correct diameter of the chimney pipe. Undersized or oversized pipes can impair venting efficiency and increase the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Tip 5: Adhere to local building codes. Familiarize yourself with all applicable building codes and regulations pertaining to chimney installations. Compliance is essential for safety and legal reasons.
Tip 6: Select corrosion-resistant materials. Opt for systems constructed from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials to withstand the harsh outdoor environment and prolong the lifespan of the installation.
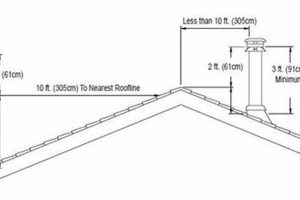
Tip 7: Maintain proper clearances. Ensure that the chimney pipe maintains adequate clearance from combustible materials throughout its entire length. This is crucial to prevent fire hazards.
Adhering to these guidelines will contribute to a safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting ventilation solution for structures with metal roofing.
The next section will explore common challenges encountered during the installation process and offer practical solutions to overcome them.
1. Metal Roof Compatibility
Metal roof compatibility is a paramount consideration in the selection and installation of a venting system. The interaction between the venting system’s flashing and the specific profile of the metal roofing panels dictates the system’s ability to maintain a watertight seal. Incompatibility introduces the potential for water ingress, leading to structural damage, mold growth, and compromised insulation performance. For instance, installing a flashing designed for corrugated metal roofing on a standing seam roof will inevitably result in gaps and leaks, regardless of the quality of the sealant used.
The design of the flashing must precisely match the rib height, panel spacing, and overall profile of the metal roof. Manufacturers offer venting solutions with flashing tailored to various metal roofing systems, including standing seam, corrugated, and ribbed panels. Failure to select the correct flashing necessitates costly modifications or, more likely, results in a perpetually leaking roof penetration. Furthermore, the chosen system should account for thermal expansion and contraction of the metal roof, preventing stress on the flashing and maintaining the integrity of the seal over time.
In summary, achieving proper metal roof compatibility is not merely an aesthetic consideration but a functional imperative. Selecting a system with appropriately designed flashing is crucial for ensuring a long-lasting, leak-free, and structurally sound installation. The financial and structural implications of neglecting this aspect are significant, underscoring the necessity for meticulous selection and professional installation practices.
2. Weather Tight Seal
Maintaining a weathertight seal is critical for any chimney installation, but it is especially vital when dealing with metal roofing systems. The unique characteristics of metal roofs, such as their susceptibility to thermal expansion and contraction, coupled with the potential for water to wick into even the smallest gaps, necessitate a robust and carefully engineered sealing solution.
- Flashing Design and Material
The design and material composition of the flashing are foundational to achieving a weathertight seal. Flashing must be specifically engineered to conform to the metal roof’s profile, creating a physical barrier against water intrusion. Materials like EPDM rubber or high-grade silicone are often incorporated due to their flexibility and resistance to degradation from UV exposure and temperature fluctuations. Improper flashing design or the use of substandard materials will inevitably lead to leaks, compromising the building’s integrity.
- Sealant Application Techniques
The application of sealant plays a crucial role in augmenting the physical barrier provided by the flashing. Specific techniques, such as backer rod installation to control sealant depth and the use of primers to promote adhesion, are necessary to ensure a long-lasting and effective seal. Over-application or improper selection of sealant types can lead to premature failure due to cracking or debonding from the metal surface.
- Storm Collar Implementation
A storm collar is a supplementary component positioned above the flashing that further protects the chimney penetration from water ingress. It deflects water away from the joint between the chimney pipe and the flashing, preventing water from running down the pipe and infiltrating the building. The storm collar must be properly sized and sealed to the chimney pipe to ensure its effectiveness.
- Addressing Thermal Expansion and Contraction
Metal roofs are subject to significant thermal expansion and contraction, which can stress the seals around the chimney penetration. A well-designed system incorporates flexible components or allows for movement without compromising the weathertight seal. Using rigid sealants or flashing materials in such an environment can lead to cracking and eventual failure of the seal.
The long-term performance of a chimney installation on a metal roof hinges on the integrity of the weathertight seal. Therefore, selecting components engineered for metal roof compatibility and employing meticulous installation techniques are crucial for preventing water damage and ensuring the longevity of the entire system.
3. Code Compliance
Code compliance is an inseparable component of any safe and effective venting solution. Regulatory bodies establish construction and safety standards to mitigate the risk of fire, carbon monoxide poisoning, and structural damage. A system failing to meet these established codes poses a direct threat to occupants and property. For instance, the International Residential Code (IRC) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) outline specific requirements for chimney height, clearances to combustible materials, and acceptable construction methods. The use of a system not adhering to these standards can result in fines, insurance complications, and, more critically, an increased risk of a catastrophic event. The installation of a system designed for a wood-burning stove on a gas appliance is a prime example of non-compliance potentially resulting in hazardous conditions.
The selection process must prioritize systems listed and labeled by recognized testing laboratories such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or Intertek. These listings signify that the product has undergone rigorous testing and meets the minimum safety standards outlined in applicable codes. Local jurisdictions often require permits and inspections for venting system installations to ensure code adherence. Furthermore, the type of appliance being vented (e.g., wood stove, furnace, fireplace) dictates specific code requirements related to chimney sizing, material specifications, and connector pipe installation. It is important to note that codes can vary by region, necessitating a thorough understanding of local regulations prior to any installation.
In conclusion, code compliance is not merely a procedural formality but a fundamental safety imperative. Neglecting to adhere to established codes when selecting and installing a system can have severe consequences. A proactive approach, involving consultation with local building officials and reliance on certified products, is essential to ensure the safe and lawful operation of any venting system. The long-term safety and well-being of occupants depend on strict adherence to these regulations.
4. Proper Sizing
The correlation between proper sizing and a system intended for a metal roof is not merely incidental but critical for optimal performance and safety. The system’s dimensions directly influence the efficiency of combustion gas evacuation. An undersized flue impedes airflow, leading to incomplete combustion, increased creosote accumulation (in wood-burning applications), and the potential for carbon monoxide backdraft into the dwelling. Conversely, an oversized flue allows for excessive cooling of exhaust gases, also promoting creosote buildup and reducing draft effectiveness. The specifications provided by the appliance manufacturer, usually in BTU/hr or heat output, dictate the necessary flue diameter and height to ensure adequate draft and complete combustion. For instance, a wood stove with a 6-inch flue outlet cannot be safely and effectively vented through a 4-inch system; the restricted airflow creates an unsafe operational environment.
Furthermore, proper sizing influences the longevity of the chimney components themselves. Overheating due to restricted airflow in an undersized system can cause premature degradation of the flue liner and other components. Similarly, excessive condensation within an oversized system can accelerate corrosion. The correct diameter and height, determined by the appliance specifications and local building codes, ensure that exhaust gases are efficiently vented while maintaining safe operating temperatures and minimizing condensation. When selecting a system for a metal roof, special attention must be given to the overall height to ensure adequate draft, particularly in areas with high wind exposure or nearby obstructions. Inadequate height can lead to downdrafts and diminished performance, negating the benefits of the metal roof systems inherent fire resistance and weather protection.
In summary, proper sizing is not an optional consideration but an essential element in the successful implementation of a metal roof chimney solution. It directly impacts safety, efficiency, and the lifespan of the entire system. Adherence to manufacturer specifications, compliance with local codes, and professional installation are paramount to ensuring the system performs as intended and provides years of safe and reliable service. Neglecting proper sizing introduces significant risks, underscoring the importance of meticulous planning and execution in every installation.
5. Material Durability
Material durability is a cornerstone of performance and longevity for any chimney system, and it assumes even greater significance when integrated with a metal roof. The inherent weather resistance of metal roofing accentuates the importance of selecting equally robust materials for the chimney components. The chimney will be exposed to the elements.Premature failure of the chimney can compromise the roof’s integrity and overall building protection.
- Resistance to Corrosion
Corrosion poses a significant threat to chimney systems, especially in environments with high humidity, coastal proximity, or exposure to acidic precipitation. Stainless steel, particularly 304 or 316 grades, provides superior resistance to corrosion compared to galvanized steel or aluminum. The use of corrosion-resistant materials prevents the weakening of the chimney structure, averting potential hazards such as flue collapse and gas leakage. For instance, a chimney constructed with lower-grade steel in a coastal environment may exhibit rust and degradation within a few years, whereas a stainless-steel chimney could last for decades under the same conditions.
- Thermal Stability
Chimneys experience extreme temperature fluctuations during operation, from the high heat of combustion gases to the cold of ambient air. Materials must exhibit excellent thermal stability to withstand these cycles without warping, cracking, or losing structural integrity. High-temperature alloys and ceramic liners are often employed to ensure the chimney maintains its shape and strength under extreme thermal stress. For example, a clay flue liner may crack and crumble after repeated exposure to high temperatures, leading to dangerous gas leaks and the need for costly repairs, while a listed stainless steel liner can withstand the cyclical extremes.
- UV Resistance
Chimney components exposed above the roofline are continuously subjected to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Prolonged UV exposure can degrade many materials, causing them to become brittle and prone to cracking. Selecting materials with inherent UV resistance, or applying protective coatings, is essential to prevent premature deterioration. Components such as storm collars and flashing, particularly those made of synthetic materials, require UV stabilization to maintain their flexibility and sealing properties over time. A plastic storm collar not rated for UV exposure will become fragile and crack, creating pathways for water infiltration which is counter to what the chimney is intended to do.
- Weatherproofing Integrity
The flashing and sealing components of a system are crucial for maintaining a weathertight barrier between the chimney and the metal roof. These components must withstand repeated exposure to rain, snow, ice, and wind without degrading or losing their ability to seal effectively. Durable materials such as EPDM rubber or high-quality silicone are often used for flashing and sealant applications, providing excellent resistance to weathering and maintaining a watertight seal for many years. Cheaper materials can result in leaks, leading to water damage and structural issues to the roof deck or to the building structure as a whole.
The careful selection of materials with robust durability characteristics is not merely a matter of extending the lifespan of the chimney but a vital aspect of ensuring the safety and integrity of the entire building. The system components working in tandem with the metal roof result in a prolonged overall life expectancy for the structure.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, installation, and maintenance of solutions specifically designed for metal roof applications.
Question 1: What are the primary advantages of utilizing a pre-fabricated system over a site-built chimney on a metal roof?
Pre-fabricated systems offer consistent component quality, engineered compatibility with various metal roof profiles, and simplified installation, reducing the risk of improper sealing and code violations compared to site-built options.
Question 2: How critical is the flashing design to the overall performance of a solution?
The flashing design is paramount. It must precisely match the metal roof’s profile to create a watertight seal, preventing leaks and subsequent structural damage. Improper flashing design is a primary cause of chimney-related roof failures.
Question 3: What materials are best suited for a system intended for a metal roof to ensure longevity?
Stainless steel (304 or 316 grade) for the chimney pipe and EPDM rubber or high-grade silicone for flashing components offer superior corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and UV resistance, maximizing system lifespan in outdoor environments.
Question 4: How often should a system be inspected, and what are the key aspects to examine?
Inspections should occur at least annually, preferably before the heating season. Key aspects to examine include the flashing for signs of cracking or corrosion, the storm collar for proper sealing, and the chimney cap for damage or debris accumulation. Any signs of water stains or leaks inside the building near the chimney penetration should be investigated immediately.
Question 5: Is professional installation recommended, or can a homeowner successfully install a system on a metal roof?
Professional installation is strongly recommended. Proper installation requires specialized knowledge of metal roofing techniques, code compliance, and safety protocols. Improper installation can compromise the system’s performance and void warranties.
Question 6: How does proper sizing of the flue affect the performance and safety of the appliance being vented?
Proper flue sizing is crucial for efficient combustion and safe venting. An undersized flue can lead to incomplete combustion and carbon monoxide backdraft, while an oversized flue can promote creosote buildup. The appliance manufacturer’s specifications must be followed to determine the correct flue diameter and height.
The information presented herein emphasizes the importance of careful planning, component selection, and adherence to best practices when implementing a system with a metal roof. Safety, efficiency, and longevity are contingent upon these factors.
The next article section will cover troubleshooting common problems.
Chimney Kit for Metal Roof
This exposition has detailed critical aspects of integrating a venting system with a metal roof. It has underscored the importance of metal roof compatibility, achieving a weathertight seal, adhering to building codes, ensuring proper flue sizing, and selecting durable materials. Each element contributes to the overall safety, efficiency, and lifespan of the system and the building it serves.
The information presented serves as a guide for informed decision-making. Prioritizing professional installation and rigorous maintenance are not merely recommended but essential for safeguarding property and well-being. Diligence in these matters mitigates potential hazards and ensures the reliable operation of the venting system for years to come.