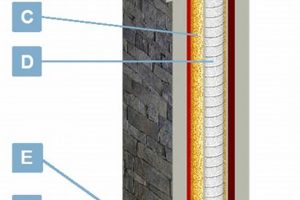
A flue lining component crafted from kiln-fired clay, it serves as a protective barrier within a chimney. This heat-resistant material shields the chimney structure from the corrosive byproducts of combustion, such as creosote and acids, thus preventing deterioration. Sections interlock to create a continuous, impermeable pathway for exhaust gases.
The presence of a sound flue system is crucial for safe and efficient venting of heating appliances. By preventing harmful gases like carbon monoxide from seeping into the living space, this barrier significantly enhances safety. Its use also contributes to energy efficiency by maintaining proper draft and reducing heat loss through the chimney walls. Historically, its adoption marked a significant improvement in chimney construction, replacing less durable materials and reducing the risk of chimney fires.
The subsequent sections will delve into the installation process, maintenance requirements, different types available, and factors to consider when selecting the appropriate option for a specific heating system.
Ceramic Flue Lining
The following points offer practical advice regarding the selection, installation, and upkeep of this critical component of a venting system.
Tip 1: Material Selection: Prioritize quality when choosing a lining. Opt for products that meet or exceed industry standards for durability and heat resistance. A compromised lining can lead to premature deterioration and potential hazards.
Tip 2: Professional Installation: Employ a certified professional for installation. Proper installation ensures a secure, leak-proof connection, maximizing safety and efficiency. Incorrectly installed linings can negate their intended benefits.
Tip 3: Sizing Considerations: Ensure the lining is appropriately sized for the appliance it serves. An improperly sized lining can impede draft and lead to inefficient combustion or dangerous backdrafting.
Tip 4: Regular Inspection: Conduct annual inspections of the chimney and lining. Early detection of cracks or damage allows for timely repairs, preventing costly replacements and maintaining optimal safety.
Tip 5: Chimney Cleaning: Schedule regular chimney cleaning to remove creosote buildup. Excessive creosote poses a significant fire hazard and can accelerate the degradation of the lining material.
Tip 6: Water Protection: Install a chimney cap to prevent water intrusion. Water can accelerate the deterioration of masonry and compromise the integrity of the lining over time.
Tip 7: Consider Fuel Type: Select a lining material compatible with the type of fuel being burned. Different fuels produce different byproducts, and some lining materials may be more resistant to specific corrosives.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures that this protective measure effectively safeguards the home and occupants from the dangers associated with flue gas emissions while maximizing system efficiency.
The concluding section will summarize the key benefits and considerations discussed throughout this document.
1. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a paramount attribute of flue systems, particularly those employing a ceramic composition. The exhaust gases produced by combustion processes contain corrosive compounds that can degrade chimney materials over time. A flue lining’s ability to withstand these corrosive elements directly impacts its lifespan and the safety of the structure it protects.
- Acidic Condensates
Flue gases often contain water vapor that condenses within the chimney, forming acidic solutions. These acids, such as sulfuric acid from burning fuels containing sulfur, attack the mortar joints and the brick or stone of the chimney itself. A ceramic material provides a barrier against this acidic attack, preventing the weakening and eventual failure of the chimney structure.
- Creosote Formation
In wood-burning systems, creosote, a highly corrosive byproduct of incomplete combustion, accumulates within the flue. Its acidic nature can penetrate and corrode chimney materials. The impermeable nature of a properly manufactured ceramic lining resists creosote penetration and minimizes its corrosive effects.
- Fuel Compatibility
Different fuels produce varying types and concentrations of corrosive byproducts. Ceramic materials are generally resistant to a broad range of these chemicals, making them suitable for use with wood, gas, and oil-burning appliances. Selecting a lining certified for use with a specific fuel type is crucial for ensuring long-term corrosion resistance.
- Temperature Fluctuations
Chimneys experience significant temperature fluctuations during heating cycles. These fluctuations can cause expansion and contraction of materials, leading to cracking and eventual failure. The inherent stability of ceramic, combined with proper installation techniques, mitigates the impact of temperature variations on corrosion resistance.
The facets outlined above emphasize the critical role of corrosion resistance in ensuring the longevity and safety of a chimney. The selection of a suitable flue system necessitates careful consideration of the materials used and their ability to withstand the specific corrosive challenges presented by the intended fuel type and operating conditions. Ceramic systems, when correctly specified and installed, provide a robust defense against corrosion, safeguarding the chimney structure and protecting occupants from the dangers of flue gas leakage.
2. Heat Containment
A primary function of a flue lining is heat containment, intrinsically linked to the safety and efficiency of a heating system. The ability of a ceramic flue to retain heat within the chimney structure directly influences the draft, or the upward flow of exhaust gases. When the flue maintains a warm internal temperature, the natural buoyancy of the gases is enhanced, facilitating their expulsion from the building. Insufficient heat containment, conversely, leads to a cooling of the flue gases, potentially resulting in diminished draft, back-puffing, and the deposition of creosote in wood-burning systems. This deposited creosote increases the risk of chimney fires. The thermal properties of ceramic contribute to efficient heat retention, minimizing these risks. For example, in colder climates, a flue constructed without proper insulation may experience significant heat loss, hindering draft establishment, especially during initial startup.
The design and installation of the ceramic flue directly affect its heat containment capabilities. Sections must be tightly fitted to prevent heat leakage through joints. Insulation surrounding the flue liner can further enhance heat retention, particularly in exterior chimneys exposed to ambient temperatures. Moreover, the thickness and composition of the material influence its insulating properties. Systems certified to meet specific thermal performance standards provide assurance of adequate heat containment under various operating conditions. Improperly sized liners or those installed without appropriate insulation may fail to maintain adequate flue gas temperatures, leading to compromised venting and reduced heating system efficiency.
In summary, heat containment is an essential attribute of a ceramic flue system. Its effectiveness dictates the system’s ability to ensure safe and efficient venting, prevent creosote buildup, and maintain optimal heating appliance performance. Understanding the principles of heat transfer and selecting and installing liners that prioritize thermal efficiency are paramount for maximizing the benefits and mitigating the risks associated with chimney operation.
3. Structural Integrity
The structural integrity of a chimney system is paramount for the safe and reliable venting of combustion byproducts. A compromised chimney poses significant risks, including structural collapse, flue gas leakage into the living space, and increased fire hazards. A sound flue lining, particularly one constructed of ceramic, is a critical element in maintaining the overall structural stability of the chimney.
- Resistance to Thermal Stress
Chimneys are subjected to extreme temperature fluctuations during heating cycles. These temperature variations induce expansion and contraction stresses within the chimney structure. A ceramic lining, with its inherent resistance to thermal shock, mitigates these stresses by providing a stable and dimensionally consistent internal surface. This stability reduces the risk of cracking and spalling in the surrounding masonry.
- Protection Against Moisture Damage
Moisture intrusion, whether from precipitation or condensation of flue gases, can severely compromise chimney integrity. Water penetration weakens mortar joints and can lead to freeze-thaw damage, accelerating deterioration. An intact ceramic liner acts as a barrier, preventing moisture from reaching the chimney’s core structure and minimizing the potential for water-related damage.
- Support for Masonry
In older chimneys, the structural integrity of the masonry may be compromised due to age, weathering, or previous damage. A properly installed ceramic liner can provide added support to the chimney structure, effectively reinforcing weakened sections and extending the chimney’s service life. The liner distributes loads more evenly, reducing stress concentrations on vulnerable areas.
- Prevention of Flue Gas Leakage
Cracks or gaps in the flue lining create pathways for flue gases to escape into the building. These gases may contain toxic compounds such as carbon monoxide. A continuous, impermeable ceramic lining ensures that flue gases are safely contained and vented to the exterior, preventing potential health hazards and structural damage caused by corrosive gases.
The aforementioned aspects highlight the indispensable role of a structurally sound flue lining in safeguarding the integrity of a chimney system. A ceramic system, when correctly specified and installed, provides a robust defense against thermal stress, moisture damage, and flue gas leakage, ensuring the long-term stability and safety of the chimney. Ignoring the importance of structural integrity in flue design and maintenance can have severe consequences, potentially endangering the occupants of the building.
4. Draft Optimization
Draft, the controlled flow of air and combustion gases within a chimney, is significantly influenced by the characteristics of the installed lining. Ceramic flue linings, owing to their smooth, consistent internal surface, promote optimal draft conditions. A properly sized and installed lining minimizes turbulence and frictional resistance, facilitating the efficient removal of combustion byproducts. Conversely, a damaged or improperly sized lining can impede draft, leading to incomplete combustion, increased creosote buildup in wood-burning systems, and the potential for dangerous backdrafting. For instance, if a lining is too large for the connected appliance, the flue gases may cool too rapidly, reducing buoyancy and hindering the upward flow. This can result in smoke and carbon monoxide entering the living space, posing a serious health risk.
The thermal properties of ceramic also contribute to draft optimization. The material’s ability to retain heat within the chimney flue helps maintain a consistent temperature differential between the flue gases and the ambient air. This temperature difference drives the natural draft process. External chimneys, particularly in colder climates, benefit significantly from ceramic linings due to their heat-retention capabilities. A cold chimney flue can inhibit draft establishment, especially during initial appliance startup. Therefore, insulation surrounding a ceramic lining can further enhance draft performance by minimizing heat loss and ensuring a consistent upward flow of gases.
In summary, draft optimization is an essential function of a well-designed chimney system, and the choice of lining material plays a crucial role in achieving optimal draft conditions. The smooth surface, appropriate sizing, and heat-retention properties of ceramic contribute to efficient venting, reduced risk of combustion byproducts entering the living space, and improved heating appliance performance. Regular inspection and maintenance of the lining are necessary to ensure continued draft optimization and safe chimney operation.
5. Combustion Safety
Combustion safety is a paramount concern in any structure utilizing fuel-burning appliances. The role of a ceramic flue lining in ensuring combustion safety is critical, as it directly impacts the containment and venting of potentially hazardous combustion byproducts.
- Prevention of Carbon Monoxide Intrusion
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and highly toxic gas produced by incomplete combustion. A compromised chimney system, characterized by cracks or deterioration, can allow CO to leak into the living space. A properly installed and maintained ceramic liner forms an impermeable barrier, preventing CO intrusion and protecting occupants from potentially fatal exposure.
- Mitigation of Chimney Fire Risk
In wood-burning systems, creosote, a flammable byproduct of incomplete combustion, accumulates within the chimney flue. If excessive creosote buildup occurs, a chimney fire can ignite, posing a significant threat to the building. The smooth surface and heat-resistant properties of a ceramic lining help minimize creosote accumulation and facilitate its removal during routine cleaning, thereby reducing the risk of chimney fires.
- Containment of High Temperatures
During combustion, flue gases can reach extremely high temperatures. A ceramic liner is designed to withstand these high temperatures without degrading or transferring excessive heat to surrounding combustible materials. This containment of high temperatures reduces the risk of ignition of adjacent building components, such as framing or insulation.
- Prevention of Acidic Condensate Damage
Combustion processes produce acidic condensates that can corrode and weaken chimney materials. A ceramic liner is resistant to these acidic compounds, preventing their penetration into the chimney structure. This resistance to corrosion preserves the structural integrity of the chimney, reducing the risk of collapse or flue gas leakage.
The connection between combustion safety and ceramic flue linings is undeniable. The liner serves as a crucial barrier against the hazards associated with fuel-burning appliances, protecting building occupants from CO poisoning, chimney fires, and structural damage. Regular inspection and maintenance of the lining are essential to ensure its continued effectiveness in maintaining combustion safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding ceramic chimney liners, providing detailed information to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of their function and application.
Question 1: What is the primary purpose of a ceramic chimney liner?
The primary purpose is to provide a protective barrier within a chimney flue, shielding the chimney structure from the corrosive byproducts of combustion, such as creosote and acids. It also ensures the safe and efficient venting of exhaust gases.
Question 2: How does a ceramic chimney liner contribute to improved heating efficiency?
By maintaining a consistent flue temperature, the liner promotes optimal draft, which in turn ensures efficient combustion and venting. This reduces heat loss through the chimney walls and minimizes the potential for backdrafting.
Question 3: What are the key advantages of ceramic over other liner materials, such as stainless steel?
Ceramic offers excellent resistance to corrosion from acidic condensates, dimensional stability at high temperatures, and a long service life when properly maintained. While stainless steel is also corrosion-resistant, ceramic provides superior insulation and thermal mass.
Question 4: How often should a ceramic chimney liner be inspected?
A comprehensive inspection should be conducted at least annually by a qualified professional. More frequent inspections may be necessary for systems subjected to heavy use or those exhibiting signs of damage.
Question 5: What are the common indicators of a failing ceramic chimney liner?
Indicators include visible cracks or spalling, evidence of water damage on the exterior of the chimney, and the presence of excessive creosote buildup in wood-burning systems. Unusual smoke patterns or backdrafting may also indicate a problem.
Question 6: Can a ceramic chimney liner be repaired, or does it always require complete replacement?
Minor cracks can sometimes be repaired using specialized refractory mortars. However, extensive damage or deterioration typically necessitates complete liner replacement to ensure continued safety and performance.
The information above provides a basic understanding. Consult with a qualified professional for specific guidance tailored to individual circumstances.
The subsequent section will explore the installation process in detail.
Ceramic Chimney Liner
This exploration has detailed the crucial role of the ceramic chimney liner in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of heating systems. The properties inherent in this material its resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, its contribution to structural integrity and optimal draft underscore its value as a protective measure against the hazards associated with combustion. The preceding information highlights the importance of selecting, installing, and maintaining this component with diligence.
Given the critical function it performs, the integrity of the liner should not be compromised. Homeowners and building professionals must remain vigilant in monitoring its condition and addressing any signs of deterioration promptly. Investing in a quality ceramic chimney liner and adhering to best practices for maintenance are essential steps toward ensuring the safety and longevity of the heating system and the well-being of building occupants.





![Why Chimney Birds Matter: [Chimney Bird] Care Tips Chimney Works – Expert Chimney Repair, Cleaning & Installation Services Why Chimney Birds Matter: [Chimney Bird] Care Tips | Chimney Works – Expert Chimney Repair, Cleaning & Installation Services](https://thechimneyworks.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-25-300x200.jpg)
