The expenditure associated with a chimney evaluation is a common inquiry among homeowners. This expense reflects the professional assessment of the chimney’s structural integrity, functionality, and safety. The price can vary based on several factors, including location, the type of inspection performed, and the complexity of the chimney system itself.
A professional evaluation offers considerable advantages. It can identify potential hazards such as creosote buildup, flue blockages, or structural damage that could lead to chimney fires or carbon monoxide leaks. Regular assessments contribute to the safety of a dwelling and its occupants. Historically, chimney inspections have been crucial in preventing property damage and ensuring the efficient operation of heating systems.
The ensuing sections will delve into the various components that influence the professional fees, different types of evaluations, and what to expect from a certified professional.
Considerations Regarding Chimney Evaluation Expenses
Prudent homeowners should carefully consider several factors to maximize the value and effectiveness of their chimney inspection expenditure. Thoughtful planning and proactive inquiry can ensure the assessment addresses critical safety and maintenance concerns.
Tip 1: Research Local Professionals: Obtain multiple quotes from certified chimney sweeps and inspection services in the area. Comparing estimates allows for a comprehensive understanding of prevailing costs and potential variations in service offerings.
Tip 2: Inquire About Certification: Verify that the chimney sweep or inspector possesses relevant certifications from reputable organizations such as the Chimney Safety Institute of America (CSIA) or the National Fireplace Institute (NFI). Certification signifies adherence to industry standards and best practices.
Tip 3: Understand the Scope of the Inspection: Clarify the type of inspection being offered (Level 1, Level 2, or Level 3) and what it entails. A Level 1 inspection is a basic visual examination, while higher-level inspections involve more in-depth assessments and may necessitate specialized equipment.
Tip 4: Schedule Inspections Regularly: A chimney should be inspected at least annually, even if it is not used frequently. Regular assessments help detect minor issues before they escalate into costly repairs or hazardous situations.
Tip 5: Document Inspection Findings: Maintain detailed records of all chimney inspections, including the date of the inspection, the inspector’s findings, and any recommended repairs or maintenance procedures. Documentation provides a valuable historical overview of the chimney’s condition.
Tip 6: Address Issues Promptly: If the inspection reveals any problems, such as creosote buildup, cracks, or damaged components, address these issues promptly. Delaying repairs can exacerbate the damage and increase the overall cost of remediation.
Tip 7: Negotiate Repair Costs: If repairs are necessary, obtain multiple quotes from qualified contractors. Negotiate repair costs and ensure that the contractor provides a detailed breakdown of the work to be performed.
Proactive management and diligent research into the cost are imperative for responsible home ownership and maintenance. These steps ensure a safe and efficiently operating chimney system.
The next section will address the long-term cost benefits in having a chimney inspection.
1. Inspection Level
The “Inspection Level” significantly influences the overall expenditure associated with a chimney assessment. Different tiers of evaluation involve varying degrees of scrutiny, time investment, and equipment utilization, thereby affecting the professional fees.
- Level 1 Inspection
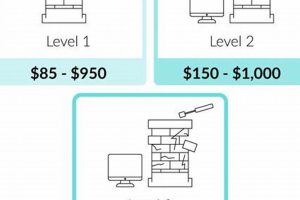
A Level 1 inspection constitutes a basic visual examination of readily accessible components of the chimney and connected appliance. It typically involves checking for obstructions and assessing the basic structural soundness of the chimney. As it requires minimal time and equipment, it is generally the least expensive type of evaluation.
- Level 2 Inspection
A Level 2 inspection is more comprehensive and is required when there are changes to the system, such as a change in fuel type or appliance replacement. It also includes a video scan of the flue. It also includes examination of accessible portions of the chimney exterior and interior, including attics, crawl spaces, and basements. Due to its more thorough nature and the potential use of specialized equipment, the cost surpasses that of a Level 1 inspection.
- Level 3 Inspection
A Level 3 inspection is the most in-depth and intrusive assessment. It is performed when a hazard is suspected and involves the removal of certain components of the building, such as walls or chimney coverings, to gain access to concealed areas. Given the extensive labor, specialized tools, and potential for property alteration, a Level 3 inspection represents the highest financial investment.
Ultimately, the necessary tier is dictated by circumstances such as system modifications, suspected damage, or adherence to safety regulations. Selecting the appropriate level ensures a cost-effective balance between thorough assessment and budgetary constraints. The expenses correlate directly to the time, tools, and intrusion needed for a full assessment.
2. Geographic Location
The “Geographic Location” exerts a demonstrable influence on the expenditure associated with a chimney inspection. Regional economic factors, such as the prevailing cost of labor, directly impact service charges. Areas with a higher cost of living generally exhibit elevated rates for professional services, including chimney assessments. Conversely, regions with lower living expenses may reflect more moderate pricing structures.
Furthermore, geographic location affects the demand for chimney services. Colder climates, where fireplaces and heating stoves are more frequently used, often experience increased demand for inspections, which can drive prices up, particularly during peak seasons. The availability of qualified professionals also varies geographically. Metropolitan areas typically have a higher concentration of certified chimney sweeps and inspectors, potentially leading to competitive pricing. Rural areas, with fewer service providers, may command higher fees due to limited competition and increased travel expenses.
In conclusion, geographic location is a critical determinant of chimney inspection expenditures. Local economic conditions, demand fluctuations driven by climate, and the availability of qualified professionals all contribute to variations in pricing. Homeowners are advised to obtain multiple quotes from local service providers to ascertain the prevailing rates and ensure cost-effective decision-making. A homeowner in New York city may encounter prices far different from those in rural Montana.
3. Chimney Condition
The pre-existing state of a chimney is a primary determinant in the pricing structure for its inspection. The complexity and time required for an assessment are directly proportional to the observable condition, potentially increasing overall professional fees.
- Creosote Buildup
Excessive creosote accumulation within the flue necessitates thorough cleaning and evaluation. Inspectors might charge additional fees to assess risks and eliminate hazardous buildup, a critical service for preventing chimney fires. The amount of creosote can dramatically influence the time and resources required for a proper inspection.
- Structural Damage
Cracks, spalling, or other forms of structural degradation require detailed evaluation to ascertain the extent of the damage and recommend appropriate repairs. Inspectors often use specialized equipment, such as cameras, to fully assess the chimney’s structural integrity, which can add to the inspection cost. The presence of damage often warrants a more detailed (Level 2 or 3) inspection.
- Presence of Obstructions
Nests, debris, or other obstructions hinder a comprehensive assessment of the chimney’s interior. Removing these blockages may require specialized tools and extra time, leading to increased labor charges. Blockages can also indicate underlying issues, such as a damaged chimney cap, which would necessitate further investigation.
- Water Damage
Signs of water intrusion, such as staining or deterioration of mortar joints, can indicate leaks that require immediate attention. Investigating the source and extent of water damage may necessitate a more invasive inspection, potentially increasing costs. Undetected leaks can lead to significant structural issues and costly repairs if left unaddressed.
The overall expenditure for a chimney assessment is significantly influenced by its initial condition. Factors such as creosote buildup, structural impairments, obstructions, and water damage all contribute to increased evaluation costs. These elements emphasize the need for regular maintenance to mitigate extensive damage and reduce inspection expenses.
4. Service Provider
The selection of a “Service Provider” is a pivotal determinant of the expense associated with a chimney evaluation. The qualifications, expertise, and business model of the chosen professional or company significantly impact the final cost.
- Certification and Expertise
Certified chimney sweeps and inspectors, particularly those holding credentials from organizations such as the Chimney Safety Institute of America (CSIA) or the National Fireplace Institute (NFI), often command higher fees. This reflects their demonstrated competence, adherence to industry standards, and commitment to ongoing education. While their services may be more expensive, they offer assurance of a thorough and accurate assessment.
- Experience and Reputation
Established service providers with extensive experience and a positive reputation may charge premium rates based on their proven track record of delivering quality services. Customer reviews, testimonials, and referrals can provide valuable insights into the reliability and expertise of a service provider. Selecting a reputable company can minimize the risk of substandard work and potentially costly errors.
- Business Model and Overhead
The operational structure and overhead costs of a service provider influence pricing. Larger companies with substantial infrastructure, marketing expenses, and administrative staff typically have higher overhead, which may be reflected in their fees. Independent contractors or smaller businesses may offer more competitive rates due to lower overhead.
- Service Inclusions and Guarantees
The scope of services included in the inspection package, as well as any guarantees or warranties offered, can affect the overall value proposition and cost. Some providers offer comprehensive packages that include cleaning, minor repairs, and detailed reports, while others offer basic inspections with additional services available at an extra cost. Guarantees or warranties provide added assurance and protection against potential issues.
The choice of service provider directly influences the final expense. Certification, experience, business model, and service inclusions all contribute to pricing variations. Prudent homeowners should carefully evaluate these factors to select a qualified and reputable professional who offers a cost-effective balance between quality and affordability. Understanding the variables in pricing helps homeowners obtain maximum value for the investment.
5. Inspection Type
The classification of an inspection directly correlates with the resources, expertise, and time invested, ultimately influencing the overall expense. Different types of assessments target specific aspects of the chimney system, demanding varying levels of scrutiny and specialized equipment.
- Visual Inspection
A visual inspection, typically the least expensive, involves a basic examination of accessible components for obvious signs of damage or deterioration. While cost-effective, its limited scope might not detect concealed issues, potentially leading to future, more expensive repairs. This type is suitable for chimneys in good condition with a consistent maintenance history.
- Video Scan Inspection
Employing specialized camera equipment to examine the flue’s interior, this method offers a more comprehensive assessment than a visual inspection. The added technology increases the price but allows for the detection of cracks, blockages, or deterioration that would otherwise remain hidden. This inspection type is often recommended for older chimneys or those suspected of having internal damage.
- Real Estate Inspection
Frequently conducted during property transactions, this assessment aims to identify any immediate safety hazards or code violations. The cost falls between that of a standard visual and a video scan inspection, focusing primarily on functionality and compliance. Lenders may require this assessment before approving a mortgage.
- Problem-Specific Inspection
Targeted inspections address specific issues such as drafting problems, smoke back-puffing, or suspected leaks. The price varies depending on the complexity of the problem and the diagnostic techniques required. This type can range from moderately to significantly more expensive, particularly if it involves specialized testing or equipment.
In summary, the type of inspection selected dictates the depth and breadth of the assessment, directly impacting the total expense. Homeowners should carefully consider their specific needs and circumstances when determining the appropriate inspection to ensure a cost-effective balance between thorough evaluation and budgetary considerations. Different types ensure the integrity of different sections of a chimney.
6. Accessibility
The ease with which a chimney can be accessed plays a considerable role in determining the expenses linked to its inspection. Difficulties in reaching the chimney’s components directly translate to increased labor hours, specialized equipment requirements, and potential safety risks for the inspector, all of which contribute to a higher service fee.
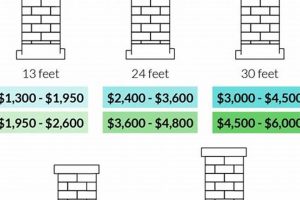
Several factors can impede accessibility. Chimneys situated on steep or high-pitched roofs necessitate the use of specialized ladders, scaffolding, or even aerial lifts, adding to the equipment costs. Dense foliage surrounding the chimney can obstruct access and require clearing, further increasing labor time. Interior accessibility can also be a factor; confined attic spaces, blocked access points, or the presence of hazardous materials like asbestos may necessitate additional precautions and specialized handling, impacting the final charges. For instance, a chimney located on a three-story house with a steeply sloped roof and surrounded by overgrown trees will invariably incur a higher inspection cost than a chimney on a single-story structure with easy roof access.
Consequently, accessibility stands as a noteworthy variable influencing chimney evaluation expenditure. Clear communication with the service provider regarding potential access challenges is advisable, allowing for accurate cost estimation and appropriate resource allocation. Addressing accessibility issues proactively, such as trimming overgrown vegetation, can potentially mitigate inspection costs and facilitate a safer, more efficient assessment.
7. Additional Services
The final expenditure for a chimney evaluation is frequently affected by the incorporation of extra services beyond the standard assessment. While a core inspection focuses on identifying potential issues and ensuring safe operation, homeowners often opt for supplementary offerings that enhance the system’s functionality and longevity, thereby impacting the overall cost.
Chimney cleaning represents a commonly requested additional service. Creosote and soot buildup, resulting from combustion byproducts, can pose significant fire hazards and impede proper drafting. Professional cleaning services, employing specialized tools and techniques, remove these accumulations, improving efficiency and safety. Similarly, minor repairs, such as patching small cracks in the mortar or replacing damaged flue tiles, address minor structural issues identified during the inspection. These proactive measures prevent further deterioration and avoid more costly repairs down the line. Another example includes the installation of chimney caps or animal guards, protecting the chimney from water damage and wildlife intrusion. While these add to the initial expense, they deliver long-term cost benefits by preventing significant damage.
The inclusion of additional services is a crucial aspect of the inspection’s financial implications. Homeowners should carefully consider their specific needs and priorities when selecting these options, balancing the immediate expenditure with the potential for long-term savings and enhanced safety. A comprehensive understanding of the various services available and their associated costs empowers informed decision-making, ensuring that the chimney inspection represents a worthwhile investment in property maintenance and fire prevention. These actions ensure the maximum value for the homeowner, alongside peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Chimney Inspection Expenses
The following questions and answers address common inquiries about the financial aspects of chimney evaluations, providing clarity and guidance for homeowners.
Question 1: What is the typical price range for a standard chimney inspection?
The expenditure for a standard chimney assessment generally falls within a range of $89 to $379. This range is subject to variance contingent upon location, type of inspection, and condition of the chimney.
Question 2: Does the cost differ significantly between a Level 1 and Level 2 inspection?
Yes, the cost differential can be substantial. A Level 1 inspection, being a basic visual assessment, is less expensive. A Level 2 inspection involves a more thorough examination, often requiring specialized equipment like cameras, resulting in a higher fee.
Question 3: Are there additional charges beyond the initial inspection fee?
Potentially, yes. Additional charges may apply for services such as chimney cleaning, minor repairs, or the removal of obstructions identified during the evaluation. These costs should be clarified before the commencement of any work.
Question 4: How often should a chimney be inspected to ensure cost-effectiveness?
Annual inspections are generally recommended, even if the chimney is not used frequently. Regular assessments can identify minor issues before they escalate into costly repairs, thus promoting long-term cost savings.
Question 5: Does the age of the chimney influence the inspection cost?
The age of a chimney can indirectly affect the assessment expenses. Older chimneys are often more prone to structural damage or deterioration, necessitating a more thorough and potentially more expensive inspection.
Question 6: Is it possible to negotiate the inspection price with the service provider?
Negotiation may be possible, particularly if multiple service providers are available in the area. Obtaining quotes from several companies and comparing their offerings can provide leverage for negotiating a more favorable price. However, prioritize qualifications and reputation over solely focusing on the lowest cost.
Understanding these aspects of chimney evaluation expenses ensures informed decisions. Proactive inquiry and careful planning result in cost-effective assessments and long-term savings.
The following section will discuss the benefits of having a chimney inspection
Concluding Remarks on Chimney Inspection Costs
This analysis has explored the factors determining how much a chimney inspection costs, emphasizing the influence of inspection level, geographic location, chimney condition, service provider qualifications, inspection type, accessibility, and additional services. Understanding these variables empowers homeowners to make informed decisions regarding chimney maintenance and safety.
Investing in regular, professional chimney inspections is not merely an expense, but a proactive measure towards ensuring the safety of a dwelling and its occupants. Prioritizing chimney maintenance prevents potential hazards and costly repairs, securing a safer and more secure living environment. Homeowners should regard professional chimney inspections as an essential element of responsible homeownership.