The expense associated with fixing a protective covering for a flue is a significant consideration for homeowners. This expenditure encompasses labor and materials required to restore a functional barrier against weather, debris, and animals from entering the chimney. For instance, replacing a rusted or damaged screen on this covering contributes to the overall price.
Maintaining a properly functioning flue protector offers considerable advantages. It prevents costly water damage to the chimney structure, inhibits nesting by birds and other wildlife, and reduces the risk of fire caused by creosote buildup or debris entering the flue. Historically, these coverings were simpler structures, but modern iterations offer enhanced protection and longevity, making timely maintenance and occasional replacement crucial investments.
Understanding the factors influencing the price of these repairs is essential for budgeting and making informed decisions. The subsequent sections will explore these factors in detail, including the type of damage, materials used, accessibility, and regional labor rates. These aspects directly impact the final sum required for ensuring a properly functioning chimney system.
The following guidance aims to provide property owners with essential advice regarding budgeting for and managing the fiscal aspects of maintaining a protective chimney component. Employing these strategies can assist in controlling expenses and ensuring the longevity of the chimney system.
Tip 1: Obtain Multiple Estimates: Secure quotations from several qualified chimney service providers before committing to any repairs. This allows for price comparison and ensures a competitive rate for the work performed.
Tip 2: Address Damage Promptly: Delaying repairs can exacerbate existing issues, leading to more extensive and costly solutions in the future. Early intervention is often the most economical approach.
Tip 3: Inquire About Material Options: Different materials offer varying degrees of durability and resistance to the elements. Discuss the pros and cons of each option with the contractor to select the most cost-effective choice for the specific application.
Tip 4: Verify Contractor Credentials: Ensure the chosen contractor possesses the necessary licenses, insurance, and experience to perform the work safely and effectively. This mitigates the risk of substandard workmanship and potential liabilities.
Tip 5: Schedule Regular Inspections: Periodic chimney inspections can identify potential problems before they escalate, preventing the need for extensive repairs or replacements. Preventative maintenance is a sound investment.
Tip 6: Understand Warranty Coverage: Inquire about warranties offered on both materials and labor. A comprehensive warranty provides protection against defects and ensures recourse in the event of premature failure.
Effectively managing expenses related to flue covering maintenance requires proactive planning, informed decision-making, and a commitment to preventative measures. These strategies can help homeowners maintain a safe and efficient chimney system while controlling costs.
The subsequent sections will address specific factors that influence pricing and explore common repair scenarios in greater detail, providing a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
1. Damage Extent
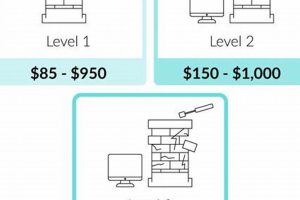
The degree of impairment directly correlates with the expense incurred for flue protector restoration. Minor corrosion, such as surface rust or a few loosened fasteners, typically necessitates minimal intervention and consequently, lower associated charges. This might involve cleaning, localized patching, or tightening of connections. Conversely, severe structural compromise, including extensive rust-through, significant physical deformation due to impact, or complete disintegration, demands full replacement. A full replacement involves material procurement, demolition of the existing compromised protector, and installation of a new unit. This operation escalates both material and labor budgets.
Real-world illustrations highlight this relationship. A flue protector exhibiting minor weathering might only require cleaning and sealant application, costing a comparatively modest sum. However, a unit suffering extensive storm damage, where the protective mesh is torn and the support structure bent, necessitates complete removal and installation of a new protector. Consequently, the cost significantly rises due to the increased labor hours and material expenses. The critical evaluation of the damage extent is pivotal in accurately predicting and managing the financial burden of flue protector maintenance.
In summary, the breadth and severity of damage sustained by a flue protector are primary determinants of restoration expenditures. Accurate assessment allows for appropriate repair strategies, ranging from minor maintenance to complete replacement. This understanding ensures efficient resource allocation and cost-effective preservation of the chimney system’s integrity. Ignoring minor damage leads to escalating problems; thus, prioritizing early evaluation and repair mitigates future financial strain.
2. Material Choice
The selection of materials directly influences the final expenditure for flue protector repair or replacement. The cost of the material itself, its longevity, and the labor involved in its installation contribute to the overall financial burden. Inexpensive options, such as galvanized steel, present a lower initial investment, but their susceptibility to rust and corrosion shortens their lifespan, potentially leading to more frequent replacements. This results in repeated labor charges and material procurement expenses over time. Higher-grade materials, such as stainless steel or copper, offer superior resistance to environmental degradation and extend the protector’s service life. For example, a stainless-steel flue protector, while costing more upfront, can withstand decades of exposure to harsh weather conditions, minimizing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Copper, known for its exceptional durability and aesthetic appeal, represents the highest initial investment but provides unparalleled longevity and resistance to corrosion. The initial financial outlay for material selection should be evaluated against the long-term cost implications of maintenance and replacement.
Beyond material cost, installation complexity also impacts the overall expenditure. Some materials, such as lightweight aluminum, are easier to handle and install, potentially reducing labor hours. However, their reduced structural integrity makes them vulnerable to damage from strong winds or falling debris. Heavier, more robust materials often require specialized tools and expertise for proper installation, increasing labor costs. For instance, installing a custom-fabricated copper flue protector necessitates skilled craftsmanship and precision fitting, adding to the overall price. Moreover, the compatibility of the chosen material with existing chimney components influences the installation process and associated costs. A mismatched material can lead to accelerated corrosion or structural issues, necessitating additional modifications or repairs. Therefore, selecting a material compatible with the chimney’s construction and designed for the local climate is essential for minimizing long-term expenses.
In conclusion, the material choice for flue protector maintenance is a critical determinant of the overall expenditure. Balancing initial investment with long-term durability, resistance to environmental factors, and installation complexity is essential for cost-effective chimney management. While lower-cost materials may seem attractive initially, their reduced lifespan and potential for premature failure can lead to increased long-term expenses. Prioritizing higher-quality, durable materials and professional installation services ensures the protector’s longevity and performance, minimizing the need for frequent repairs or replacements and preserving the integrity of the entire chimney system. The challenge lies in finding the optimal balance between upfront cost and long-term value, tailored to the specific needs and conditions of the property.
3. Accessibility Hurdles
The ease with which a chimney can be accessed significantly impacts the overall expense of flue protector maintenance. Complex accessibility translates to increased labor hours and potentially specialized equipment, thereby elevating the final cost.
- Chimney Height
Elevated chimneys necessitate the use of specialized scaffolding or aerial lifts to reach the flue protector. This specialized equipment incurs rental fees and demands experienced operators, adding to the labor costs. Consider a three-story house compared to a single-story ranch; the former will invariably cost more to service.
- Roof Pitch and Condition
Steep roof pitches present safety challenges for technicians, requiring additional safety measures and potentially specialized climbing gear. Fragile or deteriorated roofing materials may restrict access or necessitate temporary repairs before work can commence. Technicians may need to reinforce the roof before accessing the chimney, increasing costs.
- Obstructions
Overhanging trees, power lines, or other structures surrounding the chimney can impede access, requiring trimming or temporary relocation of these obstructions. Limited space around the base of the chimney may also hinder the placement of ladders or scaffolding. If a tree is dangerously close to the chimney, that has to be trimmed before any work takes place, incurring more fees.
- Interior Access Limitations
In some cases, accessing the flue from within the building (e.g., through an attic hatch) might be necessary. Limited attic space, structural impediments, or the presence of insulation can complicate access, adding time and effort to the repair process. The technician has to climb up the attic, which leads to safety hazards. This increase the cost and the overall work required.
Accessibility hurdles represent a substantial variable in determining flue protector maintenance expenses. These challenges not only inflate labor costs but also demand specialized equipment and safety precautions. Property owners should recognize that addressing accessibility concerns prior to engaging a contractor can potentially mitigate the overall financial impact. Clear communication and collaboration with the contractor regarding existing accessibility limitations are essential for accurate cost estimations and efficient project execution.
4. Regional Labor Rates
The geographical location of a property exerts a significant influence on the expenditure for flue protector maintenance, primarily due to variations in regional labor rates. Labor constitutes a substantial portion of the total associated costs, and differences in prevailing wages for skilled tradespeople directly impact the financial burden. Areas with a higher cost of living and increased demand for skilled labor generally exhibit elevated rates, translating to increased maintenance charges. For example, the hourly rate for a qualified chimney technician in a major metropolitan area can be substantially higher than that in a rural region. Consequently, the same flue protector repair may incur significantly different expenses based solely on location.
The effect of regional labor rates extends beyond hourly wages. It encompasses factors such as insurance premiums, payroll taxes, and overhead costs, which are often correlated with the cost of doing business in a particular region. Densely populated urban areas, characterized by higher operating expenses for businesses, typically reflect these costs in their service fees. Conversely, regions with lower operating expenses and less stringent regulatory requirements may offer more competitive rates. The supply and demand of qualified technicians also play a role. Areas with a limited pool of experienced professionals often experience higher labor costs due to increased competition for their services. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for accurate budgeting and cost comparison when seeking flue protector maintenance.
In conclusion, regional labor rates represent a pivotal factor influencing the expenditure for flue protector maintenance. Property owners must acknowledge these geographical variations when obtaining estimates and comparing service providers. Factors such as the cost of living, demand for skilled labor, and local business expenses contribute to the disparity in rates. Recognizing this influence allows for informed decision-making and realistic expectations regarding the financial implications of maintaining a chimney system. A thorough investigation of local market conditions is prudent for effectively managing costs and securing optimal value for flue protector repairs.
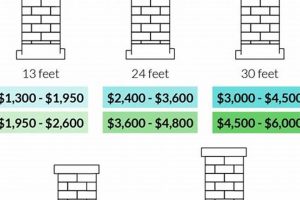
5. Chimney height
The vertical dimension of a chimney significantly influences the expenditure associated with flue protector repair. This is due to the augmented complexity and resources required to access and service elevated structures.
- Increased Labor Hours
Greater chimney height necessitates more time for technicians to ascend, descend, and maneuver around the structure. This increased labor time directly translates into higher labor costs. For instance, repairing a protector on a three-story building invariably demands more labor hours than one on a single-story dwelling.
- Specialized Equipment Requirements
Tall chimneys frequently necessitate the use of specialized equipment such as scaffolding, aerial lifts, or extended ladders. The rental or operational costs of such equipment are added to the overall project expenditure. For example, a chimney exceeding 30 feet often requires an aerial lift, incurring daily rental fees.
- Enhanced Safety Protocols
Working at elevated heights demands stringent safety protocols, including harnesses, safety lines, and potentially additional personnel for monitoring and support. These safety measures contribute to the total project cost by increasing labor needs and equipment requirements. Risk mitigation measures are vital at such heights.
- Material Handling Challenges
Transporting materials, such as replacement protectors or tools, to the top of a tall chimney presents logistical challenges. This may require hoisting equipment or multiple trips, adding to the labor and time required to complete the repair. The process is significantly complicated by the height.
These factors collectively underscore the direct relationship between chimney height and the expense of flue protector maintenance. Elevated chimneys require increased labor, specialized equipment, enhanced safety measures, and logistical solutions for material handling, all contributing to higher overall expenditure.
6. Contractor Experience
The proficiency of the professional engaged to undertake flue protector maintenance exerts a direct influence on the overall expenditure. Contractor experience acts as a determinant of efficiency, precision, and long-term reliability, all of which affect the ultimate investment. An inexperienced contractor might require more labor hours to diagnose and rectify issues, potentially misidentifying problems or implementing ineffective solutions. This inefficiency translates to increased labor costs and the possibility of recurring problems that necessitate repeated repairs. Conversely, a seasoned professional, equipped with extensive knowledge and practical skill, can swiftly and accurately assess the situation, implementing effective and durable repairs in a timely manner. For example, an experienced technician can promptly identify subtle signs of chimney deterioration that a novice might overlook, addressing minor issues before they escalate into costly problems. Furthermore, expertise often leads to better material selection and application techniques, ensuring the longevity of the repair and minimizing the risk of future expenses. A contractor with years of experience knows which materials best withstand the local climate and can properly install them to maximize their lifespan.
The practical significance of engaging an experienced contractor extends beyond immediate repair costs. A skilled professional is more likely to adhere to industry best practices and building codes, ensuring the safety and structural integrity of the chimney system. Failure to comply with these standards can result in costly fines, legal liabilities, or even hazardous conditions. Furthermore, experienced contractors often possess the necessary insurance coverage and licenses to protect homeowners from potential damages or injuries that may occur during the repair process. For instance, if a contractor without proper insurance damages the roof during a flue protector replacement, the homeowner could be held liable for the repair costs. Selecting a contractor with a proven track record and demonstrable expertise mitigates these risks, providing peace of mind and potentially saving considerable expense in the long run. An experienced contractor also has a network of suppliers, which may give them access to better material prices, which they can pass down to their clients.
In conclusion, while the allure of lower initial bids from less experienced contractors may be tempting, the long-term benefits of engaging a seasoned professional often outweigh the perceived cost savings. Contractor experience directly impacts the efficiency, precision, and safety of flue protector maintenance, influencing the overall expenditure and the long-term performance of the chimney system. Prioritizing expertise and demonstrable experience ensures effective and durable repairs, mitigates potential risks, and ultimately safeguards the investment in the property. The slightly higher cost of an experienced professional is often an investment rather than simply an expense.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns regarding the expenditure associated with maintaining or replacing flue protectors. The information provided aims to clarify factors influencing costs and provide a basis for informed decision-making.
Question 1: What constitutes the primary determinants of the final price for flue protector maintenance?
The price is influenced by the extent of damage, materials selected, accessibility challenges, regional labor rates, and the qualifications of the service provider. Each of these elements contributes to the overall expenditure.
Question 2: Is delaying flue protector maintenance a viable cost-saving strategy?
Delaying maintenance is generally not advisable. Neglecting minor damage can lead to more extensive and costly repairs in the future. Early intervention is typically more economical.
Question 3: How frequently should flue protectors undergo inspection?
Annual inspections are recommended to identify potential problems before they escalate. Regular inspections allow for timely maintenance and can prevent the need for major repairs.
Question 4: Are there specific materials that offer superior cost-effectiveness for flue protectors?
Stainless steel represents a balance between initial cost and long-term durability. While more expensive than galvanized steel, stainless steel offers enhanced resistance to corrosion and extends the protector’s lifespan.
Question 5: Do all chimney service providers offer comparable pricing for similar repairs?
Pricing can vary significantly between providers due to differences in overhead costs, labor rates, and service quality. Obtaining multiple estimates is essential for identifying a competitive and reputable contractor.
Question 6: Does the presence of a warranty on flue protector repairs offer financial protection?
A comprehensive warranty on both materials and labor provides financial protection against defects and premature failure. Verifying warranty terms before commencing repairs is prudent.
In summary, understanding the factors influencing flue protector expenditures and adopting a proactive approach to maintenance can help property owners manage costs effectively. Regular inspections, timely repairs, and informed material selection are essential for preserving the integrity of the chimney system.
The subsequent section will address strategies for minimizing maintenance expenses and maximizing the lifespan of flue protectors.
Conclusion
This exploration has detailed the multifaceted nature of expenditures associated with maintaining a flue protector. Key factors, including damage extent, material choice, accessibility, regional labor rates, chimney height, and contractor experience, collectively determine the overall cost. A comprehensive understanding of these elements empowers property owners to make informed decisions and budget effectively for essential chimney maintenance.
Proper maintenance and timely intervention are crucial for preserving the structural integrity of a chimney system and mitigating potentially significant expenses. Neglecting minor issues can lead to escalated problems and more costly repairs in the future. Vigilance and proactive engagement with qualified professionals are essential for safeguarding property and ensuring the long-term performance of the chimney.