A component employed in venting systems, particularly those connected to heating appliances, modifies the height of a flue. This addition is often cylindrical or rectangular and constructed from materials such as stainless steel or galvanized steel, designed to withstand high temperatures and corrosive byproducts of combustion. As an example, the installation of a wood-burning stove in a home may necessitate the use of this supplementary segment to ensure proper draft and efficient exhaust of smoke and gases.
Proper functioning of a venting system is critical for safety and efficiency. Extending the flue can improve draft, preventing backdrafting of dangerous gases like carbon monoxide into the living space. This improvement in draft also contributes to more complete combustion within the appliance, leading to increased heating efficiency and reduced creosote buildup. Historically, the need for flue modifications has been recognized as buildings have changed, appliance technology has evolved, and local building codes have been implemented to protect occupants.
The subsequent sections will delve into various aspects including the selection, installation, and maintenance considerations related to these components. Furthermore, the discussion will address regulatory compliance and potential issues that may arise during use.
Essential Guidance
The following recommendations address crucial aspects of dealing with vertical flue extensions, ensuring safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Tip 1: Evaluate Draft Requirements: Prior to installation, calculate the necessary effective height based on appliance specifications, local building codes, and environmental factors. Insufficient height can lead to backdrafting and inefficient combustion.
Tip 2: Select Appropriate Materials: Choose construction materials rated for the specific appliance and fuel type. For example, a high-efficiency furnace requires stainless steel due to its acidic exhaust, whereas a wood-burning appliance may tolerate galvanized steel.
Tip 3: Ensure Proper Sealing: All joints and connections must be sealed with high-temperature sealant approved for venting systems. Improper sealing can allow flue gases to escape, posing a health hazard.
Tip 4: Comply with Local Codes: Familiarize with and adhere to all local building codes and regulations regarding flue height, clearances, and materials. Failure to comply can result in fines or mandatory remediation.
Tip 5: Inspect Regularly: Conduct routine inspections for signs of corrosion, damage, or creosote buildup. Address any issues promptly to prevent system failure and potential hazards.
Tip 6: Professional Installation Recommended: While DIY installation may seem tempting, engaging a qualified professional installer ensures correct application, code compliance, and overall safety.
Tip 7: Address Wind Effects: In areas prone to high winds, consider installing a wind cap or other device to prevent downdrafts that can negatively impact appliance performance. Consult with a professional for optimal selection.
Adherence to these guidelines minimizes risks associated with modified venting systems. Correct implementation enhances appliance performance, ensures occupant safety, and avoids costly future repairs.
The subsequent segment of this document provides details about potential problems and their effective solutions.
1. Draft Improvement
Effective venting systems rely on sufficient draft, a phenomenon that facilitates the upward flow of combustion byproducts through the flue. Insufficient draft leads to issues such as backdrafting, where dangerous gases like carbon monoxide enter the living space, and incomplete combustion, resulting in reduced heating efficiency and increased creosote buildup. A vertical flue extension directly addresses this deficiency by increasing the overall height of the venting system. This augmentation enhances the pressure differential between the appliance and the outside atmosphere, thereby promoting stronger draft. For instance, a wood-burning stove situated in a valley where surrounding terrain obstructs natural airflow may require such an addition to achieve adequate draft.
The improvement in draft achieved through the application of a vertical extension is not merely a matter of height. Proper selection of materials and adherence to installation best practices are crucial. A smooth interior surface reduces frictional resistance, further enhancing airflow. Additionally, the diameter of the extension must be appropriately sized to maintain consistent flow velocity. A real-world example involves instances where homeowners install an extension of an incorrect diameter, resulting in diminished, rather than improved, draft. Such outcomes underscore the significance of professional consultation during the design and installation process.
In summary, extensions are vital components for optimizing draft in venting systems. This enhancement directly impacts safety, efficiency, and the longevity of heating appliances. While the basic principle is straightforward, achieving optimal results requires careful consideration of various factors, including appliance specifications, environmental conditions, and adherence to relevant codes. Therefore, a thorough understanding of these elements, coupled with expert guidance, is essential for ensuring satisfactory and safe performance.
2. Material Compatibility
Material compatibility is a paramount consideration in the context of vertical flue extensions. The selected material must withstand the specific conditions within the venting system to ensure safety, longevity, and efficient operation. Failure to account for material properties can result in corrosion, structural failure, and the leakage of harmful combustion byproducts.
- Corrosion Resistance
Different fuel types produce exhaust gases with varying chemical compositions. High-efficiency gas furnaces generate acidic condensates that rapidly corrode materials like galvanized steel. In such instances, stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant alloys are essential. Wood-burning appliances, while producing less acidic exhaust, still create corrosive compounds, necessitating careful selection. Neglecting corrosion resistance leads to premature degradation and potential system failure.
- Temperature Tolerance
Venting systems experience significant temperature fluctuations, particularly during appliance start-up and shut-down. Materials used in flue extensions must maintain their structural integrity across this range. Excessive heat can cause warping, cracking, or even melting, compromising the system’s ability to contain and vent gases safely. A real-world scenario involves the use of PVC piping (intended for plumbing) in a venting application, resulting in catastrophic failure due to heat exposure.
- Expansion and Contraction
Thermal expansion and contraction rates vary among different materials. When dissimilar materials are joined in a venting system, differential expansion can lead to stress at the connection points, potentially causing leaks or structural damage. For instance, connecting a cast iron appliance outlet directly to a galvanized steel extension without a suitable transition piece can create such issues. Proper design incorporates flexible connectors or expansion joints to accommodate these movements.
- Fuel Type Specificity
Materials must be specifically certified and rated for the intended fuel type. Using components designed for gas appliances with solid fuel systems, or vice versa, presents substantial risks. Solid fuel systems, for example, require higher temperature ratings than many gas appliance systems. Deviation from approved fuel-specific materials can invalidate warranties and jeopardize homeowner safety.
These material compatibility considerations directly impact the performance and safety of vertical flue extensions. Selecting the appropriate materials for the appliance, fuel type, and operating conditions is crucial to ensure a long-lasting and reliable venting system, thus highlighting the need for careful evaluation and professional guidance in the selection process.
3. Secure Connections
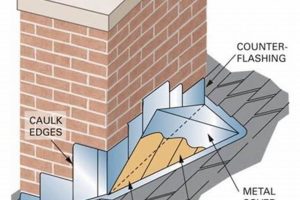
The integrity of a vertical flue extension relies heavily on the establishment of secure connections between individual components. These connections form a critical line of defense against the leakage of harmful combustion byproducts and the ingress of external elements that could compromise system performance. Consequently, the methods and materials employed in creating these joints directly influence the safety and effectiveness of the entire venting apparatus.
- Joint Integrity and Gas Leakage
Inadequate sealing or loose connections provide pathways for flue gases, including carbon monoxide, to escape into the surrounding environment. This poses a significant health hazard to building occupants. Secure connections, achieved through proper sealing techniques and appropriately sized fasteners, prevent such leakage, maintaining a safe indoor air quality. Examples include the use of high-temperature sealant at each joint and the application of locking bands or screws to maintain a tight fit. A compromised connection could lead to carbon monoxide poisoning, emphasizing the need for meticulous installation practices.
- Structural Stability and Wind Resistance
Vertical flue extensions are exposed to external forces, notably wind. Secure connections contribute to the overall structural stability of the system, enabling it to withstand wind loads without separating or collapsing. Properly fastened joints prevent sections from becoming dislodged during high winds, which could damage the venting system and potentially create hazards for nearby structures or individuals. For instance, coastal regions with frequent storms necessitate particularly robust connections to prevent wind-related failures.
- Corrosion Prevention at Joints
Connection points are often vulnerable to accelerated corrosion due to moisture accumulation or electrochemical reactions between dissimilar metals. Secure connections, achieved through proper material selection and the use of corrosion-resistant fasteners, minimize these risks. For example, stainless steel connectors are often preferred in systems handling corrosive exhaust gases to prevent premature degradation at the joints. Proper joint design can also minimize the trapping of moisture that could promote corrosion.
- Compliance with Installation Standards
Building codes and manufacturer specifications mandate specific connection methods and materials for vertical flue extensions. Secure connections, installed in accordance with these requirements, ensure that the system meets safety standards and performs as intended. Failure to comply with these standards can result in inspection failures, fines, or even legal liabilities. Adherence to industry best practices, such as using listed components and following manufacturer instructions, is crucial for achieving compliant and reliable connections.
In conclusion, the implementation of secure connections within a vertical flue extension is not merely a matter of assembly, but rather a critical aspect of ensuring safety, structural integrity, and regulatory compliance. These connections safeguard against gas leakage, withstand environmental forces, prevent corrosion, and adhere to established standards. Their proper execution directly translates to a reliable and safe venting system, underlining their importance in overall system performance.
4. Code Compliance
Code compliance is inextricably linked to the installation and modification of venting systems, including those incorporating a vertical flue extension. Building codes, developed and enforced by local jurisdictions, establish minimum standards for safety and performance. These regulations dictate permissible materials, dimensional requirements, installation practices, and clearance distances for venting systems. Non-compliance can result in failed inspections, mandatory remediation, and potential legal repercussions. For example, a common code requirement specifies the minimum height a flue must extend above the roofline to ensure adequate draft and prevent downwash, a condition where wind forces exhaust gases back into the building. Neglecting this requirement necessitates a vertical extension to achieve code conformity.
The application of code compliance to a vertical flue extension encompasses multiple facets. It involves ensuring that the extension itself is constructed from materials approved for the specific fuel being vented (e.g., stainless steel for high-efficiency gas appliances). Furthermore, the installation must adhere to prescribed clearances from combustible materials to prevent fire hazards. The extension’s height must comply with minimum standards relative to nearby structures and terrain features. For instance, if a neighboring building is taller, the flue must extend above that structure to mitigate the risk of exhaust gases entering the adjacent property. Building codes often reference industry standards, such as those promulgated by organizations like the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), to provide detailed guidance on acceptable practices. These examples emphasize the proactive approach required to comply with all prevailing standards before, during, and after installation.
In summary, code compliance is not merely a procedural formality but a critical component of a safe and effective venting system incorporating a vertical flue extension. It provides a framework for ensuring that the system functions as intended, minimizes risks to occupants and property, and conforms to established industry best practices. While navigating the complexities of building codes can be challenging, adherence to these regulations is paramount to achieving a reliable and compliant venting system. Neglecting code compliance can have significant financial and safety implications, underscoring the importance of seeking expert guidance and adhering to all applicable regulations.
5. Regular Inspection
The operational lifespan and safety of a vertical flue extension are intrinsically linked to the implementation of a regular inspection regime. These extensions, subjected to harsh environmental conditions and corrosive byproducts of combustion, require periodic evaluation to identify and address potential issues before they escalate into significant hazards. The absence of routine inspections can lead to undetected deterioration, compromising structural integrity and potentially causing the leakage of harmful gases into occupied spaces. For instance, creosote buildup within the extension, particularly in wood-burning systems, can create a fire hazard if not removed during regular cleaning. Inspection frequency depends on the type of appliance, fuel used, and local regulations, often necessitating annual assessment at a minimum.
Regular inspection of a vertical flue extension encompasses several critical areas. Inspectors assess for signs of corrosion, such as rust or pitting, particularly at joints and seams. The structural integrity of the extension is evaluated, checking for any warping, cracking, or displacement. The condition of any weatherproofing elements, such as rain caps or flashing, is assessed to ensure they are functioning effectively in preventing water ingress. Creosote buildup is measured in solid fuel systems, and appropriate cleaning measures are undertaken. Blockages caused by debris or animal nests are identified and removed to maintain unimpeded airflow. A practical example involves inspecting and clearing obstructions in the extension to maintain proper ventilation, preventing carbon monoxide backflow into the home. These routine check-ups ensure the continued safe and efficient operation of the chimney system.
In conclusion, the routine inspection of vertical flue extensions is not a discretionary activity but rather a fundamental component of responsible system maintenance. The detection and remediation of potential problems, achieved through regular assessment, contribute significantly to the prevention of hazards, the extension of system lifespan, and the maintenance of safe indoor air quality. Overlooking this aspect introduces substantial risks, underscoring the necessity of incorporating regular inspection into the long-term management of any venting system equipped with an extension.
6. Professional Installation
The correct integration of a vertical flue extension is directly contingent upon professional installation. Inexperienced handling can lead to improper assembly, material selection errors, and a failure to meet mandatory safety codes. The consequence of these errors can range from reduced heating efficiency and premature system failure to far more serious outcomes, including carbon monoxide leaks and structural fires. For instance, selecting the wrong type of sealant for high-temperature environments can result in joint failures and exhaust gas leaks, a hazard easily avoided with professional expertise. The absence of a qualified installer often results in an inadequate system, creating potential dangers and incurring added remediation costs.
Professional installers possess specialized knowledge regarding applicable building codes, material compatibility, and venting system design. They can accurately assess the specific needs of a given installation, taking into account factors such as appliance type, fuel source, and local environmental conditions. This comprehensive understanding facilitates the selection of appropriate components and the implementation of installation techniques that ensure optimal performance and safety. For instance, a professional will correctly determine the necessary height for the extension to achieve proper draft, a calculation often overlooked by unqualified installers. Furthermore, they possess the tools and equipment necessary to execute the installation with precision and adherence to safety protocols. These resources ensure a proper and enduring installation.
In summary, professional installation is not merely a recommended practice but a fundamental requirement for ensuring the safe and effective utilization of a vertical flue extension. The intricacies of venting system design, code compliance, and material compatibility demand specialized expertise. Entrusting the installation to qualified professionals minimizes risks, optimizes system performance, and safeguards against potential hazards, representing a prudent investment in long-term safety and efficiency.
7. Wind Mitigation
Wind exerts a significant influence on the performance of venting systems, and mitigating its adverse effects is often a crucial consideration when employing a vertical flue extension. High winds can induce downdrafts, reversing the intended flow of combustion byproducts and forcing them back into the dwelling. This phenomenon not only reduces heating efficiency but also poses a serious health risk due to the potential introduction of carbon monoxide and other harmful gases. Therefore, wind mitigation strategies frequently necessitate the use of specialized components in conjunction with flue extensions to counteract these negative pressures. For instance, a chimney cap designed with wind-resistant features can effectively shield the flue opening from prevailing winds, preventing downdrafts.
Flue extensions, by increasing the height of the venting system, can inadvertently exacerbate wind-related issues if not properly designed. A taller flue presents a larger surface area for wind to act upon, potentially increasing the likelihood of downdrafts. Consequently, wind mitigation becomes an integral consideration in the design and implementation of flue extensions. Techniques such as employing aerodynamic caps, strategically positioning the flue exit relative to surrounding structures, or incorporating windbreaks can significantly reduce the impact of wind forces. In coastal regions or areas prone to high winds, these considerations are especially critical. A chimney located on the windward side of a building, for example, requires robust wind mitigation measures to ensure reliable venting.
Effective wind mitigation, when coupled with a vertical flue extension, ensures a safer and more efficient heating system. Recognizing the interplay between wind forces and flue design is essential for preventing downdrafts, optimizing combustion, and safeguarding building occupants from hazardous gases. The integration of appropriate wind mitigation strategies represents a practical investment in both performance and safety, demonstrating a comprehensive approach to venting system design.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the purpose, installation, and maintenance of vertical flue extensions.
Question 1: What is the primary function of a chimney extender?
The primary function is to increase the height of a venting system, thereby improving draft and facilitating the safe and efficient expulsion of combustion byproducts. This can mitigate issues like backdrafting and incomplete combustion.
Question 2: When is a chimney extender typically required?
A vertical flue extension is typically required when the existing flue height is insufficient to create adequate draft, when local building codes mandate a specific height, or when nearby obstructions interfere with proper venting.
Question 3: What materials are suitable for a chimney extender?
Suitable materials depend on the fuel type and appliance. Stainless steel is often recommended for high-efficiency gas appliances due to its resistance to acidic condensates. Galvanized steel may be appropriate for some wood-burning applications. Selection should always align with manufacturer specifications and relevant codes.
Question 4: Can a chimney extender be installed as a do-it-yourself project?
While DIY installation may seem appealing, it is strongly advised to engage a qualified professional. Incorrect installation can compromise safety, violate building codes, and lead to system malfunctions. Professional expertise ensures proper assembly and adherence to all applicable standards.
Question 5: How does wind affect the performance of a chimney extender, and how can this be mitigated?
Wind can induce downdrafts, reversing the flow of combustion byproducts. This can be mitigated through the use of specialized chimney caps, strategic flue placement, or windbreaks. These measures minimize the impact of wind forces on the venting system.
Question 6: What maintenance is required for a chimney extender?
Regular inspection is essential to detect signs of corrosion, damage, or creosote buildup. Cleaning and repairs should be performed as needed to ensure continued safe and efficient operation. Neglecting maintenance can lead to system failure and potential hazards.
The key takeaways from this FAQ section is: Selecting the proper materials, ensuring safe installation, and regular inspection of all chimney extensions are vital for your property safety.
The following part describes conclusion about vertical flue extensions.
Conclusion
This examination has delineated the essential role of vertical flue extensions in ensuring the safe and effective operation of venting systems. Proper design, material selection, installation, and maintenance are paramount. Failures in any of these areas can compromise system integrity, leading to potentially hazardous conditions. The principles discussed herein provide a foundation for understanding the complexities associated with these components.
Given the critical safety implications and the potential for substantial property damage, engagement with qualified professionals is not merely advisable, but necessary. Continued vigilance and adherence to established codes and best practices remain indispensable for the long-term reliability and safety of any venting system incorporating a chimney extender.