A complete system designed for safely venting combustion appliances, these kits facilitate the passage of exhaust gases from a heating appliance through the roof of a structure. Characterized by a specific diameter, they include all necessary components to ensure proper installation and compliance with safety standards, offering a pre-engineered solution for venting needs. An example includes a package containing sections of double-wall pipe, a flashing, a storm collar, and a termination cap, specifically sized for a six-inch diameter flue.
The implementation of such a system is vital for preventing hazardous backdrafts and ensuring efficient expulsion of potentially harmful byproducts of combustion, such as carbon monoxide. Properly installed and maintained, these kits contribute significantly to improved indoor air quality and reduced risk of fire. Their development represents an evolution in venting technology, addressing the inherent risks associated with improperly vented heating appliances, providing a safer and more reliable alternative to site-built solutions.
Therefore, a thorough understanding of the components, installation procedures, and applicable codes is paramount. Key considerations include selecting the appropriate kit for the specific appliance type and fuel, ensuring proper sealing of roof penetrations, and conducting regular inspections for signs of deterioration or blockage. These factors contribute to the long-term performance and safety of the venting system.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper installation and ongoing maintenance are critical to the safe and efficient operation of a venting system. Adherence to these guidelines ensures optimal performance and minimizes potential hazards.
Tip 1: Appliance Compatibility. Verify the kit is specifically rated for the type of heating appliance being used (e.g., wood stove, furnace, boiler) and the fuel type (e.g., wood, gas, oil). Mismatched components can lead to dangerous operating conditions.
Tip 2: Code Compliance. Adhere strictly to all local and national building codes regarding chimney installation. Obtain necessary permits and inspections to ensure compliance. Local codes may have specific requirements regarding height above the roofline and clearances to combustible materials.
Tip 3: Proper Sealing. Ensure all joints and connections are securely fastened and properly sealed with high-temperature sealant. This prevents leakage of exhaust gases into the building and ensures optimal draft performance.
Tip 4: Flashing Installation. Correct flashing installation is paramount to prevent water damage. The flashing must create a watertight seal around the chimney where it penetrates the roof. Use appropriate flashing materials for the roof type.
Tip 5: Clearance to Combustibles. Maintain the specified minimum clearance to combustible materials throughout the chimney’s entire run. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions and building codes for the required clearances. Use heat shields where necessary.
Tip 6: Regular Inspections. Conduct regular inspections of the system, at least annually, for signs of damage, corrosion, or blockage. Pay particular attention to the chimney cap, flashing, and any visible sections of pipe.
Tip 7: Professional Cleaning. Schedule professional chimney cleaning on a regular basis, especially when burning solid fuels. Creosote buildup can pose a significant fire hazard.
Tip 8: Draft Testing. After installation and periodically thereafter, perform a draft test to ensure the system is drawing properly. A weak or reversed draft can indicate a blockage or other issue.
Implementing these recommendations enhances the safety, efficiency, and longevity of the venting system, reducing the risk of fire, carbon monoxide poisoning, and other hazards.
Following these practical steps will contribute to a safer and more efficient heating experience.
1. Diameter Compatibility
Diameter compatibility constitutes a fundamental requirement for the effective and safe operation of any venting system, particularly concerning the defined product. Mismatched diameters can compromise draft efficiency, leading to incomplete combustion and the potential for hazardous backdrafts. Proper matching ensures optimal performance and adherence to safety standards.
- Appliance Flue Outlet Size
The diameter of the flue outlet on the heating appliance directly dictates the required inner diameter of the venting system. A six-inch diameter kit is specifically designed to interface with appliances featuring a six-inch flue outlet. Employing a smaller diameter will restrict airflow, while a significantly larger diameter can result in insufficient draft, both leading to performance degradation and potential safety hazards. For example, connecting a wood stove with a six-inch outlet to a smaller diameter chimney can cause smoke spillage into the living space.
- Code and Manufacturer Specifications
Building codes and appliance manufacturer specifications invariably mandate specific flue diameters based on appliance type, fuel, and BTU output. These requirements are not arbitrary; they are calculated to ensure adequate ventilation and safe operation. Deviating from these specifications can void warranties and create significant safety risks. For instance, a gas furnace installation may require a six-inch flue based on its energy output, a requirement that must be strictly observed.
- Draft Performance and Efficiency
The diameter of the chimney directly influences draft performance, which is the natural upward flow of exhaust gases. An appropriately sized flue ensures adequate draft, facilitating the complete removal of combustion byproducts. Inadequate draft can lead to creosote buildup in wood-burning systems and carbon monoxide accumulation in gas-fired systems. Selecting the correct diameter, as prescribed by the kit’s specifications, is crucial for maintaining efficient combustion and minimizing the risk of hazardous conditions.
- System Component Matching
A system encompasses various components, including chimney pipes, connectors, and termination caps. All these components must maintain consistent internal diameters to ensure a smooth and unobstructed flow of exhaust gases. A six-inch kit is engineered to provide a matched set of components, guaranteeing seamless integration and optimal performance. Introducing mismatched components can create bottlenecks or turbulence, negatively impacting draft and potentially compromising system safety. For example, using a reducer to connect a five-inch pipe section to a six-inch chimney can significantly restrict airflow.
The preceding considerations underscore the critical importance of diameter compatibility in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a venting system. A six-inch system is designed for appliances with a corresponding six-inch flue outlet, and adherence to this principle is essential for achieving optimal performance, maintaining code compliance, and safeguarding against potential hazards. Deviating from the specified diameter can compromise the entire venting system, negating its intended safety and efficiency benefits.
2. Material Durability
The lifespan and operational safety of a system designed to vent combustion byproducts through a roof depend heavily on the durability of the materials used in its construction. For a six-inch diameter system, material selection directly impacts its ability to withstand prolonged exposure to high temperatures, corrosive gases, and external environmental elements. Substandard materials compromise the system’s structural integrity, leading to potential exhaust leaks, fire hazards, and premature failure. For example, using single-wall galvanized steel in place of listed double-wall stainless steel components can result in rapid corrosion and eventual collapse of the chimney, posing a significant safety risk to the building and its occupants.
The connection between material durability and the system’s performance manifests in several critical areas. Resistance to thermal degradation ensures that the chimney can maintain its structural properties under extreme heat generated during combustion, preventing warping, cracking, or deformation. Corrosion resistance is equally important, particularly in applications involving the combustion of fuels with high sulfur content, which can produce corrosive acids that attack metal components. Furthermore, the materials must withstand the rigors of weather exposure, including rain, snow, wind, and ultraviolet radiation, which can accelerate degradation. An example of this is the deterioration of rubber flashing components due to UV exposure, leading to water leaks around the chimney penetration.
In summary, material durability is not merely a desirable attribute but a fundamental requirement for a safe and reliable system. Selecting a six-inch diameter through-the-roof system constructed from high-quality, corrosion-resistant, and thermally stable materials is essential for ensuring long-term performance and mitigating the risks associated with venting combustion appliances. Neglecting this crucial aspect can have severe consequences, including property damage, health hazards, and potential loss of life. The initial investment in durable materials proves more cost-effective in the long run by minimizing maintenance, repairs, and the risk of catastrophic failure.
3. Installation Integrity
Installation integrity is paramount for the safe and effective operation of a six-inch through-the-roof chimney system. Proper installation directly impacts the system’s ability to contain and vent exhaust gases, preventing carbon monoxide leaks, chimney fires, and structural damage to the building. Deviations from the manufacturer’s instructions or applicable building codes can compromise the system’s integrity, creating a hazardous situation. For instance, failure to properly seal joints between chimney sections allows exhaust gases to escape into the building, potentially leading to carbon monoxide poisoning. Similarly, improper flashing installation can result in water leaks, which can damage the chimney structure and surrounding building materials.
The integrity of the installation extends beyond merely connecting the components. It encompasses ensuring proper clearances to combustible materials, securing the chimney against wind loads, and implementing appropriate measures to prevent water penetration. For example, inadequate clearance between the chimney and nearby wood framing can lead to a fire hazard, as the framing may ignite from prolonged exposure to high temperatures. Similarly, failure to adequately support the chimney can cause it to sway or collapse during high winds, potentially damaging the roof and creating a pathway for water entry. Proper installation also involves selecting the correct type of chimney support and ensuring that the chimney is properly anchored to the building structure.
In conclusion, installation integrity is not a secondary consideration but an integral component of a six-inch through-the-roof chimney system. It directly affects the system’s safety, efficiency, and longevity. Strict adherence to manufacturer’s instructions and applicable building codes, coupled with meticulous attention to detail during installation, is crucial for ensuring the system operates as intended and mitigating potential hazards. Neglecting installation integrity can have severe consequences, underscoring the importance of engaging qualified professionals for chimney installation and inspection.
4. Code Compliance
Adherence to building codes is not an optional aspect of installing a system but a mandatory requirement directly impacting safety and legality. The installation of a six-inch through-the-roof system must comply with relevant national and local building codes, fire safety regulations, and manufacturer’s specifications. These codes address crucial aspects such as minimum chimney height above the roof, clearances to combustible materials, proper flashing techniques, and the type of chimney suitable for specific appliances and fuels. For instance, the International Residential Code (IRC) stipulates specific requirements for chimney height relative to nearby structures to ensure adequate draft and prevent backdrafting. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in failed inspections, denial of insurance claims in the event of a fire, and potential legal liabilities. Examples include homeowners being forced to dismantle non-compliant installations or facing legal action following fire incidents attributed to code violations.
The impact of code compliance extends beyond immediate safety concerns. Proper adherence to regulations ensures the system functions efficiently and reliably over its intended lifespan. Building codes often incorporate best practices and engineering standards that address potential long-term issues such as corrosion, creosote buildup, and structural integrity. Utilizing listed and labeled components within a six-inch system demonstrates compliance with recognized safety standards, as these components have undergone rigorous testing to meet specific performance criteria. Code-compliant installations also facilitate smoother property transactions, as potential buyers often scrutinize building permits and inspection records to ensure the structure meets all applicable regulations. Situations where property sales have been delayed or cancelled due to unpermitted or non-compliant chimney installations underscore the practical significance of code compliance.
In summary, code compliance is an indispensable element of a six-inch through-the-roof system. It ensures safety, legality, and long-term operational reliability. Homeowners and installers must prioritize adherence to all relevant building codes, fire safety regulations, and manufacturer’s specifications to mitigate risks, protect property, and safeguard lives. Neglecting code compliance can have severe consequences, ranging from failed inspections to catastrophic fire incidents. Therefore, consulting with qualified professionals and obtaining necessary permits are essential steps in ensuring a safe and code-compliant system installation.
5. Weather Sealing
Weather sealing represents a critical aspect of any system designed to penetrate a building’s roof, directly impacting the structure’s integrity and the longevity of the chimney installation itself. For a six-inch through-the-roof system, effective weather sealing prevents water intrusion, which can lead to structural damage, mold growth, and compromised insulation. The following facets outline the key components and considerations for achieving robust weather sealing in this context.
- Flashing Design and Material
The flashing serves as the primary barrier against water penetration around the chimney. Its design must conform to the roof’s pitch and material, creating a watertight seal where the chimney intersects the roof. Common materials include aluminum, galvanized steel, and copper, each offering varying degrees of corrosion resistance and longevity. Incorrect flashing installation or the use of incompatible materials can result in leaks, leading to rot and structural damage. An example is the use of aluminum flashing with a copper roof, which can lead to galvanic corrosion and eventual failure of the seal.
- Storm Collar Function and Placement
The storm collar is a component designed to deflect rainwater away from the chimney pipe and down onto the flashing. Its placement above the flashing and secure connection to the chimney pipe are essential for preventing water from running down the chimney exterior and infiltrating the roof assembly. A properly installed storm collar creates a physical barrier that diverts water, minimizing the risk of leaks. For instance, a storm collar not properly sealed to the chimney pipe allows rainwater to wick between the collar and the pipe, eventually finding its way into the roof.
- Sealant Application and Maintenance
Sealants play a crucial role in creating a watertight seal between the flashing, storm collar, and roofing materials. High-quality, weather-resistant sealants are required to withstand temperature fluctuations, UV exposure, and prolonged contact with water. Regular inspection and maintenance of sealants are necessary to address cracks or deterioration, which can compromise the weather seal. Silicone-based sealants are often preferred for their flexibility and durability. An example of sealant failure is the hardening and cracking of a low-quality sealant, allowing water to seep in during rainstorms.
- Roofing Material Compatibility
The type of roofing material significantly influences the choice of flashing and installation techniques. Different roofing materials, such as asphalt shingles, metal roofing, or tile, require specific flashing designs and attachment methods to ensure a secure and watertight seal. Compatibility between the flashing material and the roofing material is also crucial to prevent corrosion or degradation. For example, installing standard flashing on a metal roof without proper insulation can cause galvanic corrosion and water leakage. The installer must ensure the flashing integrates seamlessly with the roofing system.
These facets collectively underscore the importance of meticulous weather sealing for a six-inch through-the-roof system. Proper flashing design, storm collar installation, sealant application, and roofing material compatibility all contribute to preventing water intrusion and maintaining the structural integrity of the building. Neglecting any of these aspects can lead to costly repairs and potential safety hazards. A comprehensive approach to weather sealing ensures the long-term performance and reliability of the venting system while protecting the building from water damage. As you can see, they all depend on each other to make weather sealing to work for “6 inch through the roof chimney kit”
6. Draft Efficiency
Draft efficiency is a critical performance parameter for any venting system, especially concerning a six-inch through-the-roof configuration. This efficiency governs the ability of the system to effectively remove combustion byproducts from the appliance, ensuring safe and optimal operation. Insufficient draft can lead to hazardous conditions, including carbon monoxide buildup and chimney fires, while excessive draft can reduce appliance efficiency. Therefore, understanding the factors influencing draft efficiency within this context is essential.
- Chimney Height and Termination
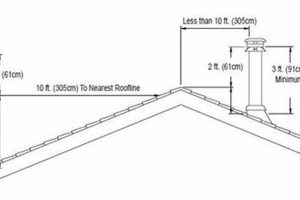
The height of the chimney stack above the roofline directly impacts draft. A taller chimney generally generates a stronger draft due to the increased column of hot gases. Building codes typically specify minimum chimney heights to ensure adequate draft, often requiring the chimney to extend at least two feet above any part of the roof within ten feet. Improper termination, such as positioning the chimney near tall trees or other obstructions, can disrupt airflow and negatively affect draft. For instance, a chimney terminating below the peak of a nearby roof may experience downdrafts, reducing draft efficiency and potentially causing smoke to enter the building.
- Flue Diameter and Appliance Matching
Matching the flue diameter to the appliance’s requirements is crucial for optimal draft. A six-inch diameter system is designed for appliances with a corresponding six-inch flue outlet. Using an undersized flue restricts airflow, leading to incomplete combustion and increased creosote buildup. Conversely, an oversized flue can cause the exhaust gases to cool too quickly, reducing draft and potentially leading to condensation within the chimney. Proper appliance matching, as dictated by the manufacturer’s specifications, ensures that the flue diameter is appropriate for the appliance’s BTU output and fuel type.
- Chimney Liner Material and Smoothness
The material and smoothness of the chimney liner influence the flow of exhaust gases. Smooth, non-porous materials, such as stainless steel, minimize friction and promote efficient draft. Rough or porous liners, such as those found in older masonry chimneys, can impede airflow and increase creosote accumulation. Upgrading to a smooth, insulated stainless steel liner within a six-inch system can significantly improve draft efficiency and reduce the risk of chimney fires. Insulated liners also help maintain exhaust gas temperatures, further enhancing draft performance.
- Air Supply and Combustion Efficiency
Adequate air supply to the combustion appliance is essential for complete combustion and optimal draft. Insufficient air can lead to incomplete combustion, producing excessive amounts of smoke and creosote, which can impede draft. Ensuring a proper air-to-fuel ratio promotes cleaner burning and reduces the burden on the venting system. Providing a dedicated air supply to the appliance, such as an outside air kit, can improve combustion efficiency and enhance draft, particularly in tightly sealed homes. For example, in newer homes with reduced air leakage, the appliance may struggle to draw enough air for combustion, leading to poor draft and increased pollutant emissions.
These facets demonstrate the interconnectedness of various factors influencing draft efficiency in a six-inch through-the-roof configuration. Optimizing chimney height, diameter, liner material, and air supply ensures that the system operates safely and efficiently, maximizing appliance performance and minimizing the risk of hazardous conditions. A holistic approach that addresses each of these aspects is crucial for achieving optimal draft and ensuring the long-term reliability of the venting system. The selection of a specifically designed “6 inch through the roof chimney kit” should consider these aspects for efficient ventilation.
7. Safety Standards
Compliance with safety standards is paramount for any venting system, particularly a six-inch through-the-roof chimney configuration. These standards, established by organizations such as UL, CSA, and building code authorities, aim to minimize the risks associated with venting combustion byproducts, ensuring the protection of property and human life. Deviation from these standards can result in fire hazards, carbon monoxide poisoning, and structural damage.
- UL 103 Standard for Factory-Built Chimneys
UL 103, a widely recognized safety standard, specifies the construction, performance, and testing requirements for factory-built chimneys. Compliance with UL 103 ensures that the components within a six-inch kit have undergone rigorous evaluation for fire resistance, structural integrity, and corrosion resistance. For example, a UL 103 listed chimney must withstand specified temperatures without deformation or failure, preventing the spread of fire to combustible materials. Systems lacking UL 103 certification may pose a significant fire hazard due to substandard construction or materials.
- Clearances to Combustibles and Firestopping
Safety standards mandate specific clearances between the chimney and combustible materials, such as wood framing, to prevent ignition. These clearances, typically defined in building codes and the manufacturer’s installation instructions, are based on the chimney’s surface temperature and the ignition point of surrounding materials. Firestopping, the practice of sealing openings around the chimney penetration with fire-resistant materials, further prevents the spread of fire through concealed spaces. Failure to maintain proper clearances or implement firestopping can result in a rapid and devastating fire. For example, neglecting to maintain the required clearance can allow nearby wood framing to ignite after prolonged exposure to heat from the chimney.
- Corrosion Resistance and Material Specifications
Safety standards dictate the types of materials suitable for chimney construction based on the fuel being burned and the expected operating conditions. Materials must exhibit sufficient corrosion resistance to withstand prolonged exposure to acidic gases and condensates produced during combustion. For instance, stainless steel alloys are often required for venting gas-fired appliances due to their superior resistance to corrosion compared to galvanized steel. Systems using substandard materials can experience rapid deterioration, leading to exhaust leaks and structural failure. For example, using single-wall galvanized steel for venting a wood stove can result in rapid corrosion and eventual collapse of the chimney, posing a significant safety risk.
- Proper Installation Practices and Inspections
Safety standards emphasize the importance of proper installation practices to ensure the system functions as intended. Building codes often require inspections by qualified professionals to verify compliance with installation requirements and safety standards. These inspections ensure that the chimney is properly assembled, supported, and sealed, minimizing the risk of leaks and malfunctions. Neglecting proper installation practices or skipping inspections can compromise the system’s safety and efficiency. For example, improperly sealed joints between chimney sections can allow exhaust gases to escape into the building, potentially leading to carbon monoxide poisoning.
These facets highlight the crucial role of safety standards in mitigating the risks associated with a six-inch through-the-roof system. Adherence to these standards, encompassing material selection, clearances, installation practices, and inspections, is paramount for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the system and protecting building occupants from potential hazards. Selecting a “6 inch through the roof chimney kit” that is certified under a safety standard like UL 103 is crucial.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, installation, and maintenance of six-inch through-the-roof chimney systems, providing concise and informative responses.
Question 1: What factors determine the suitability of a six-inch system for a specific appliance?
Appliance compatibility hinges on the flue outlet diameter and BTU output. A six-inch system is generally appropriate for appliances with a six-inch flue outlet and BTU ratings that align with the system’s specifications. Consult the appliance manufacturer’s guidelines and local building codes to confirm suitability.
Question 2: What are the primary safety concerns associated with improper installation of a chimney system?
Improper installation can lead to several hazards, including carbon monoxide leaks, chimney fires, and structural damage. Failure to maintain proper clearances to combustibles or adequately seal joints can compromise the system’s integrity and pose a significant safety risk.
Question 3: How frequently should a chimney system be inspected and cleaned?
Regular inspections are recommended at least annually, with more frequent inspections for systems that burn solid fuels. Cleaning frequency depends on usage and fuel type, but professional cleaning is typically advised every one to three years to remove creosote buildup.
Question 4: What materials are considered acceptable for a six-inch through-the-roof chimney system?
Acceptable materials typically include stainless steel, which offers excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance. Galvanized steel may be suitable for certain applications, but its lifespan is generally shorter. Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications and local building codes for approved materials.
Question 5: What steps are necessary to ensure proper weather sealing of a chimney penetration?
Proper weather sealing involves using appropriate flashing materials, installing a storm collar, and applying high-quality sealant to create a watertight barrier. The flashing must be compatible with the roofing material, and the sealant must be rated for outdoor use and extreme temperature fluctuations.
Question 6: What is the role of building codes in chimney system installation, and where can these codes be found?
Building codes dictate the minimum safety requirements for chimney system installation, including chimney height, clearances to combustibles, and material specifications. Local building departments or online resources can provide access to relevant building codes and regulations.
Proper selection, installation, and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a system. Compliance with safety standards and building codes is paramount for mitigating potential hazards.
The following section explores best practices for selecting a qualified chimney installer.
Concluding Remarks
The preceding discourse has comprehensively examined the critical aspects of a six-inch through-the-roof chimney system. The discussion spanned material durability, code compliance, installation integrity, weather sealing, draft efficiency, and adherence to safety standards. These elements collectively define the performance and reliability of such systems, underscoring the importance of informed decision-making in their selection, installation, and maintenance.
Ultimately, a six-inch through-the-roof chimney system represents a critical safety component within any structure utilizing combustion-based heating appliances. Its proper implementation is not merely a matter of convenience but a fundamental necessity for ensuring the well-being of occupants and the preservation of property. Therefore, prioritize safety, code compliance, and professional guidance to mitigate risks and ensure long-term performance.