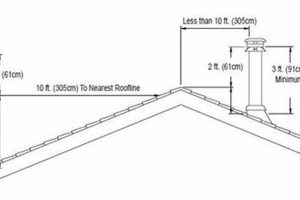
Structures providing overhead protection and ventilation for buildings are essential elements of construction. These components, typically installed by specialized contractors, shield structures from the elements and facilitate the safe expulsion of combustion byproducts. Maintenance and regular inspection are vital to ensure the continued integrity and functionality of these systems.
Properly maintained, such systems significantly extend the lifespan of a building. These elements contribute to energy efficiency, preventing heat loss and water damage. Historically, these features have evolved alongside architectural styles, reflecting changing materials and construction techniques, serving fundamental functions from early dwellings to modern buildings.
The following sections will address different aspects of these systems, focusing on material choices, installation procedures, common repair issues, and best practices for ensuring long-term structural health and safety standards.
Key Maintenance Considerations for Roofing and Ventilation Systems
Proper upkeep ensures longevity and safety for building infrastructure. Consistent monitoring and timely intervention are crucial.
Tip 1: Conduct Regular Inspections. Thorough visual assessments should occur bi-annually, preferably in the spring and fall. Inspect for missing, damaged, or displaced components, as well as any signs of water intrusion. Document all findings.
Tip 2: Address Minor Damage Promptly. Small issues, such as a single cracked component or loose flashing, can escalate quickly. Timely repairs prevent more extensive and costly problems. Engage a qualified professional for assessment and remediation.
Tip 3: Maintain Clear Ventilation Pathways. Obstructions in ventilation systems, caused by debris or nesting animals, hinder proper airflow. Clear obstructions to ensure efficient and safe removal of exhaust gases, reducing the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Tip 4: Monitor for Material Degradation. Weather exposure and aging cause material deterioration. Regularly check for signs of rust, rot, cracking, or crumbling. Address degradation immediately to maintain structural integrity.
Tip 5: Ensure Proper Sealing and Flashing. Sealants and flashing materials are essential for preventing water penetration. Inspect these areas regularly for damage or wear. Repair or replace compromised sealants and flashing to maintain watertight seals.
Tip 6: Schedule Professional Assessments. While visual inspections are valuable, a qualified professional can conduct more detailed evaluations. Schedule comprehensive assessments every three to five years to identify potential issues not visible to the untrained eye.
Consistent adherence to these practices will help maintain the safety, functionality, and longevity of your roofing and ventilation systems.
The following sections will delve deeper into specific repair techniques and common problem areas requiring specialized attention.
1. Material Durability
The longevity and performance of overhead structures and ventilation systems are intrinsically linked to the durability of the materials used in their construction. The selection of robust and resilient materials is crucial for withstanding environmental stressors and ensuring the continued functionality of these systems.
- Resistance to Weathering
Materials exposed to the elements must withstand cycles of freezing and thawing, intense solar radiation, and prolonged moisture exposure. Roofing shingles, for example, are subjected to constant weathering. Durable materials, such as slate or certain synthetic composites, exhibit superior resistance to these conditions compared to less robust options, thereby extending the lifespan and reducing maintenance needs.
- Chemical Stability
Atmospheric pollutants and chemical runoff can degrade roofing and ventilation components over time. Materials with inherent chemical stability, like stainless steel chimney liners, resist corrosion and erosion, ensuring the safe passage of combustion byproducts and preventing structural damage. The selection of chemically inert materials is especially critical in areas with high levels of industrial pollution.
- Structural Integrity Under Load
Roofing materials must support their own weight, as well as withstand snow loads, wind forces, and potential impacts from falling debris. Durable materials, such as reinforced concrete tiles or metal roofing panels, maintain their structural integrity under heavy loads, preventing sagging, cracking, or collapse. Adequate load-bearing capacity is essential for ensuring safety and preventing costly repairs.
- Resistance to Biological Growth
Moisture and organic debris can promote the growth of algae, moss, and fungi on roofing surfaces. Durable materials, treated with anti-microbial agents or naturally resistant to biological growth, inhibit the formation of these organisms, preventing surface degradation and maintaining aesthetic appeal. Regular cleaning and preventative treatments further enhance resistance to biological colonization.
The careful consideration of material durability is paramount for ensuring the long-term performance and reliability of roofing and ventilation systems. By selecting materials with inherent resistance to weathering, chemical degradation, structural stress, and biological growth, property owners can minimize maintenance costs, extend the lifespan of their buildings, and ensure the safety of occupants.
2. Ventilation Efficiency
Ventilation efficiency within roofing and chimney systems plays a pivotal role in maintaining structural integrity, indoor air quality, and overall building safety. Proper ventilation manages moisture, regulates temperature, and facilitates the safe exhaust of combustion byproducts.
- Moisture Control
Efficient ventilation systems mitigate moisture buildup within attics and roof cavities. Without adequate airflow, condensation can lead to mold growth, wood rot, and compromised insulation. For example, soffit and ridge vents work in tandem to promote continuous airflow, removing moisture-laden air and preventing structural damage, thus extending the roof’s lifespan.
- Thermal Regulation
Effective ventilation helps regulate attic temperature, reducing heat buildup in summer and minimizing heat loss in winter. This reduces the strain on HVAC systems, lowering energy costs. An under-ventilated attic can lead to excessively high temperatures, which degrades roofing materials prematurely.
- Combustion Byproduct Exhaust
Chimney systems rely on proper ventilation to safely exhaust combustion gases, such as carbon monoxide, from furnaces, fireplaces, and other heating appliances. Inadequate ventilation can result in backdrafting, where dangerous gases enter the living space, posing a significant health risk. Proper flue sizing and unobstructed pathways are critical.
- Material Longevity
By preventing moisture accumulation and regulating temperature, efficient ventilation extends the lifespan of roofing and chimney components. Reduced moisture minimizes corrosion and decay, while temperature regulation prevents premature degradation of materials like shingles and wood framing.
In summary, ventilation efficiency is integral to the proper functioning and longevity of roofing and chimney systems. It ensures safety, protects structural integrity, and contributes to energy efficiency, making it a critical consideration in building design and maintenance.
3. Weather Resistance
Weather resistance is a crucial attribute of roofing and chimney systems due to their constant exposure to environmental elements. The primary function of a roof is to shield the building’s interior from precipitation, solar radiation, and wind. Chimneys, similarly, are exposed to these elements, compounded by the corrosive effects of flue gases. Inadequate weather resistance leads to water intrusion, material degradation, and ultimately, structural compromise.
For instance, prolonged exposure to rain and snow can cause asphalt shingles to deteriorate, losing granules and compromising their water-shedding ability. This can result in leaks, damaging underlying roof decking and insulation. Similarly, chimneys constructed with porous materials, such as unsealed brick, are susceptible to water absorption, which can lead to cracking and spalling during freeze-thaw cycles. The selection of weather-resistant materials, like metal roofing or properly sealed chimney liners, mitigates these risks. Regular maintenance, including inspections and repairs, is essential for preserving weather resistance and extending the lifespan of these systems.
In conclusion, the weather resistance of roofing and chimney systems is directly linked to their longevity and performance. Choosing appropriate materials and implementing proactive maintenance strategies are essential for mitigating the damaging effects of environmental exposure, ensuring the structural integrity of buildings, and preventing costly repairs. Neglecting weather resistance ultimately undermines the functional capabilities of these vital building components.
4. Structural Stability
The structural stability of roofing and chimney systems is paramount to the overall safety and longevity of any building. These systems are integral components that must withstand various external forces, including wind, snow, and the weight of the materials themselves. Compromised structural stability can lead to catastrophic failures, posing significant risks to occupants and property.
- Load Distribution and Bearing Capacity
Roofing structures must effectively distribute loads across supporting walls and foundations. Adequate bearing capacity ensures that the weight of roofing materials, accumulated snow, and potential wind uplift forces are safely transferred to the building’s structural framework. Failure to properly distribute loads can result in localized stress concentrations, leading to cracking, sagging, or eventual collapse of the roof. For chimneys, a stable base is essential to support the vertical load and resist lateral forces. Improperly supported chimneys are prone to leaning or toppling, especially in areas prone to seismic activity or high winds.
- Material Integrity and Degradation
The materials used in roofing and chimney construction must maintain their structural integrity over time. Degradation due to weathering, moisture, or chemical exposure can weaken these materials, reducing their ability to withstand applied stresses. Regularly inspect roofing materials for signs of cracking, rotting, or corrosion. For chimneys, examine mortar joints for deterioration and ensure the flue liner remains intact. Addressing material degradation promptly prevents further structural weakening and potential failure.
- Connection Strength and Fastening Systems
The connections between roofing components, such as sheathing and rafters, or chimney sections, are critical for maintaining structural stability. Proper fastening systems, including nails, screws, and adhesives, ensure that these connections can resist shear and tension forces. Inspect connections for looseness or corrosion. Replace damaged or inadequate fasteners to maintain the structural integrity of the system. For chimneys, ensure that flashing is properly installed and sealed to prevent water intrusion, which can corrode fasteners and weaken the connection between the chimney and the roof.
- Impact of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as high winds, heavy snow, and seismic activity, can significantly impact the structural stability of roofing and chimney systems. Design considerations must account for these factors to ensure that the systems can withstand anticipated loads and stresses. In regions prone to high winds, roofing materials should be securely fastened to resist uplift forces. In areas with heavy snowfall, roofs must be designed to support the weight of accumulated snow. In seismic zones, chimneys should be properly reinforced to resist lateral forces and prevent collapse. Regular inspections after extreme weather events can help identify and address any damage that may compromise structural stability.
In conclusion, the structural stability of roofing and chimney systems is a multifaceted issue that requires careful attention to load distribution, material integrity, connection strength, and environmental factors. Implementing proactive maintenance strategies, including regular inspections and prompt repairs, is essential for preserving structural stability and ensuring the long-term safety and performance of these critical building components.
5. Code Compliance
Strict adherence to building codes is paramount in the installation and maintenance of roofing and chimney systems. These codes, established by local and national regulatory bodies, dictate minimum standards for materials, construction techniques, and safety measures. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant legal ramifications, including fines, mandatory corrections, and potential liability in the event of property damage or personal injury.
Roofing code compliance often involves specifying approved materials with adequate fire resistance and structural integrity. Chimney codes address flue sizing, liner requirements, and clearance distances to combustible materials to mitigate fire hazards and ensure proper ventilation of combustion gases. For instance, the International Residential Code (IRC) provides comprehensive guidelines for residential roofing and chimney construction, covering aspects such as shingle overlap, flashing installation, and chimney height requirements. Deviation from these standards can lead to water intrusion, premature material failure, and increased risk of chimney fires or carbon monoxide poisoning.
The practical significance of code compliance extends beyond avoiding legal penalties. It ensures the safety and well-being of building occupants by minimizing the risk of structural failure, fire, and exposure to harmful substances. Furthermore, code-compliant installations typically exhibit superior performance and longevity, reducing long-term maintenance costs and increasing property value. Understanding and adhering to relevant building codes is therefore essential for all stakeholders involved in the design, construction, and maintenance of roofing and chimney systems, promoting both safety and sustainability.
6. Regular Inspections
Routine examinations are vital for maintaining the integrity and functionality of overhead and ventilation systems. These assessments identify potential issues before they escalate, preventing costly repairs and ensuring structural safety.
- Early Detection of Water Intrusion
Periodic assessments can reveal subtle signs of water damage, such as staining, blistering, or dampness, indicating compromised roofing or chimney flashing. Early detection allows for targeted repairs, preventing extensive water damage to underlying structures. Neglecting these signs often leads to rot, mold growth, and significant structural deterioration.
- Identification of Material Degradation
Inspections expose weathering effects on materials, including cracking, corrosion, and granule loss on roofing shingles. Identifying material degradation enables proactive intervention, such as sealing or replacement, before structural integrity is compromised. Failure to address these issues results in reduced lifespan and increased vulnerability to environmental stressors.
- Assessment of Ventilation System Performance
Routine checks confirm unobstructed airflow within ventilation systems, ensuring proper exhaust of combustion byproducts and moisture control. Blocked vents or chimneys can lead to carbon monoxide buildup or moisture accumulation, posing significant health and safety risks. Regular assessments verify compliance with safety standards and optimize system efficiency.
- Verification of Structural Stability
Visual evaluations assess the structural stability of roofing and chimney systems, detecting sagging, leaning, or displacement of components. Early identification of structural issues enables timely repairs, preventing potential collapse or significant damage. Neglecting these signs can result in hazardous conditions and costly structural remediation.
These routine assessments, therefore, are not merely procedural, but rather critical safeguards that preserve the functionality, safety, and longevity of these essential building systems. Their value lies in proactive problem detection and mitigation, ensuring continued structural integrity and occupant safety.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Roofing and Chimney Systems
The following questions address common concerns and misconceptions related to the maintenance, repair, and performance of roofing and chimney systems. Answers provided are intended to offer clarity and promote informed decision-making.
Question 1: How often should a roof be inspected?
A roof should undergo professional inspection at least every three to five years. More frequent inspections are warranted after severe weather events or if visible signs of damage are present.
Question 2: What are the key indicators that a chimney requires repair?
Indicators of chimney damage include spalling brickwork, cracked flue liners, crumbling mortar joints, and water stains on adjacent surfaces. Any of these signs necessitates immediate professional evaluation.
Question 3: Can minor roof leaks be addressed with DIY repairs?
While temporary patches may provide immediate relief, lasting repairs demand professional expertise. Improperly executed DIY repairs can exacerbate the problem and lead to more extensive damage.
Question 4: What factors influence the lifespan of a roofing system?
The lifespan of a roof is affected by material quality, installation methods, climate conditions, and maintenance practices. Adhering to manufacturer recommendations and performing regular maintenance can significantly extend a roof’s service life.
Question 5: Is it necessary to clean a chimney regularly?
Regular chimney cleaning is essential for removing creosote buildup, a highly flammable byproduct of combustion. Failure to clean a chimney can lead to chimney fires and carbon monoxide poisoning.
Question 6: What are the benefits of installing a chimney liner?
A chimney liner protects the chimney structure from corrosive flue gases, improves draft, and enhances heating system efficiency. Properly installed liners are a critical safety component.
Proper maintenance, prompt repairs, and code-compliant installations are crucial for ensuring the long-term safety and performance of roofing and chimney systems.
The next section addresses specific techniques for enhancing weather resistance and extending the lifespan of these critical building components.
Expressway Roofing and Chimney
This exploration has underscored the critical importance of maintaining robust roofing and chimney systems. From material selection to rigorous inspection protocols and code compliance, each element contributes to the overall safety and longevity of buildings. Prioritizing weather resistance, structural stability, and proper ventilation are paramount in safeguarding property and well-being.
Neglecting the upkeep of these systems invites significant risk. Therefore, ongoing vigilance and professional intervention are not merely recommended, but essential. The sustained structural health of a building hinges upon a commitment to these practices, ensuring a secure and durable environment for all occupants.