A protective component affixed to the top of a flue system associated with solid fuel appliances, specifically those designed for combustion of timber within residential heating units. This safeguard prevents the ingress of precipitation, debris, and animals, thereby maintaining the operational efficiency and safety of the venting system. For instance, a homeowner might install this safeguard to prevent rainwater from entering the flue, which could cause deterioration and reduce the heating apparatus’s effectiveness.
The utilization of such protective devices yields several advantages. It mitigates the risk of flue blockage, ensures proper draft, and extends the lifespan of the overall structure by safeguarding against corrosion and physical damage. Historically, rudimentary forms of these protections were employed to shelter hearths from the elements; modern iterations incorporate advanced materials and designs optimized for optimal performance and longevity. These are integral for safe operation of solid fuel appliances.
The following discussion will delve into various types of these protective components, installation considerations, maintenance protocols, and factors influencing their selection for optimal application. Addressing common issues and providing guidance on ensuring compliance with relevant safety codes will also be explored.
Essential Considerations
Optimal performance and safety of solid fuel appliances rely on careful selection, installation, and maintenance. The following provides crucial guidelines.
Tip 1: Material Selection: Prioritize corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or copper. These withstand high temperatures and acidic byproducts of combustion, ensuring longevity.
Tip 2: Sizing and Design: Ensure appropriate dimensions based on flue diameter and appliance specifications. Correct sizing promotes optimal draft and prevents backdrafting.
Tip 3: Professional Installation: Engage certified professionals for installation. Improper installation can lead to hazardous conditions, including carbon monoxide leaks.
Tip 4: Regular Inspections: Conduct annual inspections to identify and address potential issues, such as damage or creosote buildup. Early detection prevents costly repairs and hazards.
Tip 5: Creosote Removal: Implement routine cleaning to remove creosote deposits. Excessive buildup poses a significant fire risk.
Tip 6: Spark Arrestor Compliance: Confirm adherence to local regulations regarding spark arrestors. These minimize the risk of embers escaping and causing wildfires.
Tip 7: Animal Intrusion Prevention: Select models with robust mesh designs to deter birds, squirrels, and other animals from nesting within the flue.
Adherence to these guidelines enhances the efficiency, safety, and lifespan of the venting system associated with solid fuel combustion appliances.
The subsequent sections will further elaborate on troubleshooting common problems and ensuring long-term operational reliability.
1. Protection
The safeguarding of solid fuel appliance flues from external elements is paramount for maintaining operational efficiency and safety. An effective protection mechanism prevents degradation and ensures consistent performance over time.
- Weather Infiltration Prevention
The primary function of the protective component is to impede the entry of precipitation, such as rain and snow. Water ingress can accelerate corrosion of the flue lining, leading to structural weakening and diminished draft. This can also saturate creosote deposits, causing them to expand and potentially obstruct the flue.
- Debris Exclusion
Leaves, twigs, and other airborne debris can accumulate within the flue, restricting airflow and increasing the risk of backdrafting. By effectively filtering out these materials, the protective device ensures unrestricted venting of combustion gases.
- Animal Intrusion Deterrence
Birds, squirrels, and other small animals often seek shelter within flues, building nests that can block the passage of exhaust gases. This can result in carbon monoxide buildup within the dwelling, posing a serious health hazard. A properly installed protective component prevents animal entry, mitigating this risk.
- Spark Arrestance and Wildfire Mitigation
Certain protective devices incorporate spark arrestors, designed to prevent the escape of embers. These embers can ignite dry vegetation, leading to wildfires, particularly in arid regions. Spark arrestors significantly reduce the risk of such incidents.
Collectively, these protective measures contribute to the safe and efficient operation of solid fuel appliances. The implementation of a robust safeguard is an essential element in ensuring the longevity and reliability of the entire heating system. Neglecting this aspect can lead to costly repairs, diminished performance, and increased safety risks.
2. Draft Enhancement
Effective venting of combustion gases from solid fuel appliances is intrinsically linked to achieving optimal draft. The component affixed to the flue termination plays a significant role in regulating airflow and preventing backdrafting, thus directly impacting the efficiency and safety of the appliance.
- Aerodynamic Design and Airflow
The design of the flue termination influences air movement around the flue outlet. Certain designs promote upward airflow, enhancing draft, while others can impede it. A well-designed component minimizes turbulence and ensures a smooth, unobstructed exit for combustion gases. For example, a conical design directs wind upward, creating a vacuum effect that pulls gases from the appliance. Conversely, a flat, poorly designed component can create a downdraft, forcing gases back into the dwelling.
- Height and Location Relative to Obstructions
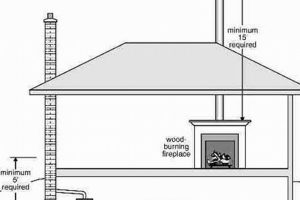
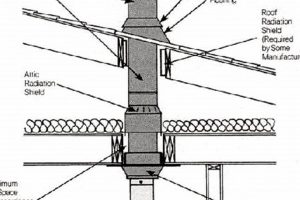
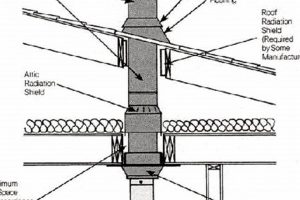
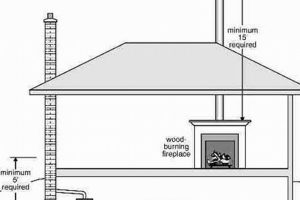
The height of the flue termination relative to nearby structures and trees affects draft performance. If the termination is too low or obstructed, wind can create negative pressure, causing backdrafting. Raising the termination above the highest point of the roof and away from obstructions ensures a more consistent and reliable draft. Building codes often specify minimum height requirements to address this issue, demonstrating its importance for safe operation.
- Internal Diameter and Flue Sizing Compatibility
The internal diameter of the termination must be appropriately sized to match the flue. A diameter that is too small restricts airflow, leading to incomplete combustion and increased creosote buildup. A diameter that is too large can result in excessive cooling of flue gases, also promoting creosote formation. Matching the termination to the flue dimensions, as recommended by the appliance manufacturer, optimizes draft and prevents related problems.
- Wind Direction and Shielding Effects
The design of the termination can provide shielding from prevailing winds, minimizing the impact of wind direction on draft performance. Certain models incorporate directional features that deflect wind away from the flue outlet, preventing downdrafts and ensuring a stable draft regardless of wind conditions. This feature is particularly beneficial in exposed locations prone to strong winds.
These factors collectively demonstrate the crucial role of the terminal component in facilitating effective draft. Proper design and installation optimize the venting process, enhancing appliance efficiency, reducing creosote accumulation, and minimizing the risk of carbon monoxide exposure. Consequently, careful consideration of these aspects is essential for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of solid fuel appliances.
3. Material Durability
Material durability is a paramount consideration in the context of solid fuel appliance flue terminations due to the harsh operational environment they endure. The combustion of timber generates high temperatures and corrosive byproducts, including acidic gases and particulate matter. Consequently, the protective component is continuously exposed to thermal stress and chemical attack. The choice of material directly impacts its ability to withstand these conditions over an extended period, influencing its lifespan and functional effectiveness. For example, a flue termination constructed from low-grade steel will rapidly corrode in the presence of acidic flue gases, leading to structural failure and necessitating premature replacement. Conversely, stainless steel or copper exhibit superior resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, extending the component’s operational life and reducing maintenance requirements. The failure of a flue termination due to material degradation can compromise the venting system’s integrity, leading to backdrafting, carbon monoxide leaks, and structural damage to the building.
Beyond corrosion resistance, mechanical strength is another crucial aspect of material durability. Flue terminations are exposed to external environmental factors, including wind, rain, snow, and ice. High winds can exert significant force on the component, potentially causing deformation or detachment. Snow and ice accumulation can add considerable weight, further stressing the material. Selecting materials with sufficient tensile strength and resistance to deformation ensures that the flue termination can withstand these external forces without compromising its structural integrity. For instance, reinforced stainless steel mesh provides both corrosion resistance and the ability to withstand high wind loads, preventing damage and maintaining its protective function. In coastal environments, where salt spray accelerates corrosion, even higher grades of corrosion-resistant alloys may be necessary to ensure long-term durability.
In summary, material durability is an indispensable attribute for flue terminations used with solid fuel appliances. The selection of appropriate materials, such as stainless steel or copper, ensures resistance to corrosion, high temperatures, and mechanical stress. This, in turn, guarantees the long-term functionality, safety, and reliability of the venting system, minimizing maintenance costs and preventing hazardous conditions. Prioritizing material durability during selection and installation represents a prudent investment in the overall performance and safety of the solid fuel appliance system. The challenges associated with material degradation underscore the importance of adhering to industry best practices and consulting with qualified professionals to ensure proper material selection and installation.
4. Spark Arrestance
Spark arrestance is a critical safety feature integrated into some flue terminations, particularly those designed for solid fuel combustion appliances. Its purpose is to mitigate the risk of embers escaping from the flue and potentially igniting surrounding vegetation or combustible materials.
- Mechanism of Operation
Spark arrestors typically consist of a metallic mesh or screen positioned within the flue termination. This mesh is designed with small openings that allow combustion gases to pass through while physically preventing larger embers from exiting. The mesh effectively captures and extinguishes these embers before they can be carried by the wind to ignite flammable materials nearby. For example, a properly functioning spark arrestor will prevent the ejection of glowing wood fragments that could land on a dry roof or in a forested area.
- Regulatory Compliance and Standards
The use of spark arrestors is often mandated by local and regional fire safety codes, especially in areas with a high risk of wildfires. These regulations typically specify the maximum allowable mesh opening size to ensure effective ember capture. Compliance with these standards is essential for safe operation and can be subject to inspection by fire safety officials. Non-compliance may result in fines or the prohibition of solid fuel appliance use.
- Maintenance and Inspection
Spark arrestors require regular maintenance to ensure their continued effectiveness. Creosote and other combustion byproducts can accumulate on the mesh, reducing airflow and diminishing its ability to capture embers. Periodic cleaning is necessary to remove these deposits and maintain the arrestor’s functionality. Regular inspection is also crucial to identify any damage to the mesh, such as holes or corrosion, which could compromise its effectiveness. Damaged spark arrestors should be promptly repaired or replaced to maintain fire safety.
- Design Variations and Effectiveness
Spark arrestors are available in various designs, each with its own advantages and limitations. Some designs are more effective at capturing embers but may also restrict airflow more significantly. The optimal design depends on the specific appliance and flue system, as well as local environmental conditions. The effectiveness of a spark arrestor is directly related to its maintenance and the integrity of its mesh. A poorly maintained or damaged spark arrestor provides little or no protection against ember ignition.
The integration of spark arrestance into flue terminations for solid fuel appliances is a fundamental safety measure, particularly in fire-prone regions. Regular inspection, cleaning, and adherence to regulatory standards are essential for ensuring the continued effectiveness of these devices in preventing wildfires and protecting property.
5. Animal Deterrence
Solid fuel appliance flue terminations frequently serve as attractive nesting sites for various animals, including birds, squirrels, and raccoons. The interior of a flue offers shelter from the elements and protection from predators. However, animal intrusion into a flue can create significant hazards. Nests constructed within the flue obstruct airflow, leading to incomplete combustion and increased creosote buildup. This obstruction can result in backdrafting, potentially causing carbon monoxide to enter the dwelling. Carbon monoxide is an odorless, colorless gas that can be fatal. A physical barrier, often integrated into the design of a protective component affixed to the flue, effectively prevents animal entry. This barrier typically consists of a robust mesh or screen that allows combustion gases to escape while denying access to animals. For example, a homeowner might install such a device following the discovery of a bird’s nest within the flue, which had significantly reduced the heating appliance’s efficiency.
The selection of appropriate mesh size and material is crucial for effective animal deterrence. The mesh openings must be small enough to prevent the entry of even small animals while still permitting adequate airflow. Durable materials, such as stainless steel, are preferred to withstand the corrosive effects of flue gases and the physical wear and tear inflicted by animals attempting to gain access. Improper installation of the animal deterrence mechanism can compromise its effectiveness. Gaps or weak points in the mesh allow animals to bypass the barrier. Regular inspection and maintenance are necessary to ensure the integrity of the animal deterrence system. Damage caused by corrosion, physical impact, or animal activity must be promptly repaired to maintain its protective function. A neglected system can fail, leading to the re-establishment of animal nesting within the flue. This is especially crucial at the change of seasons.
In conclusion, integrating animal deterrence into the design and maintenance of solid fuel appliance flue terminations is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the heating system. Animal intrusion poses significant risks, including flue obstruction, carbon monoxide exposure, and reduced heating efficiency. The implementation of a robust animal deterrence system, coupled with regular inspection and maintenance, effectively mitigates these risks and safeguards the well-being of occupants and the integrity of the building structure. Therefore, animal deterrence is a fundamental consideration in the selection and installation of flue terminations. Ignoring the potential for animal intrusion can have severe consequences, underscoring the importance of proactive measures to prevent it.
6. Code Compliance
Adherence to established building codes and safety standards is paramount in the installation and maintenance of solid fuel appliance flue terminations. These regulations, often promulgated by local municipalities, national organizations, or insurance providers, dictate specific requirements concerning the materials, dimensions, installation methods, and performance characteristics of such components. The overarching objective of code compliance is to minimize the risk of fire, carbon monoxide poisoning, and structural damage associated with the operation of these appliances. Consequently, a flue termination that does not meet code requirements poses a significant safety hazard. For instance, a termination constructed from substandard materials may fail prematurely, leading to flue gas leaks or structural collapse. Similarly, a termination that is improperly sized or installed may impede airflow, resulting in incomplete combustion and increased creosote buildup, a leading cause of flue fires. Failure to comply with these standards carries legal ramifications, potentially resulting in fines, mandatory corrective actions, or the revocation of occupancy permits. A real-world example involves a homeowner who installed an undersized flue termination without obtaining the necessary permits. Following a routine inspection, the homeowner was required to replace the termination with a code-compliant model and pay a substantial penalty. The practical significance of this example lies in the demonstrable cost and inconvenience associated with non-compliance.
Code compliance extends beyond the initial installation phase, encompassing ongoing maintenance and periodic inspections. Regulations often mandate regular flue cleanings to remove creosote deposits, as well as inspections to identify any signs of damage or deterioration. These measures are intended to ensure that the flue termination continues to meet safety standards throughout its operational life. Furthermore, codes may specify requirements for spark arrestors in areas prone to wildfires, mandating the use of terminations equipped with mesh screens to prevent the escape of embers. The absence of a spark arrestor in such areas constitutes a code violation and increases the risk of igniting surrounding vegetation. Practical application of code compliance principles requires a thorough understanding of the relevant regulations, as well as the proper selection, installation, and maintenance of the flue termination. This necessitates consulting with qualified professionals, such as certified installers and chimney sweeps, who possess the requisite knowledge and experience to ensure adherence to all applicable standards. Moreover, proper documentation, including permits, inspection reports, and maintenance records, is essential for demonstrating compliance and mitigating potential liability.
In conclusion, code compliance is an indispensable element in the safe and effective operation of solid fuel appliances. By adhering to established regulations, property owners and installers can minimize the risk of fire, carbon monoxide poisoning, and structural damage. The consequences of non-compliance can be severe, ranging from financial penalties to potentially life-threatening hazards. Overcoming the challenges associated with code compliance requires a commitment to ongoing education, proper training, and collaboration with qualified professionals. The broader theme underscores the importance of prioritizing safety and adhering to industry best practices in all aspects of solid fuel appliance installation and maintenance, ensuring the well-being of occupants and the protection of property.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding protective components integrated with solid fuel combustion appliances.
Question 1: What constitutes a suitable material for a chimney cap utilized with a wood burning stove?
Corrosion-resistant alloys, such as stainless steel (304 or 316 grade) and copper, are preferred due to their ability to withstand the acidic byproducts of combustion and high temperatures. Galvanized steel is generally discouraged due to its limited lifespan in such environments.
Question 2: What is the correct method for determining the appropriate dimensions for a chimney cap relative to a wood burning stove flue?
The internal diameter of the cap must correspond precisely with the flue’s outer diameter. Additionally, the cap’s height must conform to local building codes, ensuring sufficient clearance above the roofline to facilitate optimal draft and prevent backdrafting.
Question 3: Is it permissible to install a chimney cap on a wood burning stove flue without professional assistance?
While technically feasible for a skilled individual, professional installation is highly recommended. Improper installation can compromise the cap’s functionality, leading to hazardous conditions such as flue gas leaks or inadequate draft. Moreover, local regulations may mandate professional installation.
Question 4: How frequently should a chimney cap integrated with a wood burning stove be inspected and maintained?
A minimum of annual inspections is advised, preferably conducted by a certified chimney sweep. Regular maintenance, including the removal of creosote and debris, is crucial for ensuring proper draft and preventing fire hazards. More frequent inspections may be necessary in areas with heavy snowfall or high winds.
Question 5: What are the potential consequences of neglecting to install a chimney cap on a wood burning stove flue?
The absence of a cap can lead to water damage within the flue, accelerating corrosion and structural deterioration. Additionally, debris and animal intrusion can obstruct airflow, resulting in inefficient combustion, increased creosote buildup, and the potential for carbon monoxide poisoning.
Question 6: Do all chimney caps for wood burning stoves incorporate spark arrestors?
Not all models include spark arrestors. However, in regions prone to wildfires, spark arrestors are often mandated by local fire safety codes. Selecting a cap equipped with a spark arrestor is essential for mitigating the risk of ember ignition and preventing wildfires.
Proper selection, installation, and maintenance are critical for ensuring safe and efficient operation of the appliance and venting system.
The next section will detail troubleshooting common issues and ensuring long-term operational reliability.
Chimney Cap Wood Burning Stove
This exploration has underscored the critical role the protective components play in the safe and efficient operation of solid fuel appliances. Material selection, proper sizing, adherence to code, and consistent maintenance are paramount. By preventing the ingress of precipitation and debris, inhibiting animal intrusion, and mitigating the risk of spark-induced fires, these devices safeguard both property and occupants.
Given the potential hazards associated with malfunctioning or improperly installed components, diligent attention to these guidelines is not merely advisable, but essential. Prioritizing quality and professional oversight contributes significantly to the longevity and operational integrity of the entire heating system, ensuring peace of mind and minimizing the risk of catastrophic events. The long-term benefits of investing in a robust chimney cap for a wood burning stove far outweigh the initial cost, representing a prudent commitment to safety and responsible homeownership.