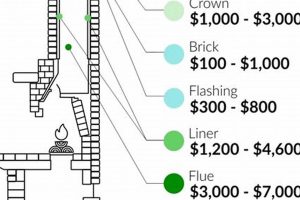
The expenditure associated with exchanging a metallic flue system component of a home is a significant consideration for property owners. This expense encompasses materials, labor, potential permits, and ancillary components necessary for a safe and compliant installation. For instance, a homeowner might budget for a new stainless steel liner and its installation within an existing masonry chimney.
The financial implication of this undertaking is important for maintaining structural integrity and preventing hazards. A functional, code-compliant flue is crucial for venting combustion byproducts efficiently, reducing the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning and chimney fires. Historically, chimney maintenance was a less formalized process, but modern building codes and safety standards mandate regular inspections and timely replacements when necessary, emphasizing the investment’s preventative nature.
Subsequently, detailed exploration of factors influencing the price, various types of metallic flue systems, and methods for securing competitive quotations will provide a thorough understanding of the process.
Essential Considerations for Metallic Flue System Expenditure
Careful planning and informed decision-making are paramount when addressing the expense related to metallic flue systems. The following points offer practical guidance for navigating this investment.
Tip 1: Obtain Multiple Estimates: Secure at least three independent quotations from licensed and insured contractors. This allows for comparison of pricing, material specifications, and proposed methodologies.
Tip 2: Scrutinize Material Quality: Inquire about the grade and gauge of the metal used. Opting for a higher grade stainless steel, for example, can extend the lifespan of the system and mitigate corrosion risks.
Tip 3: Verify Compliance with Local Codes: Ensure the proposed system and installation adhere to all applicable local building codes and regulations. Non-compliance can result in fines and require rework.
Tip 4: Assess Chimney Condition: A professional inspection of the existing chimney structure is essential. Underlying structural issues may necessitate repairs beyond the flue system itself, impacting the overall expenditure.
Tip 5: Inquire About Warranties: Understand the warranty terms offered by both the manufacturer of the system and the installer. Clarify the scope of coverage, including labor and materials.
Tip 6: Explore Energy Efficiency: Consider systems designed to improve energy efficiency. Although the initial investment may be higher, long-term savings on heating costs may offset the difference.
Tip 7: Plan for Accessibility: Ensure the system is installed in a manner that allows for future inspections and maintenance. Difficult access can increase the expense of subsequent service calls.
Careful adherence to these recommendations enables a more informed approach to the investment required for metallic flue systems, ultimately contributing to safety, efficiency, and long-term value.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific system types and detailed cost breakdowns, providing further clarity for informed budgetary decisions.
1. Material type
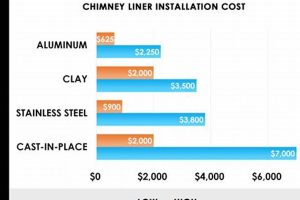
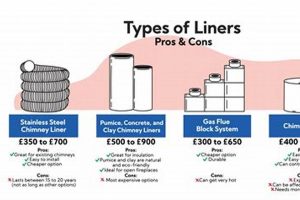
The selected material for a metallic flue system directly impacts the financial outlay required for its renewal. Different metals possess varying characteristics that influence their price and suitability for specific applications. Stainless steel, known for its corrosion resistance and durability, typically commands a higher price point than aluminum. The grade of stainless steel further influences the price, with higher grades offering increased resistance to degradation. The use of more durable materials, although initially more expensive, can lead to long-term cost savings by extending the system’s lifespan and reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacement. For instance, a homeowner replacing an existing aluminum liner that has deteriorated due to acidic flue gases might opt for a stainless-steel liner, incurring a higher initial expenditure but mitigating future corrosion-related problems.
The choice of material also affects labor costs. Stainless steel, being more rigid and heavier than aluminum, can require more specialized tools and installation techniques, potentially increasing labor time and expense. Moreover, certain materials may necessitate specific joining methods, such as welding for stainless steel, which requires skilled labor and adds to the overall expenditure. Proper material selection requires careful consideration of the appliance being vented, the type of fuel used, and the local climate conditions. Failure to select an appropriate material can lead to premature system failure, necessitating further replacement expenses.
In summary, the material chosen for a metallic flue system is a primary determinant of the replacement expense. Selecting the most cost-effective material necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the system’s operational requirements, potential environmental stressors, and the long-term implications of material choice on system longevity and performance. A thorough assessment should weigh initial expenditure against potential long-term savings and the avoidance of future costly repairs or replacements.
2. Chimney Height
Chimney height is a salient factor influencing the overall expenditure associated with metallic flue system renewal. The vertical dimension of the chimney directly correlates with several cost-driving elements, making it a key consideration in project budgeting and execution.
- Material Quantity
Taller chimneys inherently require a greater quantity of metallic flue liner to achieve a complete and code-compliant installation. This increased material demand directly translates into higher material costs, as the price is typically calculated on a per-linear-foot basis. For example, a chimney measuring 30 feet will require significantly more liner material than one measuring 15 feet, leading to a proportional increase in material expenditure.
- Labor Intensity and Duration
The height of the chimney affects the complexity and duration of the installation process. Working at greater heights necessitates specialized equipment, safety precautions, and often, a larger installation team. This increased labor intensity translates to higher labor costs, as contractors must factor in the additional time, risk, and resources required for the job. A high chimney, for instance, might require scaffolding or a crane to safely access and install the liner, adding to the labor expenditure.
- Accessibility Challenges
Increased chimney height often correlates with increased accessibility challenges. Reaching the top of a tall chimney for inspection, preparation, and liner installation can be difficult, especially if the chimney is located on a steep roof or in a confined space. Overcoming these accessibility challenges may require specialized equipment or techniques, further increasing labor costs. The use of aerial lifts or rope access techniques, for example, can significantly add to the overall project expenditure.
- Structural Reinforcement Needs
In some cases, taller chimneys may require additional structural reinforcement to ensure stability and safety. This is particularly true if the existing masonry is deteriorated or if the chimney is exposed to high winds. The need for structural reinforcement can add significantly to the overall project expense, as it involves additional materials, labor, and engineering expertise. For instance, a tall chimney with cracked masonry may require the installation of steel bands or the rebuilding of sections to ensure structural integrity before or during the liner installation.
In conclusion, chimney height is a critical determinant of the total outlay associated with metallic flue system replacement. The correlation between height and material quantity, labor intensity, accessibility challenges, and potential structural reinforcement needs underscores the importance of accurate chimney height measurements and thorough site assessments during the project planning phase. Accurate estimation and cost-benefit analysis for material selection considering chimney height will helps to reduce the expenditure.
3. Accessibility Challenges
Constraints surrounding access to a chimney significantly influence the expenditure required for metallic flue system renewal. Difficult access directly translates into increased labor costs and may necessitate specialized equipment, thereby elevating the overall project expense. The degree of difficulty in reaching the chimney’s location, whether due to height, roof pitch, obstructions, or confined spaces, acts as a multiplier on standard labor rates. For instance, a chimney located on a steep, multi-story roof requires more time and effort to access safely, often involving the use of scaffolding, aerial lifts, or specialized rope access techniques. This increased complexity directly impacts the final financial outlay.
Accessibility challenges can also dictate the choice of materials and installation methods. Limited access may preclude the use of heavier or bulkier materials, necessitating the selection of lighter, more manageable options, which may come at a higher cost per unit. Furthermore, the installation process may require modifications to accommodate restricted workspaces, potentially prolonging the project timeline and increasing labor hours. Consider a scenario where a chimney is enclosed within a densely wooded area, making it difficult to maneuver equipment or materials to the site. In such cases, manual carrying of materials and equipment becomes necessary, adding to the time and physical labor involved.
In summary, accessibility challenges are a critical factor in determining the financial investment required for metallic flue system renewal. Addressing these challenges necessitates careful planning, specialized equipment, and skilled labor, all of which contribute to increased expenditure. Recognizing and accurately assessing accessibility limitations during the initial assessment phase is crucial for generating realistic cost estimates and avoiding unforeseen expenses during the project execution.
4. Labor Costs
Labor expenditure is a substantial component of the overall metallic flue system renewal investment. This cost reflects the time, skill, and effort required to safely and effectively remove the existing system and install a new, code-compliant one. The intricacy of the installation process, influenced by factors such as chimney height, accessibility, and the chosen metallic flue system type, directly affects the total labor hours and, consequently, the associated expenses. For example, replacing a simple, straight flue liner in an easily accessible chimney will require fewer labor hours than installing a complex, multi-offset system in a tall, difficult-to-reach chimney. Qualified technicians are necessary to assess the system, select appropriate parts, perform any structural remediation needed to support metallic flue systems and install the new system according to building codes.
Geographical location also exerts a significant influence on labor costs. Metropolitan areas and regions with a higher cost of living typically have higher prevailing wage rates for skilled tradespeople, thereby impacting the overall expenditure. Furthermore, the demand for qualified chimney technicians within a specific area can affect pricing, with higher demand potentially driving up labor rates. Seasonal variations can also play a role, as increased demand during peak heating seasons may lead to higher labor costs due to increased workload and scheduling constraints. The presence of asbestos or other hazardous materials also contributes to labor cost. Certified labor must be hired to perform the removal, abatement, and disposal of these materials during the chimney replacement.
Understanding the dynamics of labor costs within the context of metallic flue system renewal is crucial for accurate budgeting and project planning. Homeowners and building managers should obtain multiple quotations from licensed and insured contractors, carefully reviewing the scope of work and the hourly or project-based labor rates. In particular, any structural remediation needed will necessitate engineering assessments and qualified laborers, which may not be apparent during an initial quote. In doing so, careful consideration of the aforementioned factors can help ensure cost-effective and satisfactory completion of the renewal process, aligning investment with both safety and performance objectives.
5. Code Compliance
Adherence to prevailing building codes is an integral aspect of metallic flue system renewal. Compliance dictates the materials, installation methods, and performance standards that must be met, directly influencing the overall expenditure.
- Material Specifications
Building codes often mandate the use of specific materials for metallic flue systems based on the type of appliance being vented and the fuel source used. These material requirements can significantly impact the material costs, as certain code-approved materials, such as stainless steel, may be more expensive than alternatives like aluminum. For example, codes may require a specific grade of stainless steel for venting high-efficiency gas appliances, leading to increased material expenditure.
- Installation Practices
Codes prescribe specific installation methods to ensure the safe and effective operation of metallic flue systems. These regulations may dictate clearances to combustible materials, proper joining techniques, and the use of specific support systems. Compliance with these installation requirements can add to the labor costs, as contractors must adhere to stringent guidelines and may need to employ specialized tools or techniques. In some instances, compliance may necessitate modifications to the existing chimney structure, further increasing labor expenses.
- Inspection Requirements
Building codes typically require inspections of metallic flue systems to verify compliance with regulations. These inspections can incur fees and may necessitate rework if deficiencies are identified. For instance, a code inspector may require adjustments to the flue system to meet clearance requirements, resulting in additional labor costs and potential delays. Failing an inspection can lead to fines and require further corrective actions, adding to the overall financial burden.
- Permitting Fees
Most jurisdictions require permits for metallic flue system replacement, necessitating additional financial output. Permitting fees offset administrative and inspection costs incurred by local building authorities. Moreover, permit acquisition requires detailed documentation and project plan submissions, adding administrative time for either the homeowner or contractor. Failure to acquire necessary permits can result in substantial fines and mandated remediation work, significantly increasing the project’s total outlay.
In summary, strict adherence to building codes during metallic flue system renewal is not merely a matter of regulatory compliance but also a critical factor influencing the project’s financial implications. Proper understanding and budgeting for code-related requirements are essential for managing overall expenditure and ensuring a safe, efficient, and code-compliant installation.
6. Permitting Fees
The expenditure required for metallic flue system replacement is directly influenced by mandatory permitting fees imposed by local jurisdictions. These charges, while often representing a smaller portion of the overall project budget, are a non-negotiable component that must be factored into cost calculations.
- Cost Variation Across Jurisdictions
Permitting fee structures vary considerably among municipalities, counties, and states. The financial outlay can range from a nominal flat fee to a percentage of the total project cost, creating inconsistencies in expenditure based solely on geographic location. For instance, replacing a metallic flue system in a densely populated urban area may incur higher permitting fees than a similar project in a rural setting due to differing administrative overhead and resource allocation.
- Inspection Coverage and Administration
Permitting fees often encompass the costs associated with inspections conducted by local building officials. These inspections are designed to ensure compliance with established safety codes and installation standards. The fees contribute to funding the salaries of inspectors and the administrative infrastructure required to manage the permitting process, linking project expenditure directly to regulatory oversight.
- Project Complexity Influence
The complexity of the metallic flue system replacement can affect permitting fees. Projects involving structural modifications or requiring variances from existing codes may be subject to increased scrutiny and, consequently, higher fees. A project involving the installation of a flue liner in a historic building, for example, may require additional reviews and approvals, resulting in elevated permitting expenses.
- Potential Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to obtain the necessary permits before commencing metallic flue system replacement can result in significant financial penalties. Jurisdictions typically impose fines for unpermitted work, potentially exceeding the original permitting fees by a substantial margin. Furthermore, unpermitted installations may be subject to forced remediation, adding additional costs to rectify code violations.
Therefore, the financial planning for metallic flue system replacement must incorporate accurate estimates of permitting fees, accounting for jurisdictional variations, project complexity, and the potential consequences of non-compliance. Accurate assessment of code and adherence to the regulation reduces overall metal chimney replacement cost.
7. Existing damage
Pre-existing deterioration within a chimney structure significantly impacts the overall financial outlay for metallic flue system renewal. Undetected or unaddressed damage often necessitates additional repairs beyond the immediate scope of flue replacement, substantially increasing project expenditure.
- Structural Instability Amplification
Existing cracks, spalling brickwork, or mortar joint degradation compromise the structural integrity of the chimney. Installation of a metallic flue system in such a compromised structure may require reinforcing measures, such as rebuilding sections of the chimney or applying structural supports. These additional interventions directly increase labor and material costs. For example, a chimney exhibiting significant leaning may necessitate partial demolition and reconstruction before a flue liner can be safely installed.
- Water Intrusion and Rot
Water damage to chimney components, especially the chase cover or flashing, can lead to rot and deterioration of adjacent building materials. Replacing a metallic flue system in the presence of water damage may necessitate addressing these related issues, such as repairing or replacing damaged roofing, framing, or sheathing. The cost of remediating water damage and associated rot can substantially increase the overall project expenditure. For instance, a rusted chase cover allowing water ingress may result in the deterioration of the chimney’s internal components and surrounding roof decking, requiring extensive repairs.
- Hazardous Material Exposure
Older chimneys may contain asbestos-containing materials (ACM) in the mortar, flue liners, or insulation. Disturbing these materials during flue system replacement necessitates abatement procedures conducted by certified professionals, significantly increasing the project’s labor costs and disposal fees. For instance, removing an existing clay tile flue liner that contains asbestos will require specialized handling, containment, and disposal protocols, adding substantially to the replacement expenditure.
- Code Compliance Challenges
Existing damage can create challenges in meeting current building codes during metallic flue system replacement. Addressing pre-existing code violations, such as inadequate chimney height or improper clearances to combustible materials, may require additional construction work and material, increasing the project’s financial outlay. An older chimney that doesn’t meet current height requirements may necessitate extending the chimney’s height to comply with code, adding to both labor and material costs.
In conclusion, the presence of existing damage within a chimney structure presents a complex interplay of factors that directly escalate the expenditure associated with metallic flue system renewal. Thorough inspection and assessment of pre-existing conditions are essential for accurate cost estimation and avoiding unforeseen expenses during the project execution.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses prevalent inquiries concerning the financial implications of renewing a metallic flue system within a residential or commercial property.
Question 1: What factors primarily influence the cost of metallic flue system replacement?
The primary determinants include chimney height, material type (e.g., stainless steel versus aluminum), accessibility challenges, labor rates prevalent in the region, compliance with local building codes, and the presence of pre-existing damage to the chimney structure.
Question 2: Is it possible to provide a general cost range for metallic flue system replacement?
Providing a precise cost range is challenging due to the variability of the influencing factors. However, a typical metallic flue system replacement may range from several hundred to several thousand dollars, contingent upon the specifics of the project.
Question 3: Does the type of appliance vented through the chimney affect the cost of replacement?
Yes, the appliance type significantly impacts the cost. High-efficiency appliances often require specific materials or installation techniques mandated by building codes, potentially increasing expenditure. The fuel type (e.g., natural gas, oil, wood) also influences material selection and code requirements.
Question 4: Are there strategies to mitigate the expenditure associated with metallic flue system replacement?
Obtaining multiple quotations from licensed and insured contractors, carefully evaluating material options to balance cost and durability, and addressing any pre-existing chimney damage proactively can help manage expenses. Ensuring code compliance from the outset prevents costly rework.
Question 5: What are the potential consequences of neglecting metallic flue system replacement when necessary?
Neglecting necessary replacement can lead to hazardous conditions, including carbon monoxide poisoning, chimney fires, and structural damage to the building. Furthermore, non-compliance with building codes can result in fines and legal liabilities.
Question 6: How often should a metallic flue system be inspected to assess its condition and potential replacement needs?
Industry best practices recommend annual inspections by a qualified chimney professional. Regular inspections allow for early detection of deterioration and timely intervention, potentially preventing more extensive and costly repairs in the future.
In conclusion, understanding the factors driving expenditure for metallic flue system renewal and proactively addressing potential issues is crucial for maintaining safety and managing financial investment.
The subsequent section will offer detailed insights into selecting qualified contractors for metallic flue system replacement.
Metallic Flue System Renewal Investment
The financial implications associated with the term metal chimney replacement cost, demand careful consideration. This analysis has explored diverse elements influencing this expenditure, ranging from material selection and chimney height to regulatory adherence and the presence of pre-existing structural deficits. A comprehensive understanding of these factors empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions, aligning budgetary constraints with safety imperatives.
Given the criticality of a properly functioning flue system for occupant safety and structural integrity, prioritizing diligent inspection and timely renewal is paramount. Strategic management of metal chimney replacement cost, coupled with adherence to established safety protocols, ensures both long-term cost-effectiveness and the safeguarding of property and well-being. Future investment in durable materials and qualified labor mitigates long-term risk and ensures optimal system performance.



![Chimney Sweep Cost: Average Cost to Clean a Chimney in [Year] Chimney Works – Expert Chimney Repair, Cleaning & Installation Services Chimney Sweep Cost: Average Cost to Clean a Chimney in [Year] | Chimney Works – Expert Chimney Repair, Cleaning & Installation Services](https://thechimneyworks.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/th-216-300x200.jpg)