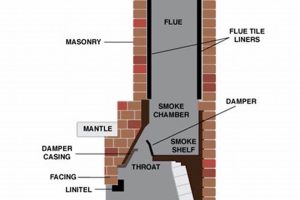
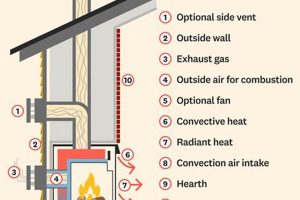
The necessity of professional chimney maintenance for gas fireplaces is a point of common inquiry. While gas-burning units produce less soot than wood-burning counterparts, they are not entirely free from generating byproducts. These combustion residues, along with potential debris from outside sources, can accumulate within the venting system over time.
Regular inspections and cleanings offer significant benefits, even for systems designed to burn gas. Obstructions can lead to inefficient operation, increasing fuel consumption and potentially posing safety hazards such as carbon monoxide leaks. Furthermore, buildup can corrode the venting components, leading to costly repairs or system failure. The practice of routine maintenance ensures optimal performance and mitigates potential risks, contributing to a safer and more efficient heating solution.
The following sections will delve into the specific reasons for scheduling professional chimney maintenance for gas fireplaces, the frequency with which it should occur, and how to identify potential problems that necessitate immediate attention.
Maintenance Guidance for Gas Fireplace Venting Systems
The following guidance outlines crucial steps to ensure the safe and efficient operation of gas fireplaces, addressing concerns about their maintenance needs.
Tip 1: Schedule Annual Inspections: A qualified professional should conduct a thorough inspection of the venting system annually. This includes checking for obstructions, corrosion, and proper connections.
Tip 2: Recognize Signs of Malfunction: Be vigilant for indicators such as unusual odors, sooting around the fireplace, or a yellow, rather than blue, flame. These could signal incomplete combustion or ventilation problems.
Tip 3: Clear Debris Regularly: Inspect the vent termination point for any external debris, such as leaves, nests, or snow accumulation, and remove it promptly.
Tip 4: Examine Burner Assembly: Have the burner assembly professionally cleaned and inspected periodically to ensure efficient gas flow and complete combustion. This prevents carbon monoxide buildup.
Tip 5: Review Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Adhere to the fireplace manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and procedures for optimal performance and safety.
Tip 6: Check Carbon Monoxide Detectors: Ensure carbon monoxide detectors are installed and functioning correctly in the vicinity of the fireplace. Test them regularly and replace batteries as needed.
Tip 7: Address Unusual Noises: Investigate any unusual noises emanating from the fireplace or venting system, as these could indicate mechanical issues requiring professional attention.
Following these recommendations significantly reduces the risk of malfunctions and ensures the ongoing safe and efficient utilization of gas fireplaces.
The concluding section will consolidate the information presented, reiterating the importance of proactive maintenance practices.
1. Combustion Byproducts
The formation of combustion byproducts represents a central consideration in evaluating the maintenance requirements of gas fireplaces. While gas-burning appliances are often perceived as cleaner than their wood-burning counterparts, the combustion process inevitably generates substances that can impact the functionality and safety of the venting system.
- Soot and Particulate Matter
Although gas fireplaces produce significantly less soot than wood, small amounts of particulate matter are still generated. Over time, this soot can accumulate within the venting system, reducing its diameter and potentially impeding airflow. This impedance can lead to incomplete combustion, further increasing the production of harmful gases.
- Water Vapor
The combustion of natural gas or propane produces water vapor as a byproduct. In colder climates, this water vapor can condense within the venting system, especially if the system is not properly insulated. This condensation can corrode metal components and create an environment conducive to the growth of mold or mildew, leading to structural damage and potential health hazards.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
High-temperature combustion processes, like those in gas fireplaces, produce nitrogen oxides. These gases are respiratory irritants and contribute to air pollution. While NOx emissions from individual gas fireplaces are relatively low, proper venting is crucial to prevent their accumulation within the living space. A malfunctioning venting system can allow NOx to leak into the home, posing a health risk to occupants.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Incomplete combustion, often resulting from insufficient oxygen or a malfunctioning burner, can lead to the production of carbon monoxide. This odorless and colorless gas is highly toxic and can be fatal. Although modern gas fireplaces are designed with safety features to minimize CO production, regular maintenance and inspection of the venting system are essential to ensure that any CO produced is safely exhausted outside the home.
The accumulation of these combustion byproducts underscores the importance of periodic inspection and cleaning of gas fireplace venting systems. These maintenance activities mitigate the risks associated with reduced airflow, corrosion, health hazards, and potential carbon monoxide exposure. Therefore, despite the relatively cleaner nature of gas combustion, routine maintenance remains critical for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of these appliances.
2. Venting Obstructions
The presence of obstructions within a gas fireplace’s venting system is a critical factor when considering the necessity of chimney maintenance. Obstructions impede the proper expulsion of combustion byproducts, leading to potential safety hazards and operational inefficiencies. The following points detail the various forms these obstructions can take and their implications.
- Debris Accumulation
Leaves, twigs, and other organic matter can enter the venting system, particularly in systems with exposed terminations. This debris restricts airflow, increasing the risk of incomplete combustion and the buildup of carbon monoxide. Regular removal of accumulated debris is crucial for maintaining safe and efficient operation. Neglecting this aspect directly relates to the need for professional chimney services.
- Animal Infestation
Birds, squirrels, and other animals may build nests within the venting system, creating significant blockages. These nests not only restrict airflow but can also introduce flammable materials into the system. Animal removal and nest clearing are often best handled by professionals, highlighting the relevance of chimney maintenance services.
- Creosote Formation (Indirectly)
While gas fireplaces produce less creosote than wood-burning units, incomplete combustion due to other obstructions can lead to a buildup of a soot-like substance that resembles creosote. This substance further restricts airflow and increases the risk of chimney fires. Professional cleaning removes this buildup, ensuring safe operation.
- Corrosion and Deterioration
Over time, venting system components can corrode or deteriorate, leading to the shedding of material into the system. This material can accumulate and create obstructions. Inspections by qualified technicians identify these issues, allowing for timely repairs or replacements. Early detection minimizes the need for more extensive and costly interventions later.
These various forms of venting obstructions underscore the importance of regular inspections and, when necessary, professional cleaning of gas fireplace venting systems. Addressing these issues proactively ensures safe and efficient operation, mitigating the risks associated with incomplete combustion and carbon monoxide buildup, directly answering the question of necessity.
3. Carbon Monoxide Risk
Carbon monoxide (CO) risk forms a crucial nexus with the question of chimney maintenance for gas fireplaces. Incomplete combustion of natural gas or propane, often a consequence of inadequate ventilation or malfunctioning components, generates this odorless, colorless, and highly toxic gas. A compromised venting system directly contributes to elevated CO levels within a dwelling. For instance, a blocked vent pipe prevents the proper expulsion of combustion byproducts, causing CO to accumulate indoors. This scenario underscores the importance of regular chimney inspections and cleaning, even in gas-burning systems, as a preventative measure against CO poisoning.
Regular chimney sweeping, in this context, serves as a safeguard. It ensures the venting system remains free of obstructions, facilitating complete combustion and efficient removal of harmful gases. Consider a case where a bird’s nest obstructs a vent, leading to reduced airflow and increased CO production. Timely sweeping removes the obstruction, restoring proper ventilation and mitigating the CO risk. Moreover, professional inspections can identify corroded or damaged venting components that might leak CO into living spaces, prompting necessary repairs before dangerous levels accumulate. The practical implication is that proactive chimney maintenance significantly reduces the likelihood of CO-related health emergencies.
In summary, carbon monoxide risk is a primary driver behind the recommendation for chimney maintenance in gas fireplaces. Blocked or damaged venting systems can lead to incomplete combustion and the dangerous buildup of CO indoors. Regular inspections and sweeping are essential for ensuring proper ventilation, preventing CO poisoning, and maintaining a safe living environment. This connection highlights the critical role of preventative maintenance in protecting occupants from the insidious threat posed by carbon monoxide.
4. Component Degradation
Component degradation within gas fireplace systems presents a compelling rationale for routine chimney maintenance. The gradual deterioration of venting and internal components can compromise functionality and safety, emphasizing the importance of regular inspections and servicing.
- Vent Pipe Corrosion
Gas fireplaces produce water vapor and acidic byproducts that can corrode metal vent pipes over time. This corrosion weakens the structural integrity of the venting system, potentially leading to leaks of combustion gases, including carbon monoxide, into the living space. Regular chimney inspections can identify corrosion early, allowing for timely repairs or replacements. Failure to address vent pipe corrosion directly answers the question of the necessity for maintenance.
- Burner Assembly Deterioration
The burner assembly, responsible for mixing gas and air for combustion, can degrade due to heat exposure and the accumulation of deposits. This deterioration can lead to incomplete combustion, resulting in increased carbon monoxide production and reduced heating efficiency. Professional cleaning and inspection of the burner assembly ensures optimal performance and minimizes safety risks.
- Pilot Light Malfunction
The pilot light, responsible for igniting the main burner, can become unreliable due to debris accumulation or thermocouple failure. An unreliable pilot light can lead to gas leaks and ignition problems. Regular maintenance includes cleaning and inspecting the pilot light assembly to ensure proper operation and prevent potential hazards.
- Gas Valve Wear
The gas valve controls the flow of gas to the fireplace. Over time, the valve can wear down or become contaminated, leading to erratic gas flow or leaks. A malfunctioning gas valve poses a significant safety risk. Professional inspection and testing of the gas valve are essential for ensuring safe and reliable operation. Addressing these issues relates directly to the need for chimney sweeping services.
These component degradations highlight the potential dangers associated with neglecting gas fireplace maintenance. Regular inspections and servicing by qualified professionals are crucial for identifying and addressing these issues before they compromise the safety and efficiency of the system. This proactive approach directly supports the argument that chimney maintenance, even for gas fireplaces, is a necessary and worthwhile investment.
5. Annual Inspection Benefit
The annual inspection of a gas fireplace system constitutes a proactive measure that directly addresses the central question of required chimney maintenance. These inspections, conducted by qualified professionals, serve as a comprehensive assessment of the system’s operational status and safety. The benefits derived from this assessment directly correlate with the necessity, or lack thereof, of subsequent chimney sweeping or maintenance activities. An inspection can reveal hidden problems such as minor blockages or early signs of corrosion that, if left unattended, could escalate into major issues requiring extensive cleaning or repairs. The ability to identify these early-stage problems underscores the inspection’s preventative role in mitigating potential hazards and maintaining system efficiency. For instance, an inspection might reveal a slight accumulation of debris in the vent, prompting a simple cleaning that prevents a more significant blockage later.
The value of the annual inspection extends beyond merely identifying existing problems; it also provides an opportunity to evaluate the overall condition of the system and to anticipate future maintenance needs. The inspector can assess the wear and tear on various components, such as the burner assembly and the venting system, and recommend proactive measures to extend their lifespan. Furthermore, the inspection includes a thorough check for gas leaks and carbon monoxide emissions, ensuring the safety of the occupants. For example, the discovery of a small gas leak during an inspection allows for immediate repair, preventing a potentially dangerous situation. The insight provided by an annual inspection aids in determining the appropriate course of action, which may or may not include a full chimney sweep.
In summary, the benefits derived from annual gas fireplace inspections are multifaceted and directly inform the question of necessary chimney maintenance. These inspections provide a comprehensive assessment of the system’s condition, identify existing and potential problems, and guide proactive maintenance measures. While not all inspections will lead to a requirement for immediate sweeping, the information gained is invaluable in ensuring safe and efficient operation, effectively addressing the core inquiry regarding the necessity of chimney maintenance for gas fireplaces. The result is increased safety, optimized performance, and informed decision-making regarding system upkeep.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries concerning the necessity of maintenance for gas fireplace venting systems, offering clarity on best practices.
Question 1: Are gas fireplaces truly “maintenance-free”?
Gas fireplaces require periodic maintenance, despite marketing claims. While producing less soot than wood-burning models, they still generate combustion byproducts and are subject to potential obstructions.
Question 2: What are the primary risks of neglecting gas fireplace maintenance?
Neglecting maintenance can lead to carbon monoxide leaks, inefficient operation, and potential system damage. Accumulated debris and corrosion can compromise venting systems.
Question 3: How frequently should a gas fireplace venting system be inspected?
A qualified professional should conduct an annual inspection of the venting system to identify potential problems and ensure safe operation.
Question 4: Can a homeowner inspect their own gas fireplace venting system?
While homeowners can visually inspect the vent termination for debris, a comprehensive inspection requires specialized knowledge and equipment best left to professionals.
Question 5: What are the warning signs that a gas fireplace needs professional attention?
Warning signs include unusual odors, sooting around the fireplace, a yellow flame instead of blue, and any malfunctions of the pilot light.
Question 6: Does the type of gas used (natural gas vs. propane) affect maintenance requirements?
The type of gas does not significantly alter maintenance requirements. Both natural gas and propane combustion produce byproducts that necessitate regular inspection and cleaning.
In summary, while gas fireplaces offer convenience, neglecting routine maintenance introduces significant risks. Annual inspections and prompt attention to warning signs are crucial.
The concluding section will reinforce the importance of professional chimney services for gas fireplaces, emphasizing the long-term benefits.
Conclusion
This discussion has thoroughly explored the necessity of professional maintenance for gas fireplace venting systems. While gas-burning units produce fewer particulates compared to wood-burning fireplaces, they are not exempt from the accumulation of combustion byproducts and the potential for venting obstructions. The risk of carbon monoxide leaks, coupled with the gradual degradation of system components, underscores the importance of periodic inspections. These inspections, conducted by qualified technicians, identify hidden problems and ensure the safe and efficient operation of the appliance.
Therefore, to ensure the continued safety and functionality of gas fireplaces, homeowners should prioritize regular venting system inspections and maintenance. Adherence to this recommendation will contribute to the longevity of the appliance, mitigate potential hazards, and provide peace of mind. Neglecting this aspect presents considerable risks that outweigh the cost and inconvenience of professional service. The responsibility for maintaining a safe and healthy living environment rests with the homeowner, and proactive maintenance of gas fireplace venting systems is an integral part of that responsibility.