Individuals or firms specializing in the assessment, maintenance, and restoration of chimney systems constitute a crucial segment of the construction and home maintenance industry. They possess specific expertise in diagnosing issues such as structural damage, blockages, and deterioration due to weather or age. Examples of their work include repairing cracks in masonry, relining flues, removing obstructions, and rebuilding damaged chimney crowns.
Their work ensures the safe and efficient venting of combustion byproducts from heating appliances and fireplaces, mitigating risks like carbon monoxide poisoning and chimney fires. Historically, chimney sweeps and masons handled these tasks; however, modern specialists possess advanced knowledge of building codes, materials science, and diagnostic techniques, leading to increased safety and effectiveness in chimney care. Properly maintained and repaired chimneys contribute significantly to property value and longevity.
The subsequent sections will delve into the qualifications and certifications often held by such professionals, the range of services offered, common chimney problems they address, and factors to consider when selecting a qualified service provider for chimney-related needs. The information will also include insight into preventative maintenance and its importance in ensuring the longevity of chimney systems.
Tips From Chimney Repair Professionals
Adhering to recommended guidelines can ensure the safety, efficiency, and longevity of chimney systems, preventing costly repairs and hazards.
Tip 1: Schedule Annual Inspections. Regular inspections by qualified personnel are essential for identifying potential problems early, before they escalate into major repairs. These inspections should include a visual assessment of the chimney’s exterior and interior.
Tip 2: Utilize Seasoned Wood. Burning dry, seasoned wood minimizes creosote buildup. Creosote is highly flammable and a leading cause of chimney fires. Allow wood to dry for at least six months before use.
Tip 3: Install a Chimney Cap. A chimney cap protects the flue from rain, snow, and debris, preventing water damage and blockages caused by animals or falling objects. It also serves as a spark arrestor.
Tip 4: Maintain Proper Ventilation. Ensure adequate airflow to the fireplace or heating appliance. Restricted airflow can lead to incomplete combustion, increased creosote production, and carbon monoxide buildup.
Tip 5: Address Water Leaks Promptly. Water penetration can cause significant damage to chimney masonry, leading to cracks, spalling, and structural instability. Identify and repair leaks as soon as they are detected.
Tip 6: Consider a Chimney Liner. If the existing flue liner is damaged or deteriorating, consider installing a new liner. Liners protect the chimney structure from corrosive combustion byproducts and ensure proper venting.
Tip 7: Clean Chimney Regularly. Regular cleaning removes creosote and other debris, reducing the risk of chimney fires and ensuring efficient venting. The frequency of cleaning depends on the type of fuel burned and the frequency of use.
Following these recommendations contributes to a safer and more efficient heating system, minimizing the risk of hazards and costly repairs. Prompt action regarding maintenance and repairs extends the lifespan of chimney structures.
The following sections will elaborate on the complexities of chimney repair processes and the importance of selecting experienced professionals to undertake such critical tasks.
1. Qualified professionals
The designation “chimney repair specialists” inherently implies a standard of competence. Qualification is the foundational element differentiating a skilled practitioner from an unqualified individual. The correlation between expertise and successful chimney maintenance rests on training, certification, and practical experience. For example, a professional holding certifications from organizations like the Chimney Safety Institute of America (CSIA) demonstrates a commitment to industry best practices and knowledge of relevant codes and standards. This ensures repairs are conducted effectively and safely.
The absence of qualified professionals in chimney maintenance can lead to detrimental consequences. Improper repairs may compromise the structural integrity of the chimney, resulting in potential collapses or hazardous venting of combustion gases into the dwelling. A homeowner engaging an unqualified individual might save money initially but risk incurring significantly higher costs later to rectify substandard work or address safety hazards. Furthermore, insurance claims related to chimney fires or carbon monoxide poisoning may be denied if work was performed by unqualified personnel.
In conclusion, engaging qualified professionals for chimney maintenance and repair is not merely a recommendation but a necessity. Their expertise mitigates risks, ensures code compliance, and protects property and lives. The practical significance lies in avoiding potential disasters and securing peace of mind regarding the safety and efficiency of the chimney system. Ongoing training and adherence to industry standards are vital for maintaining the qualifications of these specialists, safeguarding homeowners from the dangers of negligent or substandard work.
2. Comprehensive inspections
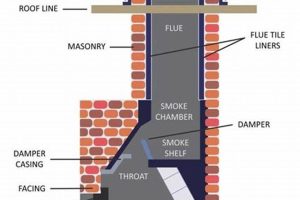
Comprehensive inspections are a cornerstone of professional chimney maintenance, acting as a systematic method by which qualified chimney repair specialists evaluate the structural and functional condition of chimney systems. These inspections go beyond a cursory visual assessment, employing advanced diagnostic techniques to identify potential issues that could compromise safety or efficiency.
- Structural Assessment
This facet involves a detailed examination of the chimney’s physical components, including the masonry, flue liner, crown, and flashing. Specialists look for signs of deterioration such as cracks, spalling, water damage, and mortar joint degradation. For instance, a thorough structural assessment might reveal hidden cracks in the flue liner, which can allow dangerous combustion gases to leak into the home. This type of finding underscores the need for timely repairs to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning and structural damage.
- Flue Obstruction Detection
Specialists utilize specialized equipment, such as video scanning tools, to identify blockages within the flue. Obstructions can include nests, debris, creosote buildup, or collapsed flue liners. A real-world example would be the discovery of a bird’s nest obstructing the flue, preventing proper ventilation and increasing the risk of chimney fires. Identifying and removing such obstructions is critical for maintaining efficient and safe chimney operation.
- Appliance Connection Evaluation
A comprehensive inspection extends to the connection between the chimney and the heating appliance it serves, whether a fireplace, furnace, or water heater. Specialists verify proper venting and ensure that the connection meets relevant safety codes. As an example, inadequate venting of a furnace can lead to carbon monoxide accumulation within the dwelling. Correct appliance connections are vital to prevent health hazards and ensure the efficient operation of heating systems.
- Water Intrusion Analysis
Water penetration can cause significant damage to chimney systems, leading to freeze-thaw damage, corrosion, and structural instability. Specialists investigate potential sources of water intrusion, such as damaged chimney crowns, faulty flashing, or porous masonry. As an illustration, a deteriorated chimney crown allows rainwater to seep into the brickwork, leading to spalling and eventual structural failure. Identifying and addressing water intrusion points are crucial for preserving the longevity of the chimney.
The insights gained from comprehensive inspections inform the recommendations for necessary repairs or maintenance, enabling specialists to address underlying issues before they escalate into costly or dangerous problems. These detailed assessments are not merely routine checks but rather proactive measures integral to responsible chimney management, ensuring safety and performance.
3. Material expertise
Material expertise constitutes a fundamental competency for chimney repair specialists. The selection and application of appropriate materials directly impact the longevity, safety, and performance of chimney systems. An understanding of the properties and limitations of various construction materials, such as different types of masonry, mortar, flue liners, and sealants, is essential for effective repair strategies. The inappropriate use of materials can result in accelerated deterioration, structural instability, and hazardous venting conditions. For example, employing a mortar mix incompatible with existing brickwork can lead to premature failure of the repair, necessitating further costly intervention. Similarly, selecting an inadequate flue liner for the type of fuel burned can result in corrosion and the release of harmful combustion byproducts into the dwelling.
Consider the practical example of repairing a chimney crown. A specialist lacking material expertise might opt for a generic concrete mix that is susceptible to cracking and water damage. A knowledgeable professional, conversely, would choose a specialized crown repair product formulated to withstand the harsh environmental conditions at the top of the chimney, ensuring a durable and water-resistant seal. Another example involves the selection of a flue liner for a wood-burning fireplace. Using a standard clay liner instead of a more durable stainless-steel liner could result in premature degradation due to the high temperatures and corrosive nature of wood smoke. This could eventually cause flue collapse and pose a significant fire hazard. The selection process requires a nuanced understanding of the specific demands placed on each component of the chimney system.
In summary, material expertise is not merely a desirable attribute but a critical requirement for chimney repair specialists. The knowledge base directly influences the quality, safety, and longevity of repair work. A specialist equipped with this knowledge can effectively diagnose problems, select appropriate materials, and implement durable solutions, mitigating risks and ensuring the efficient operation of the chimney system. Choosing a specialist who demonstrates a thorough understanding of materials science is a prudent investment that safeguards property and protects occupants from potential hazards associated with compromised chimney systems.
4. Safety adherence
Safety adherence forms a cornerstone of ethical and effective practice for chimney repair specialists. The profession intrinsically involves working at heights, handling potentially hazardous materials, and dealing with systems designed to contain combustion. A commitment to safety protocols is not merely a regulatory requirement but a fundamental responsibility to protect both the specialist and the property occupants. A disregard for safety can lead to severe consequences, including falls, burns, exposure to harmful substances like creosote or asbestos, and even catastrophic structural failures resulting in property damage or loss of life. For instance, failure to properly secure scaffolding or wear appropriate fall protection equipment while working on a chimney stack can result in serious injury or death. Similarly, inadequate ventilation during creosote removal can expose specialists to toxic fumes, causing respiratory problems or other health issues.
The practical application of safety protocols extends beyond the immediate work environment. Specialists must also ensure the safety of the chimney system itself. This includes proper installation of liners to prevent carbon monoxide leaks, correct sealing of chimney crowns to prevent water damage and structural decay, and thorough inspection to identify and address potential fire hazards. An example of this would be ensuring that a newly installed chimney liner is correctly sized and sealed to prevent the escape of combustion gases into the home. Improper installation can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning, a potentially fatal hazard. Adherence to safety standards and best practices is paramount in preventing such incidents.
In conclusion, safety adherence is inextricably linked to the credibility and effectiveness of chimney repair specialists. It encompasses not only the well-being of the professionals performing the work but also the safety and security of the property and its inhabitants. Rigorous training, adherence to industry standards, and a commitment to continuous improvement in safety practices are essential components of a responsible chimney repair service. The inherent risks associated with chimney work necessitate a safety-first approach, making safety adherence a non-negotiable aspect of professional competency in this field.
5. Structural integrity
The maintenance of structural integrity is a paramount concern in chimney systems, directly impacting the safety and functionality of the entire structure. Chimney repair specialists play a crucial role in ensuring this integrity by diagnosing and rectifying issues that compromise the chimney’s stability and resilience. Deterioration, often resulting from weather exposure, age, or improper construction, can weaken the chimney’s components, leading to cracks, spalling, or even collapse. For example, repeated freeze-thaw cycles can cause masonry to crumble, necessitating expert intervention to prevent further degradation. Without proper attention, such issues can escalate, posing significant risks to the property and its occupants.
Chimney repair specialists employ a range of techniques and materials to restore structural integrity. These include tuckpointing to repair mortar joints, relining flues to prevent gas leaks, and rebuilding damaged sections to restore stability. The selection of appropriate methods depends on the specific nature and extent of the damage. Consider the case of a chimney damaged by a lightning strike, where the upper portion may require complete reconstruction. Specialists ensure that the rebuilt section adheres to building codes and is properly integrated with the existing structure. Furthermore, preventative measures, such as applying waterproof sealants, can protect the chimney from future damage, extending its lifespan and minimizing the need for extensive repairs.
Preserving structural integrity through regular inspections and timely repairs is essential for maintaining the safety and functionality of chimney systems. Neglecting these issues can result in hazardous conditions, including chimney fires, carbon monoxide poisoning, and structural collapses. By engaging qualified chimney repair specialists, property owners can mitigate these risks and ensure the long-term stability and performance of their chimneys. This proactive approach safeguards property and protects the well-being of occupants, highlighting the practical significance of understanding the connection between structural integrity and the expertise of chimney repair professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns regarding chimney repair, providing clarity and valuable insight.
Question 1: What are the most common signs that indicate a chimney requires repair?
Observable signs often include spalling or crumbling brickwork, cracked or missing mortar joints, water stains on interior walls adjacent to the chimney, and visible damage to the chimney crown or flue liner. Soot buildup in unusual areas and a noticeable odor are further indicators.
Question 2: How often should a chimney be inspected for potential problems?
It is recommended that chimneys undergo professional inspection at least once per year, regardless of usage frequency. Chimneys serving regularly used fireplaces or heating appliances may require more frequent inspection schedules.
Question 3: What are the dangers of neglecting necessary chimney repairs?
Neglecting necessary chimney repairs can result in several hazards. These include carbon monoxide poisoning due to improper venting, chimney fires caused by creosote buildup, and structural collapse due to deterioration of the chimney’s components. Water damage within the home is also a possible consequence.
Question 4: Can a homeowner perform chimney repairs, or is professional intervention always required?
While certain minor maintenance tasks, such as cleaning debris from the firebox, can be performed by homeowners, most chimney repairs necessitate professional intervention. Qualified specialists possess the knowledge, tools, and experience to address complex issues safely and effectively.
Question 5: What qualifications or certifications should a chimney repair specialist possess?
Ideal qualifications include certification from organizations such as the Chimney Safety Institute of America (CSIA). Licensing and insurance coverage are also crucial considerations. Verifying these credentials ensures the specialist possesses the necessary expertise and complies with industry standards.
Question 6: What is the typical lifespan of a chimney, and what factors can affect its longevity?
The lifespan of a chimney varies depending on factors such as materials used, construction quality, maintenance practices, and exposure to environmental conditions. Properly maintained chimneys can last for several decades, while neglected chimneys may require significant repairs or replacement within a shorter timeframe. Regular inspections and timely repairs are crucial for maximizing longevity.
Understanding these key questions helps prioritize chimney safety and maintenance.
The next section will explore common chimney problems that specialists routinely address.
Chimney Repair Specialists
The preceding discussion elucidated the crucial role of chimney repair specialists in maintaining safe and efficient chimney systems. From comprehensive inspections to material expertise and adherence to safety protocols, these professionals possess the skills necessary to diagnose and address a wide range of chimney-related issues. The significance of their work extends beyond mere aesthetic improvements, directly impacting the structural integrity of buildings and the well-being of occupants.
Given the inherent risks associated with compromised chimney systems, engaging qualified specialists is not simply a matter of convenience, but a prudent decision that safeguards property and lives. Prioritizing regular inspections and timely repairs ensures the continued performance and longevity of chimney structures, mitigating potential hazards and providing peace of mind. The diligence invested in chimney maintenance reflects a commitment to safety and responsible property management.