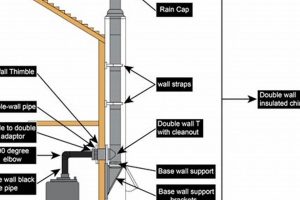
The process of setting up a venting system comprised of metallic components on the outer side of a structure to safely expel combustion byproducts from heating appliances is critical to the functionality and safety of residential and commercial buildings. This typically involves securing sections of specialized pipe together and adhering to strict building codes.
A properly executed setup ensures the efficient removal of dangerous gases, like carbon monoxide, mitigating potential health risks and property damage. It also protects the building’s structural integrity by channeling heat away from combustible materials. The design and implementation of these systems have evolved over time, improving safety standards and energy efficiency.
This discussion will explore key considerations during planning and execution including selection of appropriate materials and crucial safety protocols. It will also cover recommended maintenance procedures for optimal system performance and longevity.
Considerations for Safe and Effective Setup
The following guidelines are designed to enhance the safety and effectiveness of the venting system. Diligent adherence to these points contributes to a secure and optimally functioning installation.
Tip 1: Prioritize Code Compliance: Local building codes and manufacturer instructions represent essential guidelines. Strict adherence to these regulations is paramount for safe operation and legal compliance.
Tip 2: Ensure Proper Clearance to Combustibles: Maintaining the specified clearance distance between the pipe and any combustible materials, such as wood framing or siding, is vital. This minimizes the risk of fire hazards. Consult manufacturer specifications for precise clearance requirements.
Tip 3: Implement Secure and Weatherproof Connections: All pipe sections must be securely joined and sealed to prevent leakage of exhaust gases and moisture penetration. Use appropriate sealing materials rated for high temperatures, and verify that each joint is properly fastened.
Tip 4: Utilize Proper Support and Bracing: The venting system requires adequate support to prevent sagging or stress on the pipe sections. Employ appropriately rated support brackets and bracing at specified intervals to ensure structural stability.
Tip 5: Implement a Rain Cap: The installation of a rain cap at the termination point prevents water and debris from entering the system. This reduces the risk of corrosion and blockage, maintaining efficient ventilation.
Tip 6: Grounding Properly: In some instances, grounding of metallic components may be necessary to prevent the buildup of static electricity, which could cause sparks near combustible gases. Refer to local codes and consult with a qualified electrician.
Tip 7: Perform Regular Visual Inspections: Periodic visual inspections of the system’s components, including pipe sections, connections, and support brackets, allow for the early detection of potential problems, such as corrosion, leaks, or structural damage. Schedule inspections at least annually, or more frequently depending on usage.
By carefully observing these guidelines, the integrity and operational efficiency of the venting apparatus can be substantially improved. The result is a safer environment for occupants, with a prolonged lifespan for the heating equipment.
The following section will cover recommended maintenance schedules to prolong system life and integrity.
1. Proper Pipe Sizing
Appropriate pipe diameter is an indispensable element of an exterior metallic venting system. Selection directly influences the performance, efficiency, and safety of the connected heating appliance. Undersized or oversized components can compromise the system’s functionality and create hazardous conditions.
- Draft Optimization
Correct dimensions are critical for establishing adequate draft. An appropriately sized pipe facilitates the efficient removal of combustion byproducts. Insufficient draft can lead to backdrafting, where exhaust gases enter the living space, posing a significant health risk. Conversely, excessive draft can lead to rapid heat loss and reduced appliance efficiency. The diameter is directly related to the flue gas velocity and needs to be properly calculated.
- Appliance Compatibility
Heating appliance manufacturers specify precise pipe diameter requirements for their products. Utilizing incorrect sizes can void warranties and compromise the appliance’s intended performance. Matching the pipe diameter to the appliance’s specifications ensures optimal combustion and heat transfer.
- Creosote Formation
Improperly sized pipes can affect the flue gas temperature. Lower temperatures can lead to increased creosote condensation within the venting system. Creosote is a highly flammable substance, and its accumulation increases the risk of chimney fires. Optimizing the diameter aids in maintaining appropriate flue gas temperatures, minimizing creosote buildup.
- Code Adherence and Safety
Building codes mandate specific pipe size requirements based on the connected appliance and the venting system’s configuration. These regulations are designed to ensure safe operation and minimize the risk of fire or carbon monoxide poisoning. Adhering to code ensures the installation meets minimum safety standards, as demonstrated by permits requiring calculations.
The foregoing demonstrates that appropriate sizing is not simply a matter of selecting a pipe that “fits.” It is a critical engineering consideration that directly affects safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Precise calculations and adherence to manufacturer specifications are paramount when establishing exterior venting systems.
2. Secure Joint Connections
Within the context of exterior metallic venting systems, secure joint connections represent a critical element for ensuring safe and effective operation. The integrity of these connections directly impacts the system’s ability to contain and expel hazardous combustion byproducts. Compromised joints serve as potential pathways for the leakage of toxic gases, including carbon monoxide, into the surrounding environment.
The implementation of robust jointing methods, such as employing appropriate sealing materials rated for high temperatures and pressures, alongside mechanical fasteners designed to withstand thermal expansion and contraction, is paramount. For example, the use of improperly sealed or loosely connected pipes during the setup process can lead to undetectable, yet persistent, emissions of carbon monoxide into a residence. This scenario underscores the importance of meticulous attention to detail and adherence to manufacturer specifications during the assembly process. Additionally, consider a scenario involving severe weather conditions where high winds or heavy snow loads exert stress on a venting system. Weakened or improperly secured joints are more susceptible to separation, potentially leading to structural damage and posing immediate safety risks to building occupants.
In summary, the significance of secure joint connections in metallic venting systems cannot be overstated. They represent a fundamental safeguard against the dangers of gas leaks and structural failure. Diligent execution, adherence to established installation protocols, and the utilization of appropriate materials are essential for ensuring the long-term safety and reliability of these systems. A proactive approach to joint security, including routine inspections and timely repairs, contributes significantly to maintaining a safe indoor environment and mitigating potential hazards associated with heating appliance operation.
3. Adequate Structural Support
The provision of adequate structural support is fundamentally intertwined with the integrity and longevity of an exterior metallic venting system. The venting system, often exposed to environmental stressors like wind, snow, and temperature fluctuations, requires a robust support structure to maintain its position and prevent failure. Absent appropriate support, the system’s weight and external forces can induce stress on the pipe sections and joints, leading to potential leaks, structural damage, and even complete collapse.
Consider the scenario of a tall, unsupported venting system subjected to high winds. The resulting oscillations and vibrations can fatigue the metal, particularly at the joints, eventually causing them to loosen or separate. This compromises the system’s ability to safely expel exhaust gases, potentially leading to carbon monoxide intrusion into the building. Furthermore, inadequate support can cause the pipe to sag or bend, restricting airflow and reducing the efficiency of the connected heating appliance. For example, the use of incorrectly spaced or undersized support brackets would fail to counteract gravitational forces and wind loads, resulting in strain on the system.
In conclusion, adequate structural support is not merely an ancillary component but a critical determinant of the venting system’s performance and safety. Proper design, selection of appropriately rated support hardware, and adherence to established installation guidelines are essential to mitigate the risks associated with environmental factors and ensure the system’s long-term reliability. Regular inspection and maintenance of the support structure are also crucial to identify and address any signs of deterioration or instability, thereby safeguarding the building and its occupants.
4. Correct Termination Height
The vertical positioning of an exhaust vent, termed the termination height, is inextricably linked to the effective function of an exterior metallic venting system. This height directly impacts the system’s ability to establish adequate draft, safely disperse exhaust gases, and mitigate potential hazards related to re-entrainment. An improperly positioned termination point can compromise system performance and jeopardize occupant safety. The termination height is governed by code and appliance specifications.
Insufficient height may result in downdrafts, where prevailing winds force exhaust gases back down the flue and into the building. This creates the potential for carbon monoxide poisoning and reduces heating appliance efficiency. Conversely, excessive height can lead to excessive draft, resulting in rapid heat loss and increased fuel consumption. Furthermore, building codes often specify minimum distances between the termination point and adjacent structures, rooflines, and vegetation to prevent the accumulation of combustible deposits and minimize the risk of fire. A common error involves neglecting to extend the termination point above the highest point of the roof within a specified radius. This can lead to snow accumulation around the vent, blocking the exhaust path and creating a hazardous condition. Correct termination is not merely aesthetic, it is a functional safety imperative.
In summary, the determination of appropriate termination height requires careful consideration of several factors, including local building codes, appliance manufacturer specifications, and prevailing wind conditions. Adherence to established guidelines ensures efficient exhaust removal, minimizes the risk of backdrafting and fire hazards, and promotes a safe and healthy indoor environment. Regular inspection of the termination point is also essential to identify and address any potential obstructions or damage, thereby maintaining the system’s overall performance and safety.
5. Weatherproof Sealing
Weatherproof sealing constitutes an indispensable aspect of the successful and enduring operation of an exterior metallic venting system. The primary function of this sealing is to prevent the ingress of moisture, including rainwater and snow, into the system’s internal components. Penetration by water can initiate or accelerate corrosion of metallic components, reduce insulation effectiveness, and ultimately compromise the venting system’s structural integrity. For example, water ingress can deteriorate internal liners, leading to compromised draft and potential gas leakage. Furthermore, the presence of moisture can create an environment conducive to the growth of mold and mildew, impacting indoor air quality.
Effective weatherproof sealing requires the application of appropriate sealing materials specifically rated for exterior use and high-temperature conditions. These materials must be resistant to UV radiation, extreme temperature fluctuations, and chemical degradation. Seals must be properly applied at all joints and connections to create a continuous barrier against moisture. Consider the consequences of neglecting to properly seal the juncture between a metallic pipe section and a roof flashing. In such a scenario, rainwater can penetrate the system, leading to rust formation and eventual structural failure. This, in turn, necessitates costly repairs and potentially poses a safety hazard. Moreover, this moisture intrusion could saturate any insulation material, reducing its effectiveness and leading to decreased efficiency.
In conclusion, weatherproof sealing represents a critical preventative measure against environmental damage and operational failure in an exterior metallic venting system. Selection and proper application of suitable sealing materials, combined with regular inspections to identify and address any breaches in the seal, are essential for ensuring the long-term performance, safety, and reliability of the system. Failure to prioritize weatherproof sealing leads to a cascade of negative consequences, ranging from reduced efficiency and increased maintenance costs to potential safety hazards and structural damage.
6. Code Compliance Verification
Code compliance verification is an inseparable component of the process involving metallic venting systems on the exterior of structures. Adherence to established building codes and regulations is not merely a procedural formality, but a critical determinant of the system’s safety, efficiency, and longevity. Failure to verify compliance can result in structural hazards, health risks, and legal liabilities. Local building codes dictate specific requirements for materials, dimensions, clearances, and installation methods to ensure the system operates safely and effectively. Verification involves confirming that the selected components meet these standards and that the installation adheres to prescribed guidelines. A key consideration is ensuring that the installer possesses the proper certifications.
The cause-and-effect relationship between code compliance and a successful installation is demonstrable. For instance, a system installed without the necessary permits and inspections may lack proper clearances to combustible materials, leading to an elevated fire risk. Similarly, the utilization of unapproved components can compromise the system’s structural integrity, increasing the likelihood of failure under adverse weather conditions. An example would be neglecting to maintain a minimum clearance from a window. These situations not only endanger the building occupants but also expose the property owner to potential legal repercussions. Code compliance verification is multifaceted. It includes obtaining necessary permits, scheduling inspections by qualified authorities, and maintaining records of all relevant documentation.
In summation, code compliance verification is not an optional addendum, but a mandatory element in the process of installing metallic venting systems. Thorough verification, involving meticulous adherence to established codes and regulations, serves as a vital safeguard against potential hazards and ensures the system operates safely, efficiently, and reliably. It is important to recognize the complexity of the code and ensure that any modifications are properly inspected and approved. The consequences of neglecting this crucial step can range from property damage and legal penalties to severe injury or loss of life.
7. Regular System Inspection
The longevity and safe operation of an exterior metallic venting system are inextricably linked to the implementation of regular system inspections. This practice is not merely a recommended maintenance procedure, but a critical component of ensuring the ongoing integrity of the initial setup. The external environment subjects these systems to a range of stressors, including temperature fluctuations, precipitation, and wind, all of which can contribute to degradation and potential failure. Routine examination facilitates the early detection of issues such as corrosion, leaks, structural damage, and obstructions. These problems, if left unaddressed, can compromise the system’s functionality and pose significant safety risks, including carbon monoxide poisoning and fire hazards.
A consistent inspection schedule allows for proactive maintenance and repairs, preventing minor issues from escalating into major, more costly problems. For instance, the identification of early signs of rust or corrosion allows for targeted treatment, extending the lifespan of the metal components. Detection of loose or damaged support brackets enables timely replacement, preventing the system from sagging or collapsing. Furthermore, the removal of debris such as leaves, nests, or snow accumulation ensures unrestricted airflow and optimal system performance. Consider a scenario where a small leak develops at a joint due to thermal expansion and contraction. Without regular inspection, this leak may remain undetected, leading to gradual water damage to the building structure and increased risk of carbon monoxide infiltration. Conversely, a routine inspection would identify the leak and allow for prompt sealing, preventing further damage and mitigating potential hazards.
In summary, regular system inspection is a vital component of ensuring the safe and efficient operation of an exterior metallic venting system. It enables the early detection and correction of potential problems, preventing costly repairs and mitigating safety risks. By prioritizing regular inspections, building owners and occupants can maintain the integrity of the system, protect their property, and safeguard their health and well-being. Neglecting this aspect can lead to a range of adverse consequences, underscoring the importance of incorporating system inspections into a routine maintenance schedule.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Metallic Venting Systems on Building Exteriors
The subsequent section addresses commonly encountered inquiries pertaining to the setup and maintenance of metallic venting systems. These questions are answered with a focus on providing clear, concise, and technically accurate information.
Question 1: What factors influence the selection of appropriate pipe diameter for an exterior metallic venting system?
The diameter is primarily dictated by the heating appliance’s specifications and local building codes. An undersized or oversized pipe can impair draft and combustion efficiency.
Question 2: How frequently should an exterior metallic venting system be inspected for potential issues?
A minimum of annual inspections is recommended. More frequent inspections may be necessary depending on usage and environmental conditions.
Question 3: What constitutes an acceptable sealing material for joint connections in an exterior metallic venting system?
Sealing materials must be specifically rated for high temperatures, resistance to UV radiation, and prolonged exposure to weather elements. Materials must also comply with local code.
Question 4: What are the potential consequences of failing to maintain adequate clearance between the vent pipe and combustible materials?
Insufficient clearance increases the risk of fire hazards, as the heat radiating from the pipe can ignite nearby combustible materials.
Question 5: How does the termination height of an exterior metallic venting system impact its overall performance?
Improper termination height can lead to downdrafts, reduced efficiency, and potential re-entrainment of exhaust gases into the building. Building code and appliance installation directions dictate proper height.
Question 6: What steps should be taken to address corrosion on an exterior metallic venting system?
Corroded sections should be replaced immediately. The source of the corrosion should be identified and addressed to prevent recurrence, like improper sealing leading to water ingress.
These are only some of the common inquiries that building owners and installers face. Strict adherence to installation guidelines and local building codes will greatly reduce future problems.
Next, we will explore common errors during setup and practical solutions to avoid them.
Exterior Metal Chimney Pipe Installation
This discussion has illuminated the critical aspects of safe and effective exterior metal chimney pipe installation. It has emphasized the importance of proper planning, meticulous execution, adherence to code, and consistent maintenance. Correct pipe sizing, secure joint connections, adequate structural support, appropriate termination height, and weatherproof sealing are not merely desirable features, but essential safeguards for building occupants and property.
The information presented serves as a foundation for informed decision-making and responsible implementation. Building owners, contractors, and installers are strongly encouraged to prioritize safety, seek professional guidance when necessary, and diligently uphold all applicable codes and regulations. A properly installed and maintained metallic venting system represents a significant investment in long-term safety, efficiency, and peace of mind.