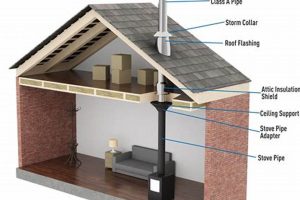
A specialized component affixed to the termination of a flue, designed to mitigate the adverse effects of gusts and downdrafts on appliance venting. These devices prevent wind from entering the chimney, which can disrupt the proper exhaust of combustion byproducts and potentially force smoke and dangerous gases back into the living space. An example is a model featuring a strategically designed hood and mesh to deflect horizontal air currents, ensuring consistent updraft.
The installation of such a device offers several key advantages. It enhances the efficiency of heating appliances by maintaining a stable draft, reduces the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning by preventing backdrafting, and minimizes the entry of rain, snow, and debris into the flue, thereby prolonging the lifespan of the chimney structure and connected systems. Historically, simple cowls served similar purposes, evolving over time into more sophisticated designs to address increasingly complex venting challenges.
The subsequent sections will delve into the specific types available, factors to consider when selecting an appropriate model, proper installation techniques, and maintenance procedures to ensure long-term effectiveness. Further discussion will include troubleshooting common issues and examining relevant building codes and safety standards.
Guidance for Optimal Performance
Effective implementation and maintenance are crucial for achieving the intended benefits of employing a device designed to mitigate wind-related venting issues. The following guidance offers practical measures to ensure its longevity and effectiveness.
Tip 1: Select a Compatible Model: Ensure the chosen device is specifically designed for the appliance and fuel type (e.g., gas, wood, oil). Compatibility information should be verified with the manufacturer’s specifications.
Tip 2: Professional Installation is Recommended: Improper installation can negate its benefits or, worse, create hazards. Engage a qualified chimney sweep or certified installer for optimal placement and secure attachment.
Tip 3: Regularly Inspect for Damage: Conduct routine visual inspections for signs of corrosion, physical damage from weather, or obstructions. Promptly address any issues to prevent performance degradation.
Tip 4: Clean Debris Annually: Leaves, twigs, and bird nests can accumulate within or around it, impeding airflow. Annual cleaning, ideally before the heating season, is essential.
Tip 5: Consider Material Durability: Stainless steel offers superior resistance to corrosion compared to galvanized steel, especially in coastal or harsh environments. Invest in higher-quality materials for extended lifespan.
Tip 6: Check for Proper Draft: After installation, verify the appliance drafts correctly. If backdrafting occurs, investigate potential obstructions or issues with the chimney itself.
Tip 7: Address Chimney Issues Promptly: If you observe excessive soot or creosote buildup during inspection, address chimney issues before considering the cap installation. Creosote buildup creates a fire hazard and affects the cap’s efficiency.
By adhering to these guidelines, property owners can maximize the operational lifespan and ensure the continued effectiveness of measures taken to protect the dwelling from wind-related venting problems.
The subsequent section will provide an overview of troubleshooting common issues encountered, followed by an examination of regulatory compliance and prevailing safety standards.
1. Draft Stabilization
Draft stabilization, the consistent maintenance of upward airflow within a chimney, is a primary function and consequential benefit derived from the utilization of a specialized flue termination device. Wind, acting upon an unprotected chimney, can induce erratic draft patterns, characterized by downdrafts or turbulent airflow. Such disturbances disrupt the combustion process, leading to inefficient fuel usage, elevated emissions, and potential backflow of harmful gases into the inhabited structure. The purpose-built design features of a device to mitigate wind effects, such as strategically angled hoods and directional vanes, are specifically engineered to counteract these disruptive forces, thereby fostering a stable and predictable draft.
For instance, consider a residential heating system operating in a region prone to strong prevailing winds. Without an appropriate flue termination device, gusts impacting the chimney’s opening could force exhaust gases back into the dwelling, triggering carbon monoxide alarms. The installation of a model featuring a robust, multi-directional hood effectively deflects the horizontal wind forces, maintaining a consistent upward draft. Similarly, in taller buildings, stack effect, combined with external wind, can create significant pressure differentials within the chimney. A device incorporating a rotating cowl dynamically adjusts to wind direction, mitigating pressure fluctuations and stabilizing the draft regardless of wind orientation.
In summary, draft stabilization is not merely a desirable attribute but a fundamental requirement for the safe and efficient operation of any venting system exposed to variable wind conditions. The proper selection and installation of these specialized devices are thus crucial for mitigating adverse wind effects and ensuring consistent, reliable flue performance, supporting both occupant safety and optimal appliance operation. The understanding of this connection is essential for homeowners, building managers, and HVAC professionals alike.
2. Backdraft Prevention
Backdraft prevention represents a critical safety function directly linked to the design and implementation of a device designed to mitigate wind’s impact on chimney performance. A backdraft occurs when the normal flow of combustion gases reverses, forcing potentially lethal carbon monoxide and other byproducts into the living space. Wind gusts interacting with an unprotected chimney outlet are a primary cause of this phenomenon. The strategic design of such devices directly addresses this hazard by physically obstructing or redirecting wind currents that would otherwise induce a backdraft.
Consider a scenario in a residential dwelling with a wood-burning fireplace. Without effective backdraft prevention, a sudden gust of wind could enter the chimney, overpowering the natural draft and pushing smoke, along with carbon monoxide, back into the room. A specialized termination device, incorporating a deflector or cowl, significantly reduces this risk by creating a zone of negative pressure around the chimney outlet, effectively preventing wind from reversing the flow of combustion gases. In industrial settings, where large combustion processes are common, wind-induced backdrafts can disrupt operations and pose significant safety risks to personnel. These devices, in such contexts, play a vital role in maintaining consistent venting and preventing the accumulation of hazardous gases.
The understanding of this critical connection is paramount for building owners, HVAC professionals, and chimney sweeps. Proper selection and installation according to manufacturer specifications, coupled with routine inspection and maintenance, ensures continued backdraft prevention and thereby safeguards building occupants from the dangers of carbon monoxide poisoning. Furthermore, adherence to local building codes and safety standards pertaining to chimney venting is essential for maintaining the effectiveness of backdraft prevention strategies.
3. Debris Exclusion
Debris exclusion, in the context of flue systems, constitutes a crucial function of a chimney termination device designed to mitigate wind effects. The accumulation of foreign materials within the chimney can impede proper venting, compromise structural integrity, and elevate the risk of fire. Devices engineered to minimize wind influence concurrently serve as barriers against the intrusion of such materials.
- Physical Barrier Functionality
This entails the employment of mesh screens or strategically designed hoods to prevent the ingress of leaves, twigs, animal nests, and other airborne debris. These physical barriers maintain unobstructed airflow while effectively filtering out particulate matter. For instance, a fine mesh screen prevents birds and rodents from entering the flue, minimizing the risk of blockage and potential chimney fires.
- Water Intrusion Mitigation
Beyond solid debris, these devices often incorporate designs that minimize rainwater and snow entry. Excessive moisture can accelerate chimney deterioration, promote mold growth, and damage connected appliances. A sloped hood, for example, effectively deflects precipitation, channeling it away from the flue opening. This reduces the risk of internal damage caused by freezing and thawing cycles during the winter months.
- Reduction of Creosote Buildup
While not directly preventing debris entry, these devices can indirectly reduce creosote buildup in wood-burning systems. By promoting consistent draft and preventing downdrafts, they contribute to more complete combustion, which, in turn, lowers creosote production. Less debris entry translates to a more consistently functioning flue, aiding in optimal combustion.
- Enhanced System Longevity
By preventing the accumulation of debris and moisture, these devices contribute to the overall longevity of the chimney and connected appliances. Reduced corrosion, minimized blockage, and consistent draft all contribute to a more reliable and durable venting system. A well-maintained system ensures the safe and efficient operation of heating appliances over an extended period.
The facets of debris exclusion are essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the chimney system. Therefore, the proper design, installation, and maintenance of a device designed to mitigate wind effects is inextricably linked to preventing the accumulation of debris, enhancing overall performance and longevity.
4. Material Durability
Material durability is a paramount consideration in the selection and performance of devices designed to mitigate wind’s effects on chimney function. The device’s ability to withstand prolonged exposure to harsh environmental conditions directly influences its effectiveness and lifespan. Choosing appropriate materials is thus essential for ensuring sustained protection against wind-induced venting problems.
- Corrosion Resistance
The materials used must exhibit high resistance to corrosion from flue gases, precipitation, and atmospheric pollutants. Stainless steel, particularly 304 or 316 grades, is frequently employed due to its superior corrosion resistance compared to galvanized steel or aluminum. In coastal environments, where salt spray accelerates corrosion, stainless steel provides a significantly longer service life. Failure to select corrosion-resistant materials leads to structural weakening, compromising the device’s ability to withstand wind forces and potentially causing failure.
- Structural Strength
The material must possess sufficient tensile strength and rigidity to withstand high wind loads without deformation or failure. Devices subjected to strong winds experience significant stress, and inadequate material strength results in bending, cracking, or detachment. For example, a device constructed from lightweight aluminum may be suitable for areas with mild winds but inadequate for regions prone to hurricanes or severe storms. Reinforced designs and thicker gauges of metal enhance structural integrity, ensuring the device maintains its shape and function under extreme conditions.
- Thermal Stability
Fluctuations in temperature, particularly during chimney operation, induce thermal stress in the materials. The chosen material must exhibit minimal expansion and contraction with temperature changes to prevent cracking or loosening of joints. Materials with high coefficients of thermal expansion, if not properly compensated for in the design, can lead to premature failure. In applications involving high-temperature appliances, such as wood stoves or industrial furnaces, material selection becomes even more critical to prevent heat-induced degradation.
- UV Resistance
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight can degrade certain materials, such as plastics or coatings, over time. UV degradation leads to embrittlement, discoloration, and loss of strength. If plastic components are used, they must be UV-stabilized to prevent premature deterioration. The use of UV-resistant coatings on metal surfaces also extends their lifespan by protecting against corrosion and fading. Selecting materials with inherent UV resistance or applying protective coatings ensures long-term durability, especially in regions with high levels of solar radiation.
The aforementioned material properties are intricately connected to the overall effectiveness of measures taken to mitigate wind effects. The selection of durable, corrosion-resistant, and structurally sound materials not only extends the lifespan of the device but also ensures consistent and reliable performance in preventing wind-induced venting problems. Careful consideration of material durability is therefore an essential component of the selection process.
5. Efficient Combustion
Efficient combustion, the complete oxidation of fuel resulting in maximum heat release and minimal emissions, is inextricably linked to the function of a chimney termination device designed to mitigate wind effects. These devices contribute to efficient combustion by stabilizing draft, preventing backdrafts, and maintaining consistent airflow, all of which are crucial for optimizing the combustion process within heating appliances. An unstable or disrupted draft, often caused by wind interference, leads to incomplete combustion, resulting in reduced heating efficiency, increased fuel consumption, and elevated levels of pollutants such as carbon monoxide and particulate matter. For instance, a wood-burning stove exposed to gusty winds may experience erratic burning, characterized by smoldering fires and excessive smoke. A chimney termination device designed to mitigate wind effects ensures a steady draft, promoting cleaner and more complete burning of the wood.
The design features incorporated in such a device directly impact combustion efficiency. Strategically angled hoods, directional vanes, and pressure-equalizing mechanisms minimize the disruptive effects of wind, fostering a stable and predictable draft within the flue. This stable draft ensures that the combustion chamber receives an adequate and consistent supply of oxygen, promoting more complete fuel oxidation. In gas-fired appliances, a stable draft prevents flame lift-off and ensures proper mixing of fuel and air, maximizing heat output and minimizing the formation of carbon monoxide. In oil-fired systems, a consistent draft prevents soot formation and incomplete combustion, reducing the risk of burner malfunctions and improving overall fuel efficiency. These examples underscore the practical significance of a device designed to mitigate wind effects, not merely as a means of preventing backdrafts and debris entry, but as a crucial component for achieving efficient and clean combustion.
In summary, efficient combustion is not merely a desirable outcome but a critical requirement for the safe and economical operation of heating appliances. The utilization of a chimney termination device designed to mitigate wind effects directly contributes to efficient combustion by stabilizing draft, preventing backdrafts, and maintaining consistent airflow. This, in turn, results in reduced fuel consumption, lower emissions, and improved appliance performance. The selection, installation, and maintenance of such a device should therefore be prioritized as integral to optimizing the overall efficiency and safety of any combustion-based heating system.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Wind-Resistant Chimney Terminations
This section addresses common inquiries concerning chimney terminations designed to mitigate wind-induced drafting issues. It provides concise, factual responses to enhance understanding of these specialized components.
Question 1: What defines a chimney termination as “wind-resistant?”
A wind-resistant design incorporates features that minimize the impact of wind gusts on the chimney’s draft. These include strategically shaped cowls, directional vanes, and pressure-equalizing mechanisms to maintain stable airflow within the flue.
Question 2: How does a wind-resistant termination prevent backdrafting?
By deflecting wind away from the chimney opening, these terminations create a zone of negative pressure that discourages the reversal of flue gas flow, thus preventing the reentry of combustion byproducts into the living space.
Question 3: Are wind-resistant terminations effective in all wind conditions?
While designed to mitigate most wind conditions, extreme wind events, such as hurricanes or tornadoes, may still disrupt draft. The effectiveness depends on the specific design and the severity of the weather.
Question 4: Do these terminations impede chimney cleaning and maintenance?
Well-designed models allow for easy removal or access for cleaning and inspection. Some even incorporate hinged or removable components to facilitate maintenance procedures.
Question 5: What materials are best suited for wind-resistant chimney terminations?
Stainless steel is generally preferred due to its corrosion resistance, structural strength, and longevity. Galvanized steel and aluminum are less durable alternatives. The selection depends on the climate and fuel type.
Question 6: How does improper installation affect the performance of a wind-resistant termination?
Incorrect installation negates its benefits and can create hazardous conditions. Secure and level attachment, along with proper sizing and compatibility with the flue, are essential for optimal performance.
Key takeaways include the recognition of the importance of wind-resistant features in chimney termination design, with proper installation as paramount.
The following section will elaborate on troubleshooting common issues related to draft control.
Concluding Remarks on the Wind Proof Chimney Cap
The foregoing discussion has illuminated the multifaceted benefits of employing a wind proof chimney cap. From draft stabilization to debris exclusion and enhanced combustion efficiency, the judicious application of this component is demonstrably crucial for ensuring safe and effective venting. The selection of durable materials, adherence to proper installation techniques, and consistent maintenance practices all contribute to optimizing performance and longevity. These are vital considerations in ensuring the health and safety of building occupants.
The implementation of the wind proof chimney cap represents a proactive measure in safeguarding against the detrimental effects of wind-induced drafting issues. Continued vigilance and adherence to best practices in chimney maintenance remain essential. Further research and development in chimney technology may lead to even more effective solutions. Until then, prioritizing the selection and upkeep of a wind proof chimney cap constitutes a prudent investment in safety and structural integrity.



![Protect Your Chimney: Menards Chimney Caps [Shop Now] Chimney Works – Expert Chimney Repair, Cleaning & Installation Services Protect Your Chimney: Menards Chimney Caps [Shop Now] | Chimney Works – Expert Chimney Repair, Cleaning & Installation Services](https://thechimneyworks.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-290-300x200.jpg)