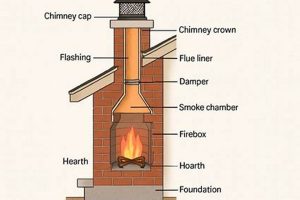
The individual dedicated to the inspection, maintenance, and repair of vertical structures that exhaust combustion byproducts is commonly associated with a vital role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of heating appliances. This professional’s responsibilities encompass tasks such as removing creosote buildup, identifying structural weaknesses, and ensuring proper ventilation to prevent hazards like carbon monoxide poisoning. For instance, a homeowner might engage this specialist to perform an annual inspection before the heating season begins, addressing any potential issues proactively.
The necessity of this occupation stems from its contribution to fire safety, energy efficiency, and the longevity of heating systems. Historically, this occupation has been essential in populated areas that relied heavily on wood-burning stoves and fireplaces for warmth. Regular service prevents dangerous chimney fires, improves draft, and reduces the risk of structural damage to homes. This practice promotes the well-being of occupants and the preservation of property.
Given the importance of maintaining these structures, further detailed discussion will cover techniques for inspection and cleaning, safety protocols, regulations related to emissions, and advancements in tools and technologies used in this field. The scope extends to cover both residential and commercial applications, addressing specific challenges associated with different types of installations and fuels.
Essential Maintenance Guidelines
Proper upkeep of venting systems is crucial for safety and efficiency. Adherence to these guidelines can minimize risks and maximize performance.
Tip 1: Schedule Annual Inspections. A certified professional should conduct yearly examinations to detect structural damage, creosote buildup, and other potential hazards. Early detection allows for timely repairs, preventing costly issues.
Tip 2: Address Creosote Accumulation. Regular cleaning is necessary to remove creosote, a flammable byproduct of combustion. Excessive buildup poses a significant fire risk. The frequency of cleaning depends on usage and fuel type.
Tip 3: Maintain Proper Ventilation. Ensure unobstructed airflow to support efficient combustion and prevent backdrafting of dangerous gases like carbon monoxide. Check for blockages from nests or debris.
Tip 4: Inspect for Structural Integrity. Cracks, spalling, or deterioration of brickwork can compromise the structural soundness of the chimney. Addressing these issues promptly prevents collapse or water damage.
Tip 5: Use Seasoned Wood. Burning dry, seasoned wood reduces creosote production compared to burning wet or unseasoned wood. Seasoned wood also burns more efficiently, providing more heat.
Tip 6: Consider a Chimney Cap. A chimney cap prevents rain, snow, and debris from entering the flue, protecting the structure and preventing blockages. It also deters animals from nesting inside.
These maintenance practices are paramount to ensuring safe and efficient operation. Neglecting these guidelines can lead to hazardous conditions and costly repairs.
The following sections will delve deeper into specific aspects of inspection techniques and repair methods.
1. Inspection Expertise
The professional assessment of venting systems is a foundational element of maintaining operational safety and structural integrity. This facet constitutes a crucial component of the services rendered by individuals specializing in chimney maintenance. Without proficiency in inspection, potential hazards such as creosote accumulation, structural defects, or improper ventilation can remain undetected, resulting in elevated risks of fire, carbon monoxide intrusion, and compromised system performance. For example, a thorough internal flue inspection, involving specialized cameras when necessary, can reveal hairline cracks invisible to the naked eye, preventing possible breaches. The effective application of inspection expertise directly affects the safety and well-being of occupants within a structure.
Inspection expertise encompasses a range of diagnostic skills, including visual assessments, pressure testing, and the utilization of specialized equipment. Technicians must be adept at interpreting the findings of these inspections to accurately diagnose existing issues and predict potential future problems. Consider a scenario where a seasoned professional identifies improper installation of a flue liner during a routine inspection; the expert’s insight prevents future hazards, such as leakage of harmful exhaust gases. This expertise translates into tangible benefits for homeowners and building managers through enhanced safety, improved energy efficiency, and reduced maintenance costs.
In summary, thorough inspection is indispensable. The ability to identify and accurately assess problems represents the cornerstone of effective chimney maintenance. This expertise not only safeguards property and lives, but also ensures the sustained performance and longevity of the systems under examination. Further education and training are essential in keeping pace with evolving standards and technologies within the field, contributing to the ongoing refinement of inspection practices.
2. Cleaning Proficiency
Cleaning proficiency is a core competency for individuals engaged in the maintenance of venting systems. The effectiveness of such professionals is intrinsically linked to their ability to thoroughly remove combustion byproducts that accumulate within these structures. This capability directly impacts fire safety, system efficiency, and the overall well-being of occupants.
- Creosote Removal
Creosote, a highly flammable residue, forms as a result of incomplete combustion. The removal of creosote is critical in preventing chimney fires. Professionals employ specialized tools, such as brushes and vacuums, to dislodge and extract creosote deposits. Failure to adequately remove creosote can lead to catastrophic fires, endangering structures and lives. The frequency of creosote removal depends on factors such as fuel type, appliance efficiency, and usage patterns.
- Obstruction Removal
Venting systems are susceptible to blockages from debris, nests, and other obstructions. These blockages impede airflow, potentially causing dangerous backdrafts of carbon monoxide into living spaces. Cleaning proficiency extends to identifying and removing such obstructions, restoring proper ventilation and mitigating the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Techniques include the use of specialized tools and inspection cameras to locate and extract obstructions.
- Equipment Maintenance
Effective cleaning relies on the proper maintenance of cleaning equipment. Brushes, vacuums, and other tools must be regularly inspected and maintained to ensure optimal performance and prevent damage to the venting system. Proper maintenance also minimizes the risk of equipment malfunction, enhancing safety and efficiency. Cleaning specialists must demonstrate competence in maintaining their tools and equipment to uphold their professional standards.
- Containment and Disposal
Cleaning processes generate significant amounts of debris, including creosote, soot, and other contaminants. Cleaning proficiency encompasses proper containment and disposal of these materials in accordance with environmental regulations. This includes utilizing appropriate collection methods and adhering to local guidelines for waste disposal. Improper handling of cleaning byproducts can pose environmental hazards and lead to regulatory penalties.
In conclusion, cleaning proficiency is not merely a procedural task, but a critical component of professional practice, directly influencing fire safety, air quality, and regulatory compliance. The effectiveness with which cleaning is performed directly impacts the overall safety and efficiency of heating appliances, thereby underscoring the importance of this skill set in comprehensive maintenance programs.
3. Repair Knowledge
The proficiency to diagnose and rectify structural or functional impairments constitutes a critical element in the skillset of an individual dedicated to chimney maintenance. This area of expertise, termed repair knowledge, directly influences the safety, efficiency, and longevity of venting systems. Its absence can lead to hazardous conditions, compromised energy performance, and accelerated deterioration of chimney structures. For example, improper mortar repair can lead to water penetration and subsequent freeze-thaw damage, necessitating extensive and costly reconstruction. Conversely, skilled application of repair knowledge prevents further degradation and ensures continued safe operation.
Practical applications of repair knowledge range from addressing minor issues such as cracks in the crown to more complex challenges involving liner replacement or complete chimney rebuilding. Selecting appropriate materials and techniques is crucial to ensure lasting repairs that meet building codes and industry standards. For instance, using incorrect mortar for tuckpointing historic brick can cause damage and require further intervention. Understanding structural principles, material compatibility, and combustion dynamics is essential to proper repair execution, mitigating potential hazards like carbon monoxide leaks or chimney fires. Furthermore, a competent professional accurately diagnoses underlying causes of damage to prevent recurrence.
In summary, repair knowledge represents a pivotal component of comprehensive chimney service. Its application safeguards properties, preserves structural integrity, and maintains efficient operation. Effective execution of repairs necessitates a thorough understanding of chimney construction, material science, and safety regulations. Continuous training and experience are imperative for staying abreast of evolving technologies and best practices, thereby ensuring consistent delivery of high-quality, reliable service. Neglecting this aspect of maintenance poses substantial risks and can lead to significant long-term costs.
4. Safety Compliance
Safety compliance is intrinsic to the professional practice of chimney maintenance. The occupation inherently involves potential hazards, including working at heights, exposure to combustion byproducts, and the risk of encountering structural instability. Strict adherence to safety protocols and regulations is therefore not merely a recommendation but a fundamental requirement for ensuring the well-being of both the professional and the occupants of the serviced property. Failure to comply with established safety standards can result in serious injuries, property damage, and legal repercussions.
The scope of safety compliance encompasses several critical areas. These include the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as respirators, safety harnesses, and eye protection; adherence to ladder safety procedures; and the safe handling and disposal of hazardous materials like creosote. Furthermore, professionals must be knowledgeable about relevant building codes and regulations pertaining to chimney construction, maintenance, and emissions. For instance, failing to properly seal a flue liner after repair could lead to carbon monoxide leaks, posing a severe health risk. Regular training and certification are essential for maintaining competency in safety practices and staying abreast of evolving standards.
The effective implementation of safety compliance directly translates into tangible benefits. It reduces the likelihood of accidents, protects the health of individuals, and minimizes the potential for property damage. Beyond these immediate benefits, a commitment to safety enhances the credibility and reputation of the professional, fostering trust with clients. By prioritizing safety compliance, the integrity and reliability of chimney maintenance services are strengthened, contributing to the overall safety and well-being of communities. Negligence in this area can have severe consequences, underscoring its central importance in the field.
5. Code Adherence
Strict conformity with established codes and regulations is a non-negotiable aspect of professional chimney service. The activities undertaken by specialists directly impact structural integrity, fire safety, and air quality, rendering adherence to prescribed standards crucial for safeguarding property and human lives. This is not merely a matter of procedural compliance, but a commitment to ensuring public safety through responsible practice.
- Material Specifications
Codes dictate acceptable materials for construction and repair. Using non-compliant materials, such as an inappropriate mortar mix, can compromise structural stability and increase the risk of premature failure. Professionals must understand and adhere to specifications for flue liners, masonry units, and other components to ensure longevity and safety. Violations can lead to costly repairs and potential hazards.
- Clearance Requirements
Maintaining adequate clearance between the chimney and combustible materials is essential to prevent fires. Codes specify minimum distances for wood framing, roofing, and other flammable materials. Professionals must accurately assess clearance during inspections and ensure compliance during installation or repair. Failure to meet these requirements poses a significant fire risk and can result in code violations.
- Inspection Protocols
Codes often mandate specific inspection protocols, including the frequency and scope of evaluations. These protocols ensure that potential hazards are identified and addressed in a timely manner. Professionals must follow prescribed procedures for assessing structural integrity, creosote accumulation, and ventilation efficiency. Proper adherence to inspection protocols contributes to preventative maintenance and minimizes the risk of catastrophic events.
- Emissions Standards
Regulations governing emissions from heating appliances are increasingly stringent. Professionals must be knowledgeable about emissions standards and ensure that venting systems comply with these requirements. This may involve advising clients on proper appliance selection, maintenance practices, and fuel choices. Compliance with emissions standards protects air quality and promotes environmental responsibility.
In summary, code adherence represents the cornerstone of responsible chimney service. By diligently adhering to established standards, professionals mitigate risks, ensure structural integrity, and contribute to public safety. Continuous education and training are essential for staying abreast of evolving codes and regulations, thereby upholding the highest standards of practice within the field.
Frequently Asked Questions about Chimney Maintenance
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the maintenance and safety of venting systems, providing essential information for homeowners and building managers.
Question 1: How frequently should a chimney be inspected?
Industry best practice dictates that venting systems undergo inspection at least annually, irrespective of usage frequency. This proactive approach facilitates the early detection of structural deficiencies, creosote accumulation, or other potential hazards that could compromise the system’s performance or safety.
Question 2: What are the indications of a potential chimney fire?
Warning signs of a chimney fire include loud cracking or popping noises, a strong, intense heat emanating from the fireplace, and the expulsion of dense smoke from the chimney. If these indicators are observed, immediate evacuation is advised, followed by contacting emergency services.
Question 3: Is creosote removal essential, and what is the process?
Creosote removal is indeed critical. Creosote, a flammable byproduct of combustion, accumulates within the flue. Trained professionals employ specialized brushes and vacuums to dislodge and extract creosote deposits, mitigating the risk of chimney fires. The frequency of this process depends on the type of fuel utilized and the appliance’s efficiency.
Question 4: Can a homeowner perform chimney inspections and cleaning?
While basic visual inspections are possible, comprehensive assessments require specialized knowledge and equipment. Professional evaluation is highly recommended due to potential safety hazards and the need for accurate diagnoses. Cleaning should be performed by qualified professionals to ensure thoroughness and prevent damage to the system.
Question 5: What is the average lifespan of a chimney liner, and what factors influence its longevity?
The lifespan of a chimney liner varies depending on the material used and the operating conditions. Clay tile liners typically last 50-100 years, while metal liners can range from 15-50 years. Factors such as fuel type, moisture exposure, and maintenance practices significantly impact liner longevity.
Question 6: Are there specific building codes pertaining to chimney construction and maintenance?
Yes, building codes establish minimum standards for chimney construction, repair, and maintenance. These codes address aspects such as material specifications, clearance requirements, and emissions standards. Adherence to these codes is essential for ensuring safety and compliance with local regulations.
Regular maintenance and inspections, performed by qualified professionals, contribute significantly to mitigating risks associated with venting systems, safeguarding property and lives.
The subsequent section will delve into the technologies employed in chimney maintenance and inspection, highlighting innovations in the field.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration has illuminated the critical role of individuals dedicated to chimney maintenance, often referred to by the keyword phrase. The discussion encompassed essential aspects of the profession, including inspection expertise, cleaning proficiency, repair knowledge, safety compliance, and adherence to relevant codes. The emphasis throughout has been on the indispensable nature of professional intervention in maintaining the safety, efficiency, and structural integrity of venting systems.
Given the potential hazards associated with malfunctioning or poorly maintained chimneys, prioritizing professional assessment and service is paramount. The long-term benefits, encompassing fire prevention, improved air quality, and extended system lifespan, far outweigh the costs associated with neglecting this crucial aspect of property maintenance. Homeowners and building managers are strongly urged to engage qualified professionals to ensure the continued safe and efficient operation of their heating appliances.