Regulations pertaining to the construction, maintenance, and inspection of venting systems for combustion appliances are crucial for ensuring structural integrity and operational safety. These regulations establish minimum standards for materials, design, installation practices, and clearance requirements, addressing concerns such as fire resistance, flue gas venting, and prevention of carbon monoxide intrusion. For instance, specific dimensions and materials may be mandated for the chimney liner based on the type of appliance it serves and the fuel it consumes.
Adherence to these prescribed standards offers numerous benefits, notably the reduction of fire hazards and carbon monoxide poisoning incidents. By dictating appropriate construction techniques and material specifications, such mandates contribute to the longevity and safe operation of venting systems. Historically, these preventative measures have evolved in response to observed failures and emerging technologies, leading to a continuous refinement of safety parameters and performance requirements.
The following sections will delve into specific requirements for various aspects of these safety standards, including material specifications, construction practices, inspection protocols, and potential consequences of non-compliance. Further discussion will address recent updates and their impact on industry practices.
Guidance on Venting System Regulations
The following recommendations address essential considerations for ensuring compliance and promoting safety in relation to venting systems. Diligent application of these guidelines can mitigate risks associated with improper construction, maintenance, or inspection.
Tip 1: Ensure Proper Material Selection: Verify that all materials utilized in the construction or repair of venting systems conform to approved standards outlined in the applicable regulations. For example, stainless steel liners are often mandated for gas-burning appliances to resist corrosion from acidic flue gases.
Tip 2: Adhere to Specified Clearance Requirements: Maintain prescribed clearances between the venting system and combustible materials. Failure to adhere to these clearances can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. Clearance distances are typically detailed within regulatory documents and manufacturer’s specifications.
Tip 3: Conduct Regular Inspections: Implement a routine inspection schedule to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. A qualified professional should perform inspections, especially when deficiencies are suspected or after events like chimney fires or significant weather events.
Tip 4: Verify Proper Draft: Ensure the venting system provides adequate draft to effectively exhaust combustion byproducts. Insufficient draft can lead to backdrafting and the accumulation of dangerous gases within the dwelling. Draft testing may be necessary to confirm adequate performance.
Tip 5: Maintain Cleanliness: Regularly remove creosote buildup in venting systems serving solid fuel appliances. Creosote is highly combustible and poses a significant fire risk. Professional chimney sweeps can perform this service effectively and safely.
Tip 6: Comply with Height Requirements: Ensure the venting system extends to the minimum required height above the roofline and nearby obstructions. Proper height promotes adequate draft and minimizes the potential for downdrafts and re-entry of exhaust gases.
Tip 7: Obtain Necessary Permits: Secure all required permits before commencing construction, alteration, or repair of venting systems. Permit processes ensure that projects are reviewed for compliance with applicable standards.
These guidelines emphasize the importance of meticulous attention to detail and adherence to established protocols when dealing with venting systems. Implementing these measures contributes significantly to the safe and efficient operation of combustion appliances.
The subsequent sections will address legal ramifications and enforcement mechanisms associated with failure to comply with the outlined regulations.
1. Material Specifications
Venting system regulations establish stringent guidelines regarding acceptable materials to mitigate the risks of fire, corrosion, and structural failure. These specifications are paramount to the safe and efficient operation of appliances, aligning directly with the objectives of promoting public safety and welfare.
- Liner Material Requirements
The composition of the liner is crucial, particularly in relation to the type of fuel being burned. For example, stainless steel liners are frequently mandated for gas-burning appliances due to their resistance to acidic condensation. Clay tile liners, while historically common, may not be suitable for all applications due to their susceptibility to cracking and degradation over time. Improper liner selection can lead to corrosion, gas leaks, and structural compromise of the venting system.
- Connectors and Vent Pipe Standards
Regulations dictate the type of connectors and vent pipes permitted, specifying materials and construction methods that ensure a gas-tight seal and prevent leakage of combustion byproducts. Single-wall vent pipes, for instance, are typically restricted in their application due to their higher surface temperatures and potential for heat transfer to adjacent combustible materials. Approved connectors must be resistant to heat and corrosion and properly sized for the appliance being vented.
- Chimney Construction Materials
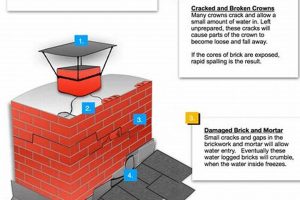
Regulations address the composition and construction of the chimney structure itself, including the type of masonry, mortar, and reinforcing materials. Requirements ensure structural stability, fire resistance, and resistance to weather exposure. Improper materials or construction techniques can lead to cracking, spalling, and eventual collapse of the chimney structure, posing a significant safety hazard.
- Cap and Termination Requirements
The material and design of the chimney cap or termination point are also subject to regulatory specifications. Caps must be constructed of durable, non-combustible materials and designed to prevent the entry of rain, snow, and debris while maintaining adequate draft. Regulations may also specify minimum height requirements and clearance from obstructions to ensure proper venting.
Compliance with material specifications is not merely a procedural formality; it directly impacts the safety and longevity of venting systems. Deviation from these mandated standards can result in compromised performance, increased risk of fire, and potential exposure to dangerous combustion byproducts. Adherence to these material specifications is therefore an essential component of regulatory compliance and responsible ownership of combustion appliances.
2. Clearance Requirements
Clearance requirements, as stipulated within chimney codes, are fundamental to fire safety, aiming to prevent the ignition of combustible materials near heat-producing venting systems. Strict adherence to these codified clearances is critical to minimize the risk of structure fires.
- Minimum Distance to Combustibles
Chimney codes specify the minimum permissible distance between the exterior surface of a venting system and any adjacent combustible material, such as wood framing, insulation, or drywall. These distances are determined based on the type of appliance, the fuel being burned, and the construction of the chimney. Failure to maintain these clearances can lead to the gradual heating and eventual ignition of nearby combustibles, resulting in a fire.
- Thimble Installation and Clearances
A thimble, a connecting sleeve between a chimney and a stovepipe, necessitates precise installation according to chimney code. Proper thimble installation ensures a secure connection and maintains the required clearances around the stovepipe as it passes through a combustible wall or ceiling. Insufficient clearance at the thimble is a common cause of residential fires.
- Clearance for Factory-Built Chimneys
Factory-built chimneys, designed for specific appliances, have clearance requirements detailed in their listing and labeling. These requirements often differ from those for masonry chimneys. Strict adherence to the manufacturer’s specified clearances is crucial for the safe operation of the appliance and the integrity of the chimney system. Deviating from the listed clearances voids the warranty and can create a fire hazard.
- Inspection and Enforcement of Clearances
Local building inspectors play a vital role in verifying compliance with clearance requirements during new construction, renovations, or appliance installations. Inspections ensure that venting systems are installed according to code, minimizing the potential for fire hazards. Homeowners also bear responsibility for maintaining these clearances and promptly addressing any issues discovered during routine inspections.
The rigorous enforcement of clearance requirements, as outlined within chimney codes, reflects a proactive approach to fire prevention. These regulations serve as a critical safeguard, mitigating the risk of fires originating from improperly installed or maintained venting systems. These standards, enforced through inspections and permits, are essential for protecting life and property.
3. Inspection Frequency
Inspection frequency, as mandated by chimney codes, directly influences the detection and mitigation of hazards associated with venting systems. The regularity of inspections dictates the likelihood of identifying deterioration, blockages, or non-compliant installations before these issues escalate into significant safety risks. For instance, creosote buildup in wood-burning systems, a leading cause of chimney fires, is best managed through routine inspections aligned with the frequency prescribed within the relevant code. The absence of regular inspections can result in undetected hazards, leading to property damage, injury, or loss of life.
Specific examples illustrate the practical significance of this connection. Chimney codes may stipulate annual inspections for systems serving solid-fuel appliances, reflecting the higher risk associated with creosote accumulation. Conversely, systems venting gas appliances might require less frequent inspections, contingent upon factors such as the appliance age, venting configuration, and previous inspection history. Jurisdictions often provide detailed schedules, outlining the minimum inspection frequency based on appliance type, fuel, and occupancy classification. These schedules underscore the critical role inspections play in upholding the safety standards established by the chimney code.
In summary, inspection frequency functions as a critical component of the overall chimney code framework. Regular inspections serve as a proactive measure, facilitating early detection and correction of potential safety hazards. Challenges remain in ensuring consistent enforcement of inspection requirements and promoting public awareness of their importance. However, the established link between inspection frequency and code compliance remains fundamental to maintaining safe and functional venting systems.
4. Draft Verification
Adequate draft within a venting system is crucial for the safe and efficient removal of combustion byproducts. Chimney codes directly address draft requirements to prevent backdrafting, carbon monoxide intrusion, and inefficient appliance operation. Draft verification ensures that the venting system functions as designed, mitigating potential hazards. For example, insufficient draft can cause incomplete combustion, leading to increased carbon monoxide production and posing a serious health risk to occupants. Chimney codes typically mandate draft testing during initial installation and after alterations to the venting system or appliance, demonstrating the importance of draft verification as a critical component of regulatory compliance.
Draft verification methods can include visual inspections, smoke tests, and the use of specialized instruments such as manometers. Smoke tests, for instance, provide a visual indication of airflow direction and venting efficiency. Manometers measure pressure differentials within the venting system to quantify draft levels and identify potential obstructions or leaks. The results of these tests are compared against minimum draft requirements specified within the relevant chimney code to determine compliance. Furthermore, proper draft contributes to appliance efficiency by optimizing combustion and reducing fuel consumption. Regular draft verification helps to maintain these benefits and ensures continued safe operation.
In summary, draft verification is an indispensable element of chimney code compliance, safeguarding against the risks associated with inadequate venting. It is not merely a technical detail, but a critical safety measure designed to protect occupants from hazardous combustion byproducts. Ensuring that venting systems meet the draft requirements outlined within the code is a fundamental responsibility for installers, inspectors, and homeowners alike.
5. Creosote Management
Effective creosote management is inextricably linked to chimney code compliance, serving as a critical component of fire prevention and safe operation of solid-fuel burning appliances. These regulations mandate specific practices and technologies to mitigate the risks associated with creosote accumulation, which is a significant contributor to chimney fires.
- Creosote Formation and Accumulation
Creosote, a byproduct of incomplete combustion in wood-burning appliances, condenses and deposits on the inner surfaces of chimneys. Chimney codes acknowledge varying stages and flammability of creosote, emphasizing the need for regular inspections and removal to prevent ignition. Factors such as wood moisture content, appliance design, and venting system configuration directly influence the rate of creosote formation, necessitating tailored management strategies compliant with local regulations.
- Inspection and Cleaning Requirements
Chimney codes stipulate minimum inspection frequencies for venting systems serving solid-fuel appliances, with annual inspections often mandated. Qualified professionals perform inspections to assess creosote buildup levels and recommend appropriate cleaning methods. Accepted cleaning techniques, such as mechanical sweeping, are essential to remove accumulated creosote and restore the venting system to a safe operational condition. These procedures must adhere to prescribed standards, ensuring effective removal without damaging the chimney structure.
- Creosote Mitigation Strategies
Chimney codes often encourage or mandate the implementation of strategies to minimize creosote formation in the first place. These include burning seasoned wood with low moisture content, ensuring adequate combustion air, and employing appropriately sized venting systems. Appliance design and operational practices that promote complete combustion contribute significantly to reducing creosote accumulation, thereby lessening the need for frequent cleaning and mitigating fire risks. Such measures must align with the requirements outlined in the chimney code.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with creosote management provisions within chimney codes can result in penalties ranging from warnings and fines to mandatory system repairs or even prohibition of appliance use. Jurisdictions enforce these provisions through inspections and investigations, holding homeowners accountable for maintaining their venting systems in accordance with prescribed standards. The severity of penalties reflects the inherent fire risk associated with uncontrolled creosote accumulation and the importance of adhering to code requirements.
The multifaceted relationship between creosote management and chimney code compliance underscores the critical importance of proactive maintenance and adherence to established safety standards. By understanding the factors contributing to creosote formation, implementing effective mitigation strategies, and complying with inspection and cleaning requirements, homeowners can significantly reduce the risk of chimney fires and ensure the safe operation of their solid-fuel burning appliances.
6. Height Regulations
Height regulations within chimney codes are paramount for ensuring proper draft and safe dispersal of combustion byproducts. These provisions address the minimum vertical distance a chimney must extend above the roofline and nearby obstructions to prevent downdrafts and promote effective venting.
- Minimum Height Above Roof
Chimney codes typically mandate a minimum height above the highest point where the chimney penetrates the roof, often specified as a certain distance (e.g., 3 feet) above the roofline. This requirement mitigates wind-induced downdrafts that can force combustion gases back into the dwelling. Inadequate height can result in carbon monoxide buildup and compromised appliance performance.
- “10-Foot Rule” for Nearby Obstructions
The “10-foot rule” stipulates that a chimney must extend at least 2 feet higher than any portion of a building within a 10-foot radius. This provision accounts for potential turbulence caused by nearby structures, ensuring that exhaust gases are dispersed effectively and do not re-enter the building or neighboring properties. The rule is essential in densely populated areas or where adjacent structures create complex wind patterns.
- Impact on Draft and Appliance Performance
Proper chimney height contributes significantly to the establishment of adequate draft, which is the natural flow of air through the venting system. Sufficient draft ensures efficient removal of combustion byproducts, prevents backdrafting, and optimizes appliance performance. Inadequate height can lead to poor draft, resulting in incomplete combustion, reduced heating efficiency, and potential safety hazards. The prescribed height regulations are, therefore, designed to maintain optimal draft characteristics for various types of appliances and fuel sources.
- Local Variations and Enforcement
While general principles of height regulations remain consistent, specific requirements may vary based on local climate conditions, building codes, and enforcement practices. Some jurisdictions may impose stricter height limits or additional considerations based on unique environmental factors. Local building inspectors are responsible for verifying compliance with height regulations during new construction and renovations, ensuring that venting systems meet prescribed standards. Failure to adhere to these requirements can result in rejected permits and potential safety hazards.
In conclusion, height regulations within chimney codes serve as a fundamental safeguard against venting system malfunctions and associated safety risks. Adherence to these provisions is crucial for promoting efficient appliance operation, preventing carbon monoxide intrusion, and protecting occupants from the hazards of improperly vented combustion byproducts. Rigorous enforcement and public awareness of these requirements are essential for maintaining the safety and integrity of venting systems within the built environment.
7. Permit Compliance
Permit compliance serves as a critical mechanism for ensuring that alterations, installations, or repairs to venting systems adhere to the stipulations outlined within chimney codes. This process facilitates oversight and accountability, minimizing the potential for hazardous conditions arising from non-compliant work.
- Mandatory Review of Plans and Specifications
Permit applications necessitate the submission of detailed plans and specifications for proposed chimney work. These documents undergo scrutiny by local building officials to verify adherence to the applicable chimney code provisions, encompassing aspects such as material specifications, clearance requirements, and height regulations. This review process serves as a proactive measure, identifying potential code violations before construction commences, thereby averting costly and potentially dangerous errors.
- On-Site Inspections During Construction
Following permit approval, on-site inspections are conducted at various stages of the project to ensure that the work progresses in accordance with the approved plans and code requirements. These inspections provide opportunities to identify deviations from the code, such as improper material installation or inadequate clearances, allowing for timely corrective action. The inspections are conducted by certified inspectors who possess the knowledge and authority to enforce compliance.
- Final Inspection and Approval
Upon completion of the chimney work, a final inspection is performed to verify overall compliance with the chimney code. This inspection encompasses a comprehensive review of all aspects of the installation, including material quality, structural integrity, and adherence to safety regulations. Successful completion of the final inspection results in the issuance of a certificate of occupancy or approval, signifying that the work meets the required standards.
- Legal Ramifications of Non-Compliance
Failure to obtain the necessary permits or to comply with the stipulations of the chimney code can result in significant legal consequences. These may include fines, stop-work orders, mandatory corrective actions, and even legal liability in the event of fire or carbon monoxide poisoning resulting from the non-compliant work. The legal ramifications underscore the importance of permit compliance as a means of ensuring public safety and protecting property.
The comprehensive permit compliance process, encompassing plan review, on-site inspections, and final approval, provides a robust framework for upholding the provisions of chimney codes. While challenges may arise in ensuring consistent enforcement and promoting public awareness, the established link between permit compliance and code adherence remains essential for maintaining safe and functional venting systems. This process underscores the interconnectedness of regulatory oversight and responsible construction practices.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Chimney Codes
The following section addresses common inquiries concerning regulations governing chimney construction, maintenance, and safety. These answers provide a general overview and do not substitute professional consultation or specific code interpretation.
Question 1: What is the primary objective of chimney codes?
The paramount objective of chimney codes is to safeguard life and property by establishing minimum safety standards for the design, construction, and maintenance of venting systems for combustion appliances. These regulations aim to minimize fire hazards, prevent carbon monoxide poisoning, and ensure efficient and safe operation of heating appliances.
Question 2: How often should a chimney be inspected?
Inspection frequency depends on factors such as appliance type, fuel source, and usage patterns. Chimney codes typically mandate annual inspections for systems serving solid-fuel appliances. Gas-burning systems may require less frequent inspections, but regular evaluation is still recommended, especially if problems are suspected.
Question 3: What constitutes an acceptable chimney liner material?
Acceptable liner materials vary based on the type of appliance and fuel being used. Stainless steel liners are commonly required for gas appliances due to their resistance to acidic corrosion. Clay tile liners may be suitable for certain applications but must be carefully inspected for cracks or deterioration. Chimney codes specify approved materials based on their performance characteristics.
Question 4: What clearance is required between a chimney and combustible materials?
Chimney codes establish minimum clearance distances between the exterior of the venting system and any adjacent combustible materials. These distances are designed to prevent overheating and potential ignition. The specific clearance requirements depend on factors such as the chimney construction, appliance type, and fuel source.
Question 5: What are the consequences of non-compliance with chimney codes?
Non-compliance with chimney codes can result in various penalties, including fines, stop-work orders, and mandatory corrective actions. Furthermore, failure to adhere to these regulations can increase the risk of fire, carbon monoxide poisoning, and legal liability in the event of property damage or injury.
Question 6: How does one find the chimney codes relevant to a specific location?
Chimney codes are typically adopted and enforced at the state or local level. Information regarding specific code requirements can be obtained from local building departments, fire marshals, or licensed chimney professionals. Consulting these resources ensures compliance with the applicable regulations in a given jurisdiction.
Adherence to chimney codes is not simply a matter of regulatory compliance; it is a fundamental component of responsible ownership and ensures the safe operation of combustion appliances. Understanding and complying with these regulations protects life, property, and the environment.
The subsequent section will delve into the impact of technological advancements on chimney code requirements.
Conclusion
This exploration has illuminated the multifaceted nature of chimney code, underscoring its critical role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of venting systems. From material specifications and clearance requirements to inspection protocols and draft verification methods, the stringent regulations outlined within these codes serve as essential safeguards against fire hazards and carbon monoxide poisoning. Understanding and adhering to these provisions is paramount for homeowners, contractors, and regulatory bodies alike.
Given the inherent risks associated with combustion appliances, ongoing vigilance and proactive engagement with evolving chimney code are imperative. Further research and education initiatives are crucial to promote widespread awareness and adherence to these vital safety standards. The continued protection of life and property hinges on a collective commitment to upholding and advancing the principles enshrined within chimney code.