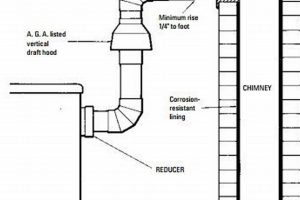
A residential venting structure located in a specific geographic area serves the primary function of expelling combustion byproducts from heating appliances, fireplaces, and other similar systems. These structures are commonly constructed of brick, masonry, or metal and are a vital component of a home’s heating and ventilation system, ensuring safe and efficient operation. For example, a homeowner might schedule an annual inspection to guarantee its integrity and proper function before the start of the heating season.
The proper functioning of these structures is crucial for preventing the dangerous buildup of carbon monoxide within a dwelling. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and inspection, is essential for optimizing heating efficiency and extending the lifespan of the structure. Historically, these structures were a central feature of home construction, reflecting the reliance on wood and coal as primary heating sources. Today, while heating technologies have evolved, their function remains critical to home safety and efficient energy consumption.
The following discussion will explore various aspects related to the inspection, maintenance, repair, and relevant safety considerations associated with these structures. Topics covered will include common problems, preventative measures, and best practices for ensuring their longevity and safe operation within a residential environment.
Essential Guidelines for Venting Structures
Maintaining the integrity of a residential venting structure is paramount for home safety and heating efficiency. These guidelines offer crucial information for homeowners to ensure their venting structure functions optimally.
Tip 1: Schedule Annual Inspections: A qualified professional should inspect the venting structure annually, ideally before the heating season. This allows for the identification of potential issues like cracks, deterioration, or blockages that could compromise safety and efficiency.
Tip 2: Prioritize Regular Cleaning: Routine cleaning removes creosote buildup, a flammable byproduct of wood-burning. Creosote accumulation significantly increases the risk of chimney fires. Professional cleaning services are recommended.
Tip 3: Address Water Damage Promptly: Water infiltration can cause significant damage, leading to structural instability and accelerated deterioration. Inspect the cap and flashing regularly for signs of leaks and address any issues immediately.
Tip 4: Ensure Proper Ventilation: Adequate airflow is essential for efficient combustion and the safe expulsion of exhaust gases. Verify that the venting structure is appropriately sized for the connected appliance and that no obstructions are present.
Tip 5: Use Appropriate Fuel: Employing the correct type of fuel for the appliance connected to the venting structure is crucial. Burning unapproved materials can generate excessive creosote and other harmful byproducts.
Tip 6: Consider Professional Repairs: Any structural damage, such as cracks in the masonry or deterioration of the liner, should be addressed by a qualified professional. Attempting DIY repairs can be dangerous and may not meet safety standards.
Tip 7: Install a Chimney Cap: A chimney cap prevents rain, snow, debris, and animals from entering the venting structure, minimizing the risk of blockages and water damage.
Adhering to these guidelines promotes a safe and efficient home heating system. Neglecting maintenance can lead to hazardous conditions and costly repairs.
The subsequent sections will delve into the specific types of repairs and preventative measures that can further enhance the longevity and safety of residential venting structures.
1. Local Building Codes
Adherence to local building codes is paramount in ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of venting structures. These codes establish minimum standards for construction, alteration, repair, and maintenance, reflecting the community’s commitment to public safety and welfare. These regulations address critical aspects of venting system design and installation to prevent hazards and promote optimal performance.
- Material Specifications
Local building codes often stipulate approved materials for venting structures, factoring in resistance to fire, corrosion, and weather. For instance, a code may mandate the use of specific grades of stainless steel for chimney liners to withstand corrosive flue gases or require brick masonry chimneys to meet particular compressive strength standards. The selection of appropriate materials is vital for preventing premature deterioration and ensuring structural integrity.
- Height and Clearance Requirements
Building codes typically outline height and clearance specifications to ensure proper draft and minimize fire hazards. These regulations may dictate minimum height above the roofline to prevent downdraft and ensure adequate dispersion of exhaust gases. Additionally, codes specify minimum clearances from combustible materials, such as wood framing, to reduce the risk of ignition. Compliance with these requirements is crucial for preventing chimney fires and carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Inspection and Permitting Processes
Local building codes often mandate inspections during construction and after completion to verify compliance with established standards. Permit requirements ensure that alterations or repairs to venting structures are reviewed and approved by qualified inspectors. These processes help identify potential deficiencies and ensure that corrective measures are implemented. Homeowners must adhere to permitting and inspection protocols when undertaking construction or renovation projects involving these structures.
- Energy Efficiency Standards
Modern building codes increasingly incorporate energy efficiency standards to minimize heat loss and reduce energy consumption. Regulations may require the installation of insulated liners or dampers to prevent heat from escaping through the chimney when not in use. These measures enhance the overall energy performance of the home and reduce heating costs. Compliance with energy efficiency standards promotes sustainable building practices and reduces environmental impact.
The consistent application of local building codes to venting structures contributes significantly to the safety and well-being of the community. Regular review and updating of these codes are essential to reflect advancements in building technology and address emerging safety concerns. Understanding and adhering to these codes are vital for homeowners, contractors, and building officials alike to ensure that these systems function safely and efficiently.
2. Seasonal Weather Impact
The cyclical variations in weather patterns exert a considerable influence on the integrity and functionality of residential venting structures. These structures, designed to expel combustion byproducts, are perpetually exposed to environmental stressors that accelerate material degradation and compromise their overall performance. Understanding the nature and extent of these impacts is crucial for proactive maintenance and the prevention of potentially hazardous conditions.
- Freeze-Thaw Cycles and Masonry Deterioration
The recurring cycle of freezing and thawing water within porous masonry materials, such as brick and mortar, is a primary cause of structural damage. Water infiltrates cracks and fissures during warmer periods and subsequently expands upon freezing, exerting internal pressure that leads to cracking, spalling, and eventual disintegration. In regions with significant temperature fluctuations, this process can rapidly accelerate the deterioration of masonry venting structures. Regular inspections and appropriate sealing measures can mitigate these effects.
- Rain and Water Infiltration
Prolonged exposure to rain and moisture can saturate masonry materials, leading to water infiltration into the chimney structure. Water penetration can damage the interior flue liner, corrode metal components, and create a damp environment conducive to mold growth. Leaks around the chimney flashing can compromise the roof structure and lead to costly repairs. A properly installed chimney cap and flashing system are essential for preventing water intrusion.
- Wind and Structural Stability
High winds can exert significant stress on venting structures, particularly those that are tall or have structural weaknesses. Wind-induced vibrations can loosen mortar joints, damage chimney crowns, and even cause structural collapse in extreme cases. Regular inspections should assess the structural stability of the chimney, and any signs of instability should be promptly addressed by a qualified professional.
- Temperature Extremes and Material Expansion/Contraction
Extreme temperature variations can cause expansion and contraction of chimney materials, leading to stress and cracking. Metal components, such as liners and dampers, are particularly susceptible to this phenomenon. Over time, repeated expansion and contraction can weaken the structure and compromise its integrity. The selection of appropriate materials that can withstand thermal stress is crucial for longevity.
In conclusion, seasonal weather patterns represent a persistent threat to the structural integrity and functionality of these structures. A comprehensive understanding of these impacts, coupled with proactive maintenance and timely repairs, is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of residential heating systems. Neglecting the effects of seasonal weather can lead to costly repairs, hazardous conditions, and ultimately, the premature failure of the venting structure.
3. Material Degradation Analysis
Material Degradation Analysis, when applied to residential venting structures located in the Rockford area, is a critical diagnostic process. It provides insights into the causes and extent of material deterioration, allowing for informed decisions regarding repair, restoration, or replacement. The environmental conditions specific to this region, including seasonal temperature fluctuations and precipitation patterns, contribute significantly to the degradation process.
- Identification of Deterioration Mechanisms
This facet involves determining the specific mechanisms responsible for material breakdown. In the context of structures found in the stated area, common mechanisms include freeze-thaw damage to masonry, corrosion of metal components due to acidic flue gases, and chemical attack from creosote accumulation. Accurate identification is crucial for selecting appropriate repair strategies and preventing further degradation.
- Assessment of Structural Integrity
Material degradation directly impacts the structural integrity of the venting system. Analysis assesses the extent of weakening or instability caused by material loss or alteration. For example, cracked or spalled brickwork in a chimney can compromise its ability to withstand wind loads and support its own weight. Similarly, corrosion of a metal flue liner can lead to gas leakage and potential carbon monoxide poisoning. Quantitative measurements of material strength and stability are essential for determining the safety and functionality of the structure.
- Selection of Appropriate Repair Materials
The choice of repair materials is directly informed by Material Degradation Analysis. Compatibility with existing materials, resistance to the identified degradation mechanisms, and long-term durability are key considerations. For instance, when repairing damaged brickwork, the selected mortar should be compatible with the original brick to prevent differential expansion and contraction, which can exacerbate cracking. Similarly, replacement flue liners should be corrosion-resistant and appropriately sized for the connected appliance.
- Prediction of Remaining Service Life
Based on the extent and rate of material degradation, analysis can provide an estimate of the remaining service life of the venting system. This information is valuable for long-term planning and budgeting for future maintenance or replacement. Factors such as environmental exposure, material properties, and past maintenance practices are considered in the assessment. Predictive modeling helps homeowners make informed decisions about investing in preventative measures to extend the life of their systems.
These facets of Material Degradation Analysis underscore its importance in maintaining the safety and efficiency of residential venting structures located in a specific geographic area. By understanding the causes and consequences of material deterioration, homeowners and professionals can make informed decisions to ensure the long-term functionality and safety of these critical building components.
4. Professional Inspection Availability
The accessibility of qualified professionals to inspect residential venting structures in a specific locality is critical for ensuring homeowner safety and code compliance. The availability of such services directly influences the proactive identification and mitigation of potential hazards associated with these structures.
- Timely Detection of Structural Deficiencies
The availability of qualified inspectors allows for the prompt identification of structural issues, such as cracks, spalling, or settling, which can compromise the integrity of the venting system. For instance, rapid freeze-thaw cycles common in the specified area can cause significant damage to masonry chimneys. Regular inspections can detect these issues before they escalate into major structural problems, preventing costly repairs and potential safety hazards.
- Early Identification of Hazardous Conditions
Professional inspectors are trained to recognize conditions that pose immediate risks to occupants, such as carbon monoxide leaks, creosote buildup, or obstructions in the flue. These conditions may not be readily apparent to homeowners, and early detection is crucial for preventing carbon monoxide poisoning or chimney fires. The availability of certified chimney sweeps and inspectors ensures that homeowners have access to the expertise needed to identify and address these hazards promptly.
- Ensuring Code Compliance and Insurance Requirements
Local building codes and insurance policies often require periodic inspections of residential venting systems. The availability of qualified inspectors allows homeowners to comply with these requirements, avoiding potential fines or loss of insurance coverage. Compliance with code ensures that the venting system meets minimum safety standards, while fulfilling insurance requirements protects homeowners from financial liabilities in the event of a fire or other damage.
- Preventative Maintenance Recommendations
Professional inspectors can provide valuable recommendations for preventative maintenance practices that extend the lifespan of residential venting structures and minimize the risk of future problems. These recommendations may include cleaning schedules, sealing damaged masonry, or installing chimney caps to prevent water intrusion. The availability of expert advice empowers homeowners to take proactive steps to maintain their venting systems and ensure their continued safety and efficiency.
The accessibility of qualified professionals specializing in residential venting systems directly impacts the safety, compliance, and longevity of these structures. Ensuring the availability of these services is a vital component of maintaining a safe and healthy living environment.
5. Historical Architectural Styles
The architectural styles prevalent during a building’s construction significantly influence the design, materials, and construction techniques employed for its venting system. Examining the historical architectural context provides insight into the evolution of venting systems and their integration into residential structures in a specific geographic location.
- Victorian Era Chimneys
The Victorian era, characterized by ornate detailing and elaborate designs, often featured brick chimneys with decorative corbels, chimney pots, and intricate brickwork patterns. These chimneys were typically larger in scale to accommodate the multiple fireplaces common in Victorian homes. The selection of materials and construction techniques reflected the aesthetic preferences and technological capabilities of the time. In the context of modern maintenance, preserving the historical integrity of Victorian-era chimneys requires specialized expertise in masonry repair and restoration.
- Craftsman Style Chimneys
Craftsman-style homes, known for their emphasis on natural materials and handcrafted details, typically featured chimneys constructed of brick or stone with simple, clean lines. These chimneys were often integrated into the overall architectural design, reflecting a focus on functionality and harmony with the surrounding environment. The materials used in Craftsman chimneys were typically sourced locally, adding to the unique character of each structure. Maintaining these chimneys involves preserving the original materials and construction techniques while ensuring structural integrity and code compliance.
- Mid-Century Modern Chimneys
Mid-century modern homes often featured chimneys constructed of concrete block or brick with minimalist designs and clean, geometric forms. These chimneys were typically smaller in scale than those found in earlier architectural styles, reflecting the shift towards smaller, more efficient heating systems. The construction techniques employed in mid-century modern chimneys often prioritized simplicity and affordability. Preserving these chimneys involves maintaining their clean lines and geometric forms while addressing any issues related to material degradation or structural instability.
- Prairie School Chimneys
Prairie School architecture, characterized by its horizontal lines and integration with the landscape, frequently incorporated chimneys as prominent design elements. These chimneys were often constructed of brick or stone and featured wide, overhanging caps that echoed the broad eaves of the house. The design of Prairie School chimneys emphasized horizontality and a connection to the natural environment. Maintaining these chimneys requires preserving their distinctive design features while ensuring structural integrity and code compliance.
The historical architectural style of a building directly influences the design, materials, and construction techniques employed for its venting system. Understanding these historical influences is essential for proper maintenance, repair, and restoration, ensuring the preservation of architectural heritage and the continued safe operation of residential heating systems.
Frequently Asked Questions About Rockford Chimneys
The following addresses prevalent inquiries and misconceptions concerning residential venting structures in the specified location. Understanding these answers facilitates informed decisions regarding maintenance, safety, and regulatory compliance.
Question 1: How frequently should a Rockford chimney be inspected?
Residential venting structures require annual inspections by qualified professionals. This frequency allows for the early detection of potential hazards, ensuring the system’s integrity before and during the heating season.
Question 2: What are the most common issues affecting Rockford chimneys?
Common problems include creosote buildup, water damage from freeze-thaw cycles, cracked or spalled masonry, and flue obstructions caused by debris or animals. The local climate exacerbates these issues.
Question 3: How does the local climate affect a Rockford chimney’s lifespan?
The region’s climate, characterized by significant temperature variations and frequent precipitation, contributes to accelerated deterioration. Freeze-thaw cycles, in particular, cause cracking and spalling of masonry, reducing structural integrity.
Question 4: Are there specific building codes for Rockford chimneys that homeowners should be aware of?
Local building codes govern the construction, repair, and maintenance of venting structures. These codes address material specifications, height and clearance requirements, and inspection protocols. Compliance is essential to ensure safety and regulatory compliance.
Question 5: What are the potential hazards of neglecting Rockford chimney maintenance?
Neglecting maintenance can lead to dangerous conditions, including chimney fires, carbon monoxide poisoning, and structural collapse. Regular maintenance mitigates these risks and ensures the safe and efficient operation of the heating system.
Question 6: What type of professional should be contacted for Rockford chimney repairs?
Repairs should be performed by qualified chimney sweeps or masonry contractors with expertise in venting systems. Selecting a licensed and insured professional ensures that repairs are conducted safely and in accordance with building codes.
Regular inspection and maintenance are vital for ensuring the safety and longevity of residential venting structures in the specific area. Addressing potential issues promptly can prevent hazardous conditions and costly repairs.
The subsequent sections will explore advanced diagnostic techniques and emerging technologies used in the assessment and maintenance of these structures.
Conclusion
The preceding discussion has provided a comprehensive overview of residential venting structures, specifically referencing those within the specified geographical region. Key points addressed include the importance of regular inspections, the impact of local weather conditions, the significance of material selection, and the necessity of adhering to local building codes. Furthermore, the exploration encompassed historical architectural styles and their influence on design and maintenance considerations.
The continued safe and efficient operation of these structures hinges on proactive maintenance and adherence to established safety protocols. Understanding the inherent risks associated with neglected venting systems and the importance of professional expertise is paramount. Homeowners are encouraged to prioritize regular inspections and maintenance to ensure the long-term safety and well-being of their households. The information presented serves as a foundation for informed decision-making regarding the care and upkeep of these critical components of residential infrastructure.